Separating Mixtures
Separating Mixtures Revision
Separating Mixtures
As we have seen, chemical reactions produce new chemical bonds between atoms and create products with different chemical properties to the reactants. However, it is possible to mix chemicals together without them undergoing a chemical reaction. This produces mixtures.
What is a mixture?
Where different substances (elements or compounds) occupy the same space, but are not chemically bonded together, they are called mixtures. Each of the components of a mixture retains its chemical and physical properties. For example, it is possible to use a magnet to remove iron filings from a mixture of iron and sulfur, as the iron filings remain magnetic in the mixture. Mixtures can be separated into their constituent parts by simple, physical separation techniques.
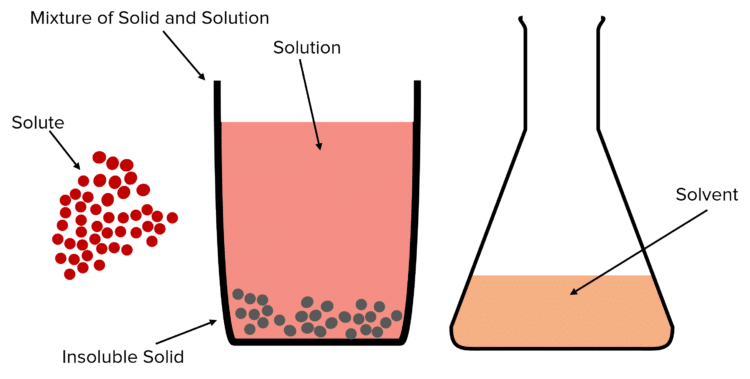
Some useful terms when discussing mixtures:
- Solution: A mixture of a liquid (solvent) and one or more dissolved solids (solutes).
- Solvent: A liquid that dissolves certain solutes to make a solution.
- Solute: A solid that can be dissolved in solvent to make a solution.
- Soluble: Can be dissolved in a given solvent.
- Insoluble: Can not be dissolved in a given solution.
Separations
Separations are techniques used to split up mixtures into their different components. The types of separation used to accomplish this will depend on the states of matter in which we find the mixtures components. For mixtures containing liquids and insoluble solids components, filtration is often used. For mixtures containing liquids (solvents) and soluble (solutes), techniques such as evaporation, crystallization, or distillation may be used. For liquid-liquid mixtures containing multiple different liquids, a range of techniques, such as Fractional distillation, can be used depending on the properties of the liquids involved. Described below are some of the most common techniques used to separate mixtures.
Filtration
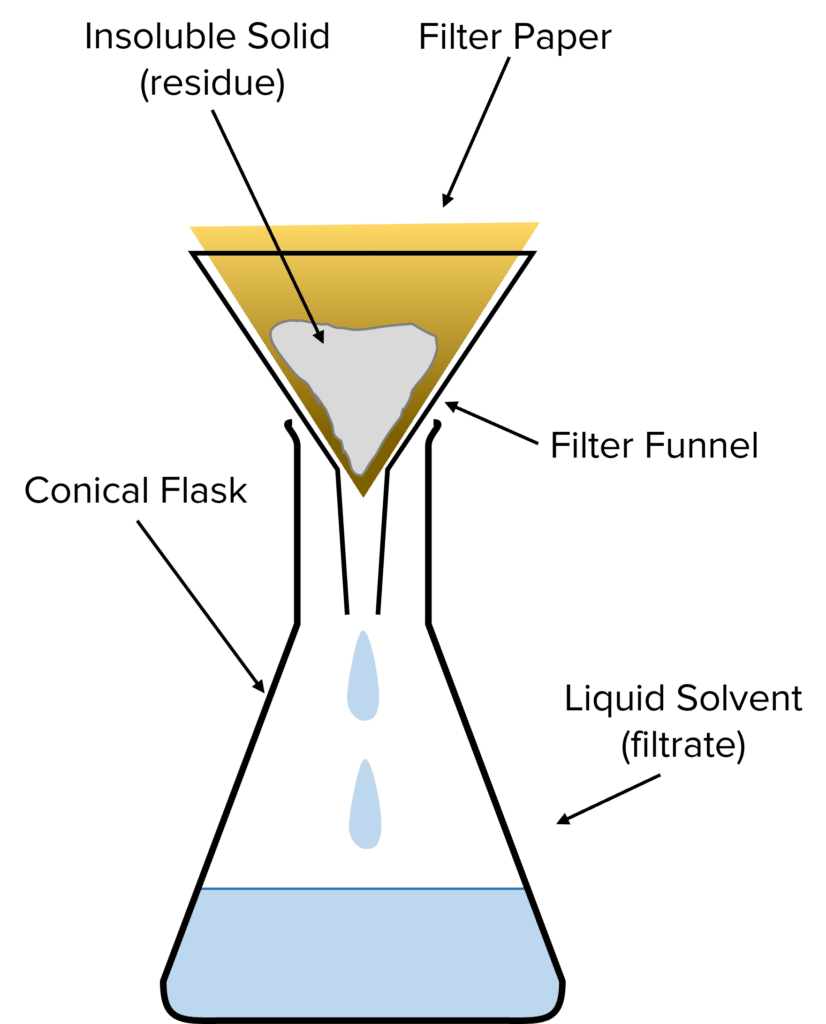
Filtration is used to separate a mixture of an insoluble solid and a liquid (e.g., to separate a mixture of sand and water).
