Useful Formulae
Useful Formulae Revision
Useful Formulae
This page contains useful formulae you may need in your exams. You should already be familiar with these equations from GCSE maths.
Area Calculations
Area is the amount of space that a 2D shape takes up.
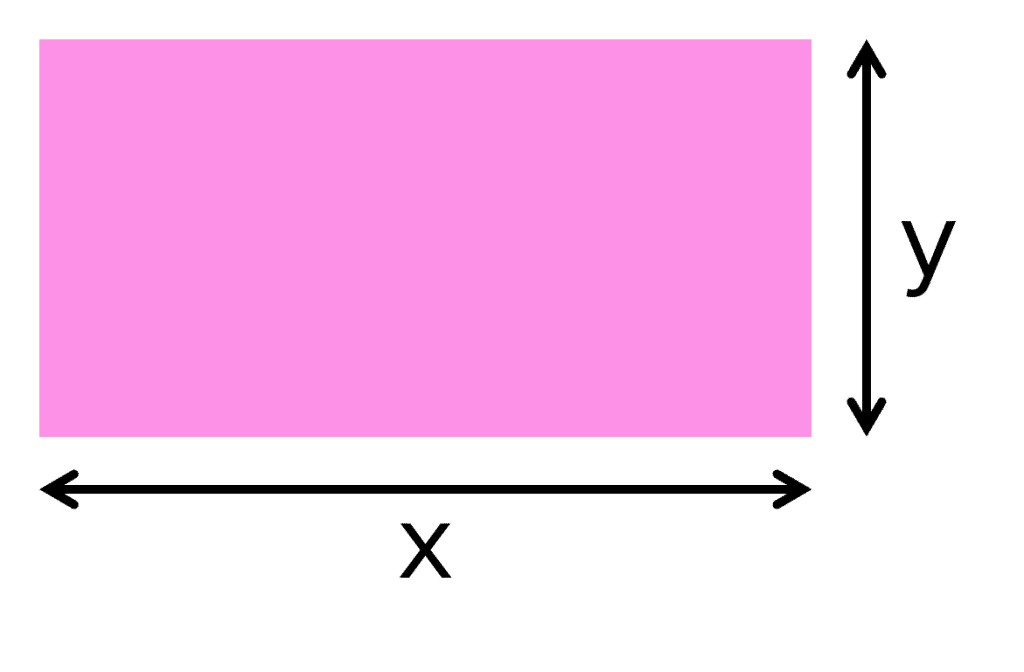

Squares and Rectangles
A=xy
- x= length
- y= height
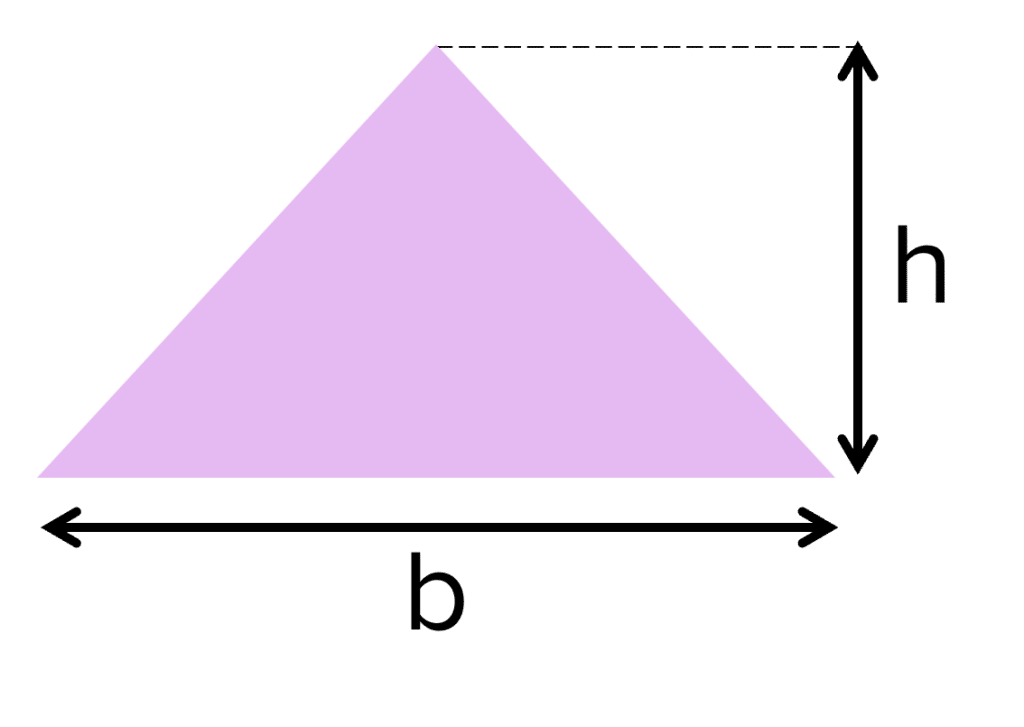

