Carboxylic Acids
Carboxylic Acids Revision
Carboxylic Acids
Carboxylic acids are another homologous series of molecules that can be derived from hydrocarbon molecules. Carboxylic acids are often weak acids and react with a number of substances including carbonates, water, and alcohols. Like all other homologous series, carboxylic acids share similar structures and properties.
What is a Carboxylic Acid?
Carboxylic acids are another homologous series of molecules. Carboxylic acids all contain the carboxylic acid functional group. This group is made up of a carbon atom that has a double bond to an oxygen atom and a single bond to an \text{OH} group. Due to the bonding present this functional group they will always be located at the ends of a hydrocarbon chain.
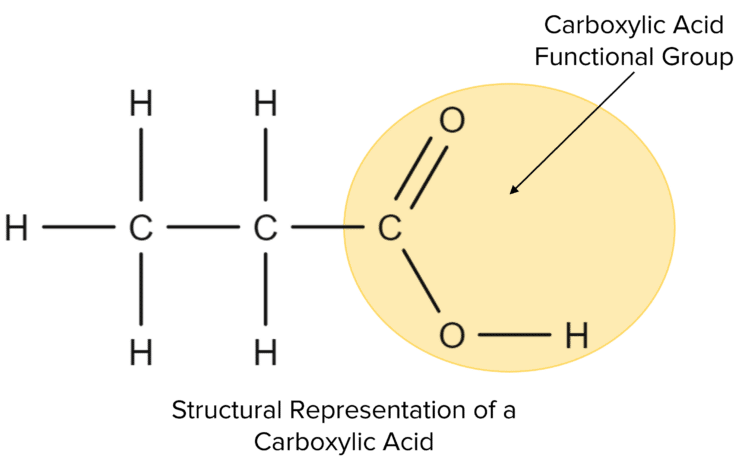
Carboxylic acids follow the general pattern for hydrocarbon molecules in terms of their nomenclature. The first four acids in the series all have generic prefixes; meth-, eth-, prop-, and but-, with the rest having the numerical prefixes. Carboxylic acids are then give then suffix -anoic acid. For the molecule shown above, there are three carbon atoms in the chain so we use the prefix prop- and add the suffix -anoic acid, giving us the name propanoic acid.
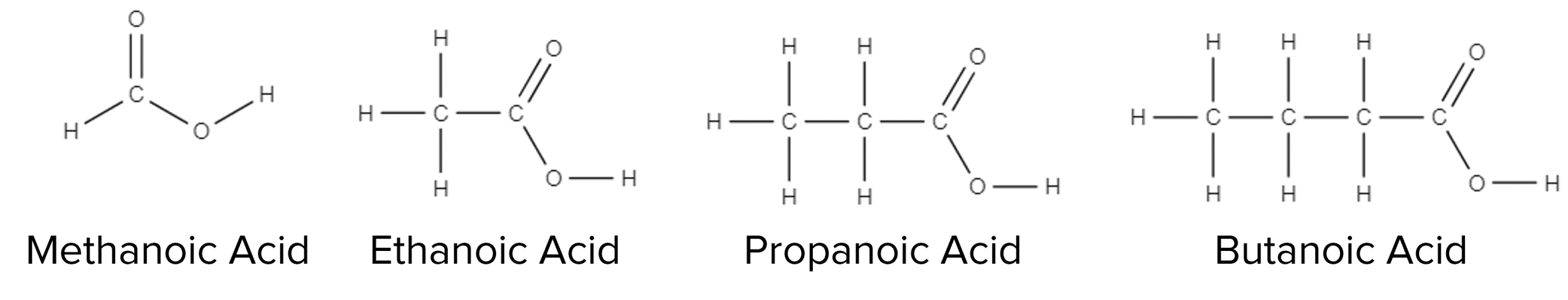
Molecular Formulae: Carboxylic Acids
Carboxylic acids have molecular formula that are constructed in a similar way to that of alcohols. The formulae of carboxylic acids will explicitly show each individual carbon within the structure. Take for example the molecular formula of propanoic acid:
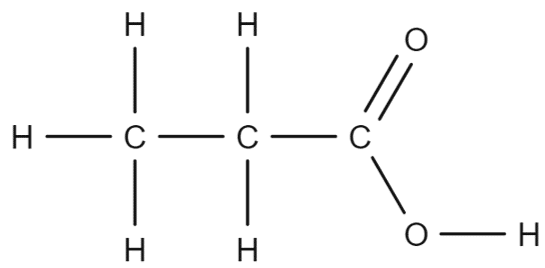
Propanoic acid has the molecular formula \text{CH}_3\text{CH}_2\text{COOH}. Each \text{CH} group will correspond to a specific part of the molecule. The first \text{CH}_3 group corresponds to the carbon found at the end of the chain:
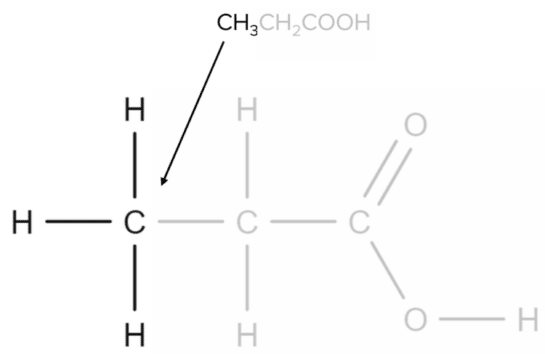
Next, the \text{CH}_2 group corresponds to the central carbon atom of the chain:
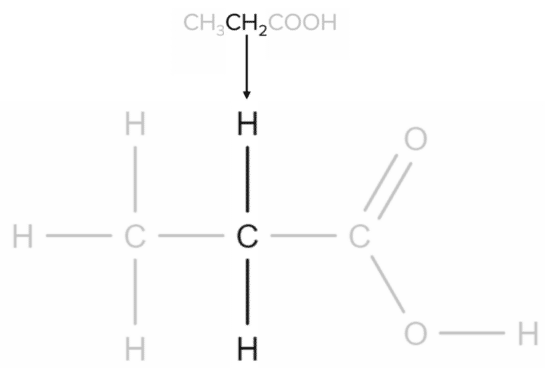
Finally, the \text{COOH} group corresponds to the carboxylic acid functional group:

Reactions of Carboxylic Acids
Carboxylic acids undergo a range of different reactions. Similar to alcohols, carboxylic acids are soluble in water. When dissolved in water, carboxylic acids will form solutions that are acidic. These solutions can then undergo standard acid-base reactions to form salts and water.
For example, propanoic acid will react with sodium carbonate to produce a sodium salt (sodium propanoate), water, and carbon dioxide:
\text{Propanoic Acid}+\text{Sodium Carbonate}\rarr\text{Sodium Propanoate}+\text{Water}+\text{Carbon Dioxide}
\text{CH}_3\text{CH}_2\text{COOH}+\text{Na}_2\text{CO}_3\rarr\text{CH}_3\text{CH}_2\text{COONa}+\text{H}_2\text{O} + \text{CO}_2
Carboxylic acids will also undergo reactions with alcohols. These reactions will produce new molecules called esters:
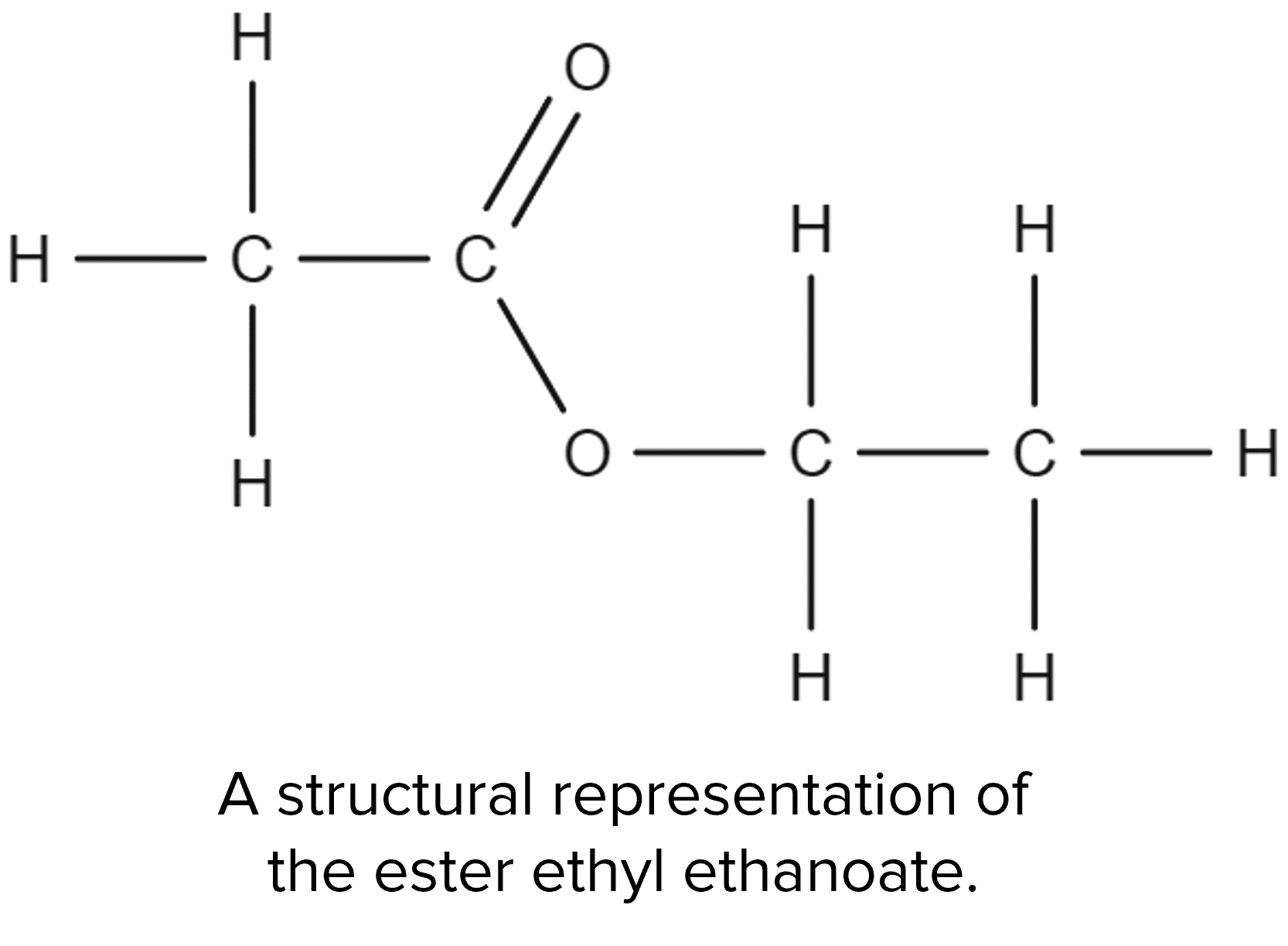
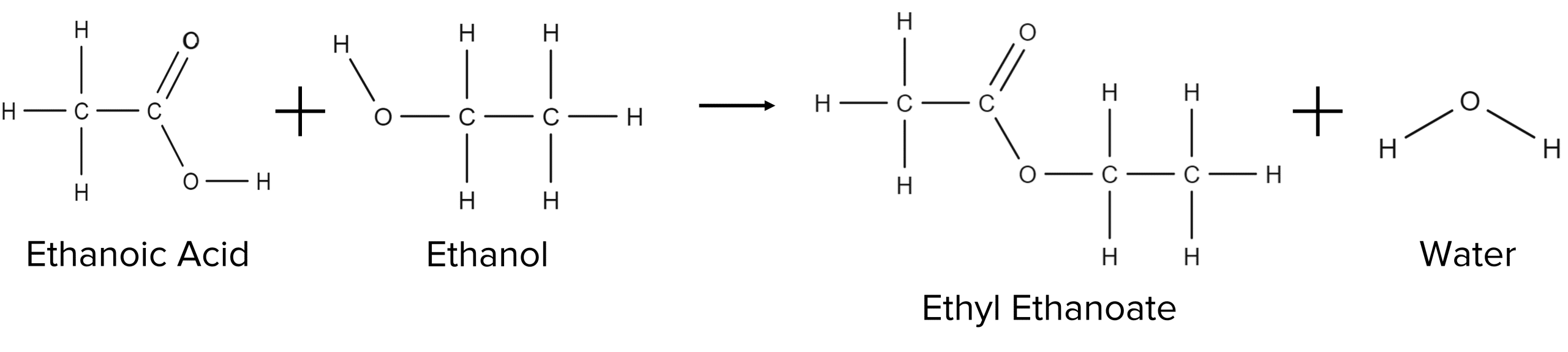