To perform filtration, filter paper is folded into a cone, and inserted into the neck of a filter funnel. This is placed into a conical flask, and the mixture is slowly poured into the filter funnel. The filter paper is designed to allow liquids to pass through, but to prevent solids from passing through, so the insoluble solid (called the residue) and liquid (called the filtrate) are separated.
Distillation
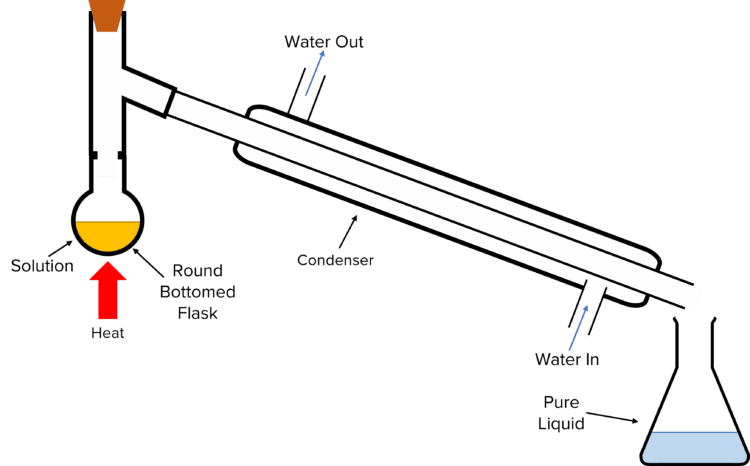
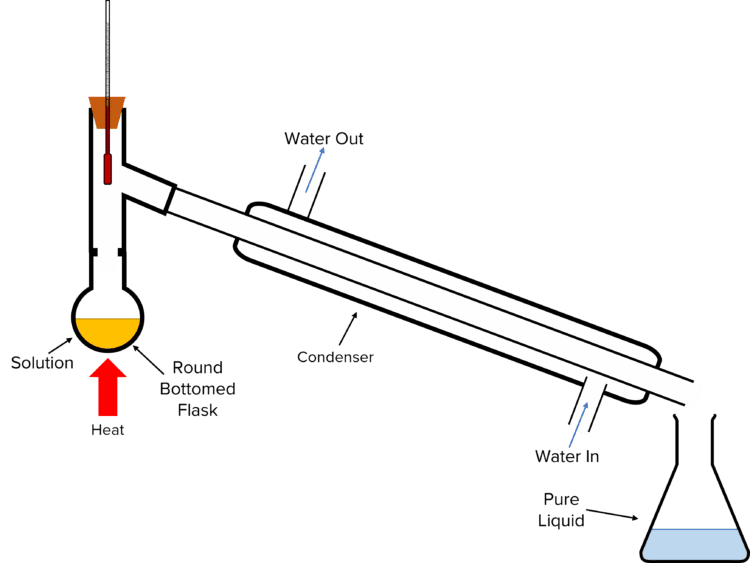
Distillation is used to separate out the solvent from a solution (e.g., to separate water from salt water solution).
To perform distillation, the solution is poured into a round-bottomed flask, connected to a water-cooled condenser all in a closed system to prevent the loss of gasses. The solution is heated causing the liquid solvent to boil and turn from liquid to gas. The gas passes through the condenser, is cooled, and condenses back into a liquid (called the distillate), which is collected. The solid solute remains as residue on the inside of the round-bottomed flask.