Triangles
A=\dfrac{1}{2}bh
- b= base
- h= height
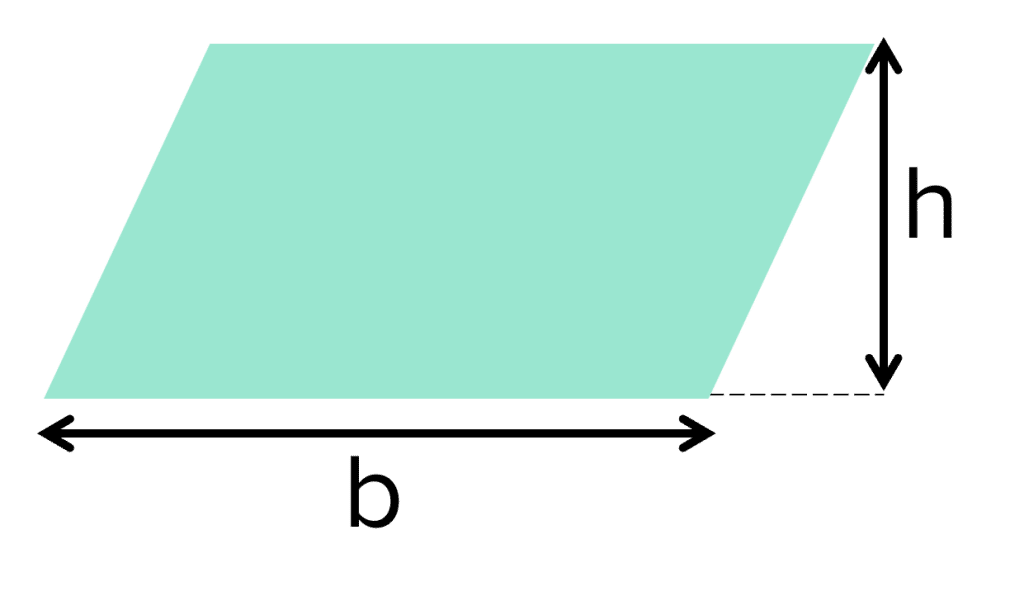

