Areas of Shapes
Areas of Shapes Revision
Areas of Shapes
The area of a 2D shape is the amount of space it takes up in 2 dimensions, and its units are always squared, e.g
\text{cm}^2,\hspace{1mm}\text{m}^2
You need to know the formulas to calculate the areas of some common shapes and be able to rearrange them. Revising rearranging formulae will help with this topic.
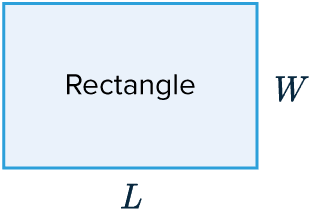
Area of Rectangle

The area of a rectangle is length \times width
\text{Area} = L \times W
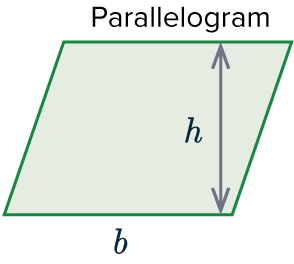
Area of a Parallelogram

The area of a parallelogram is base \times vertical height
\text{Area} = b\times h
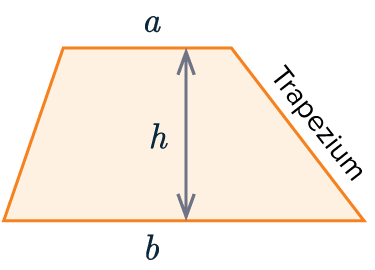
Area of a Trapezium

The formula to calculate the area of a trapezium is:
\text{Area} = \dfrac{1}{2}(a+b)h
where a and b are the lengths of the parallel sides and h is the vertical height.
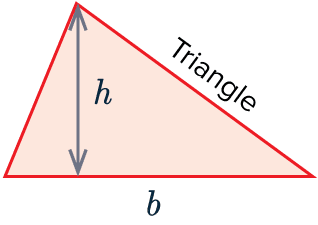
Area of a Triangle 1

The equation to calculate the area of a triangle is:
\text{Area} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times b \times h
Where b is the base width of the triangle and h is the vertical height.
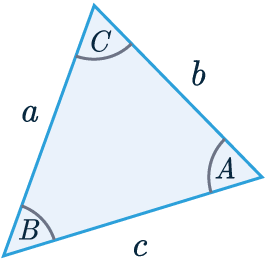
Area of a Triangle 2

Another way to calculate the area of a triangle is as follows:
\dfrac{1}{2} \times a \times b \times \sin(C)
Where a and b are side lengths and C is the angle between the side lengths.
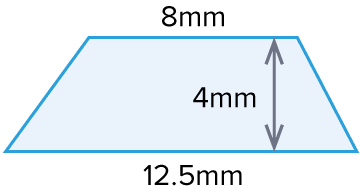
Example 1: Finding the Area of a Trapezium
The shape is a trapezium with a perpendicular height of 4mm.
Calculate the area of the trapezium.
[2 marks]

Formula: \text{Area}=\frac{1}{2}(a+b)h,
where a = 8,\hspace{1mm}b = 12.5, and h = 4 .
\begin{aligned}\text{Area } &= \dfrac{1}{2}(8+12.5) \times 4 \\ &=\dfrac{1}{2} \times 20.5 \times 4 \\ &= 41\text{ mm}^2 \end{aligned}
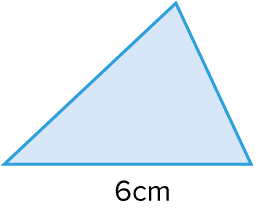
Example 2: Area of a Triangle
The triangle has a base of 6cm and an area equal to 24\text{ cm}^2.
Calculate its perpendicular height.
[2 marks]