These reactions are called esterification reactions and will also produce water. Take for example the esterification of ethanoic acid by ethanol:
The Strength of Carboxylic Acids
Carboxylic acids are typically weak acids. As such, solutions of weak acids tend to have a higher \text{pH} than those of ionic acids such as sulfuric or hydrochloric acid.
The weakness of carboxylic acids is a result of the their behavior in solution. Unlike strong acids, carboxylic acids do not dissociate completely in solution. This means that only a small proportion of the acid molecules become ionised, producing a low concentration of \text{H}^+ ions.
\text{CH}_3\text{COOH}_\text{(aq)}\rightleftharpoons\text{CH}_3\text{COO}^{-}_\text{(aq)}+\text{H}^+_\text{(aq)}
Carboxylic Acids Example Questions
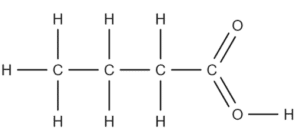
Question 1: From the following molecular formula, give the structure of butanoic acid;
\text{CH}_3\text{CH}_2\text{CH}_2\text{COOH}
[1 mark]
Question 2: Predict the salt formed when butanoic acid reacts with sodium carbonate.
[1 mark]
Sodium butanoate
OR
\text{CH}_3\text{CH}_2\text{CH}_2\text{COONa}
Question 3: A student measures the \text{pH} of two solutions. One solution is known to contain hydrochloric acid and the other methanoic acid. Using the data below, determine which solution contains methanoic acid.
| Solution | A | B |
| \text{pH} | 1.10 | 3.47 |
Explain your answer.
[3 marks]
- Solution B contains methanoic acid.
- Solution B has the higher \text{pH}.
- Methanoic acid is a weak acid and so will have the higher \text{pH}.