Parallelograms
A=bh
- b= base
- h= perpendicular height
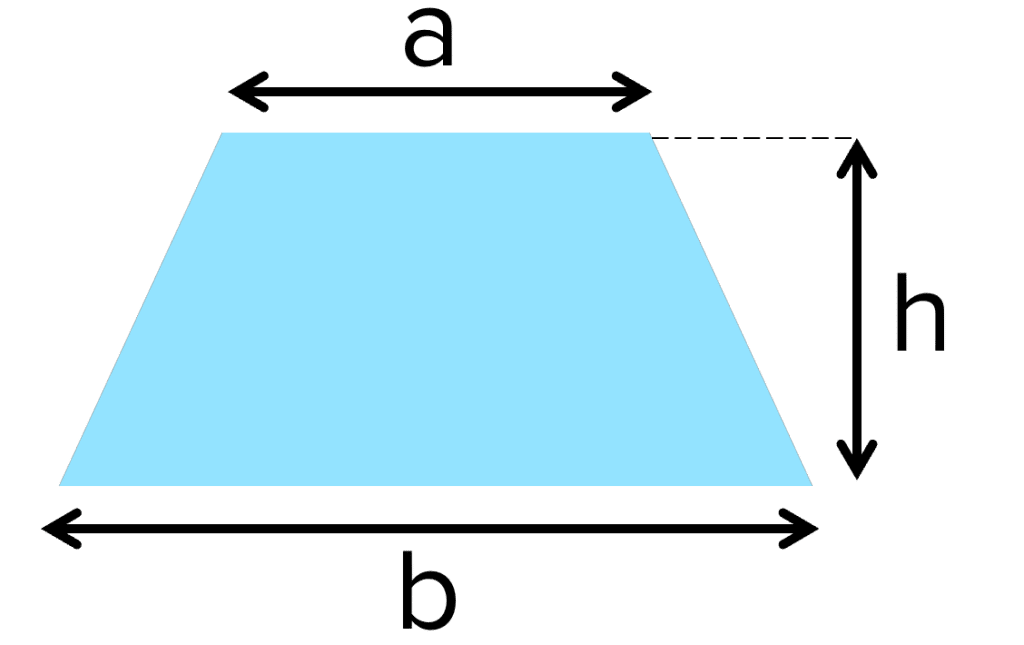

Trapezia
A=\dfrac{1}{2}(a+b)h
- a= width of the short side
- b= width of the long side
- h= height
Circles
You should know what the following words mean when talking about circles:
- Radius – the distance between the entre of the circle and any point on the edge of the circle.
- Diameter – the distance between two opposite edges of the circles, passing through the centre.
- Circumference – the distance around the edge of the circle.
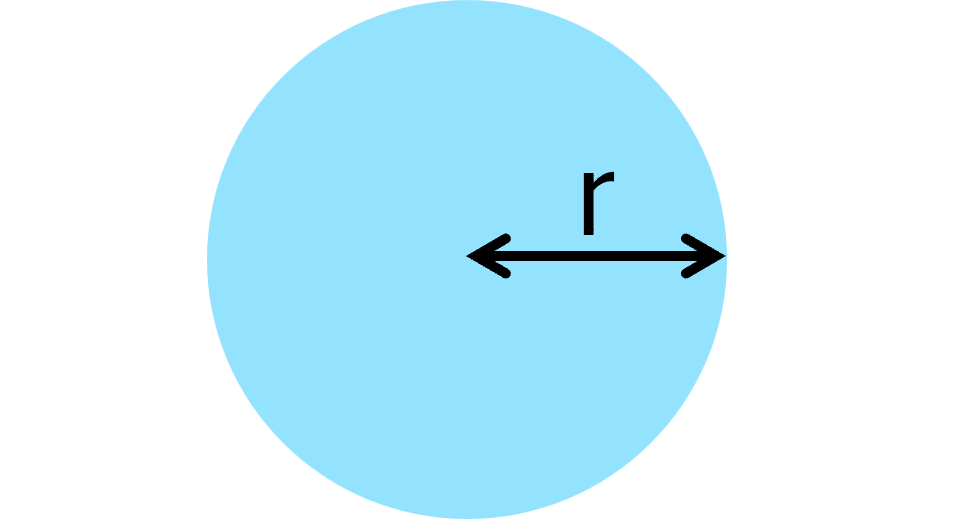