Evaporation
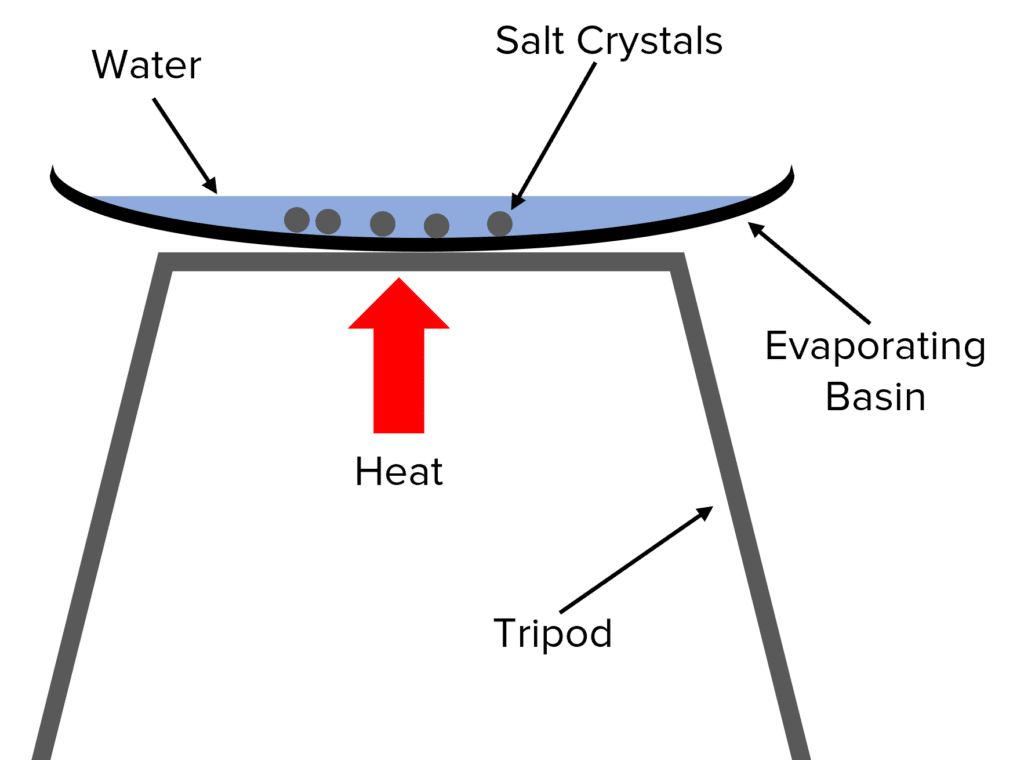
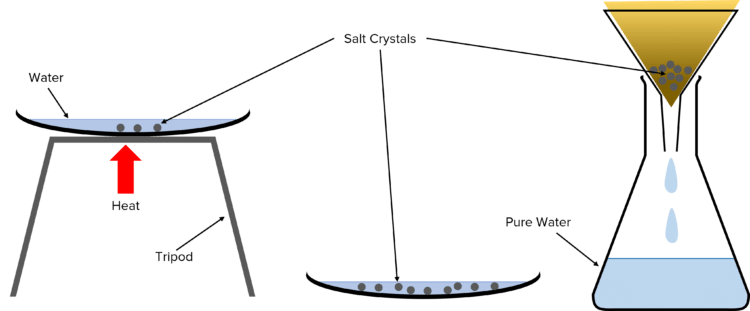
Evaporation is used to separate out the solute from a solution, e.g. to separate salt from salt water solution.
To perform evaporation, the solution is poured into an evaporating basin and heated. The liquid solvent boils off, leaving the solid solute as residue in the evaporating basin. This technique should only be used when the solute does not break-down at high temperatures, otherwise it can both degrade the solute and release potentially harmful gases.
Crystallisation
Crystallisation is also used to separate out a solute from a solution, e.g. to separate salt from salt water solution, but specifically when the solute will thermally decompose (break down at high temperatures).
To perform crystallisation, the solution is poured into an evaporating basin and gently heated, causing liquid solvent to evaporate, until crystals start to form. The evaporating basin is then removed from the heat and allowed to slowly cool, encouraging the formation of crystals of the solute in residual solution. Once cool, any remaining solution can be removed by filtration, and the crystals patted dry.
Fractional Distillation
Fractional distillation is used to separate a mixture of two or more liquids with different boiling points, e.g. the separation of a mixture of different hydrocarbons in crude oil.
To perform fractional distillation the mixture of liquids is poured into a round-bottomed flask, connected to a water-cooled condenser. A thermometer is also included to allow measurement of temperature of the gases as they pass through the glassware. The mixture is heated, and the temperature of the mixture reaches a point where it equals the lowest boiling point in the mixture. The liquid with that boiling point in the mixture turns into a gas and passes through the condenser, where it is cooled and condenses back into a liquid. The temperature is kept constant during this process until no more liquid boils off. This liquid (referred to as a “fraction”) can then be collected. Once all of the first fraction has been collected, the temperature is raised until it reaches the next lowest boiling point, and the process is repeated to collect the second fraction. This is repeated until all of the liquids in the mixture have been separated by their boiling point.
Chromatography
Chromatography can be used to separate mixtures according to the solubility of the components. One common technique is paper chromatography (discussed in more detail here). Chromatography makes use of the attraction of a substance to a stationary phase and to a solvent to separate mixtures along a chromatography medium. There are a wider range of chromatography techniques, including column, gas, and thin layer chromatography.
Separating Mixtures Example Questions
Question 1: What is the definition of a mixture?
[1 mark]
Two or more substances that occupy the same space but are not chemically bonded together.
Question 2: What is the difference between a solute and a solvent?
[2 marks]
A solute is a solid that dissolves in a liquid. A solvent is the liquid that dissolves the solute.
Question 3: Describe how a mixture of sand and salt water can be separated into sand and water.
[2 marks]
Use filtration to separate the sand from the salt water solution.
Use distillation to separate the water from the salt water solution.