Formula: \text{Area} = \dfrac{1}{2}\times b \times h
So we can add the numbers we know into the equation and solve for h:
24= \dfrac{1}{2}\times 6 \times h
24= 3 \times h
\dfrac{24}{3}= h
h = 8\text{cm}
Areas of Shapes Example Questions
Question 1: The triangle below has a base of 11.5 cm and a perpendicular height of 12 cm.
Calculate its area.
[2 marks]
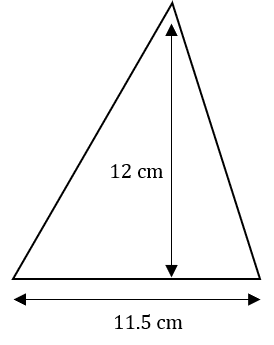
The formula for the area is \frac{1}{2} \times b \times h, where b = 11.5 \text{ and } h = 12. So, we get:
\text{Area } = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 11.5 \times 12 = 69\text{cm}^2
Question 2: Below is a trapezium with sides of length 8cm, 5cm, and 5cm as shown below.
Calculate the perpendicular height and use it to find the total area.
[2 marks]
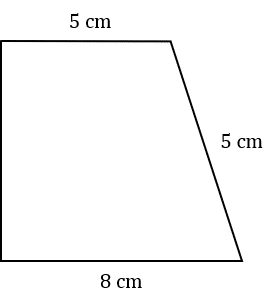
To work out the area, we will need to find the perpendicular height by forming a right-angled triangle,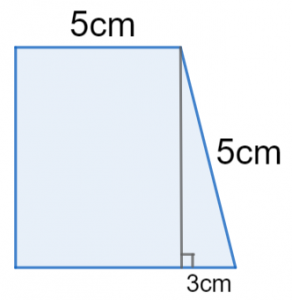
The hypotenuse of the right-angled triangle is 5cm and the base is 3cm (8cm-5cm=3cm), so we get the perpendicular height of the trapezium as,
\text{Perpendicular height} = \sqrt{5^2 - 3^2} = \sqrt{16} = 4\text{cm}
Now we know the perpendicular height, we can calculate the area.
\text{Area} = \dfrac{1}{2}(a + b)h = \dfrac{1}{2}(5 + 8) \times 4 = 26\text{cm}^2
Question 3: Calculate the area of the parallelogram shown below.
[2 marks]
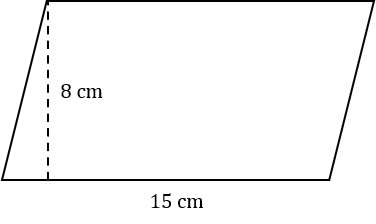
Area of a parallelogram is given by the formula,
\text{Area}=\text{base}\times\text{height}.
Therefore,
\text{Area}=8 \times 15 =120\text{cm}^2
HIGHER ONLY
Question 4: The triangle below has area 1.47\text{m}^2.
Work out the length of x to 2 decimal places.
[3 marks]
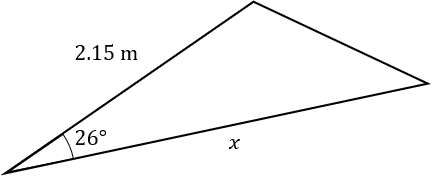
As we need to find a missing side-length rather than the area, we’re going to have to set up an equation and rearrange it to find x. The formula for the area we’ll need here is
\dfrac{1}{2}ab \sin(C),
so, our equation is
\dfrac{1}{2} \times 2.15 \times x \times \sin(26) = 1.47
Simplifying the left-hand-side, we get
1.075 \sin (26) \times x = 1.47
Finally, dividing through by 1.075\sin(26), and putting it into a calculator, we get
x = \dfrac{1.47}{1.075\sin(26)} = 3.12\text{m (2 d.p.)}
Areas of Shapes Worksheet and Example Questions
(NEW) Areas of Shapes Exam Style Questions - MME
Level 4-5Level 6-7GCSENewOfficial MMEAreas of Shapes Drill Questions
Area and Volume - Drill Questions
Level 4-5GCSE
MME Premium Membership
£19.99
/monthLearn an entire GCSE course for maths, English and science on the most comprehensive online learning platform. With revision explainer videos & notes, practice questions, topic tests and full mock exams for each topic on every course, it’s easy to Learn and Revise with the MME Learning Portal.
Sign Up Now