Area of a Circle
A=\pi r^2
- r= radius
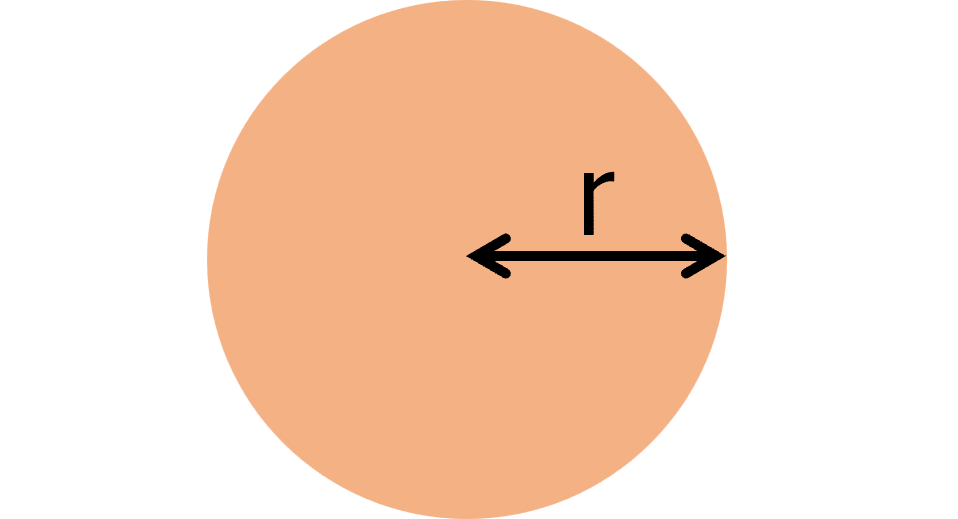

Circumference
C=2 \pi r = \pi d
- r= radius
- d= diameter =2r
Volume Calculations
Volume is the amount of space a 3D shape takes up.
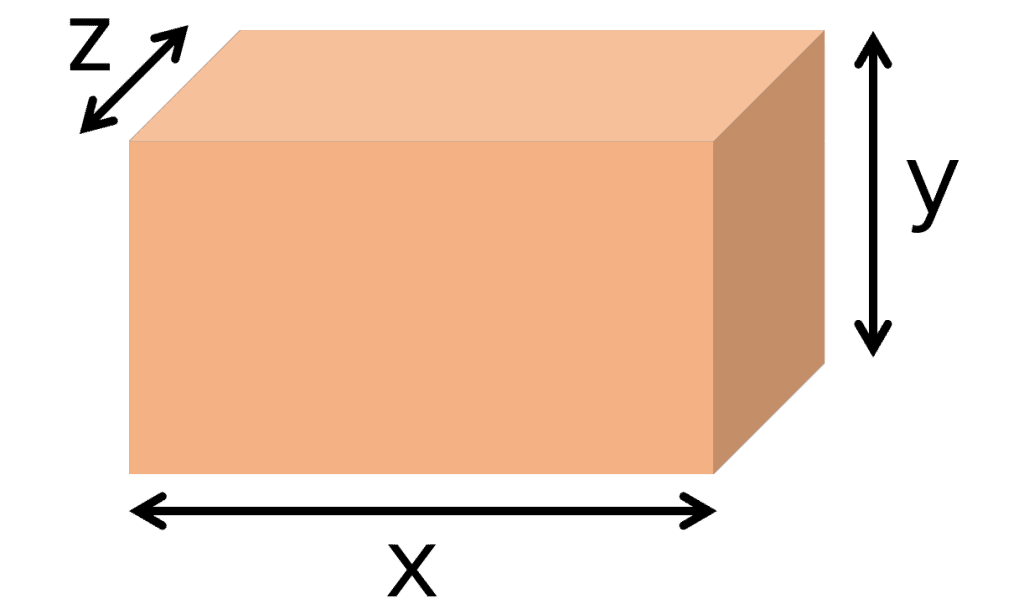

Cuboid
V=xyz
- x= width
- y= height
- z= length
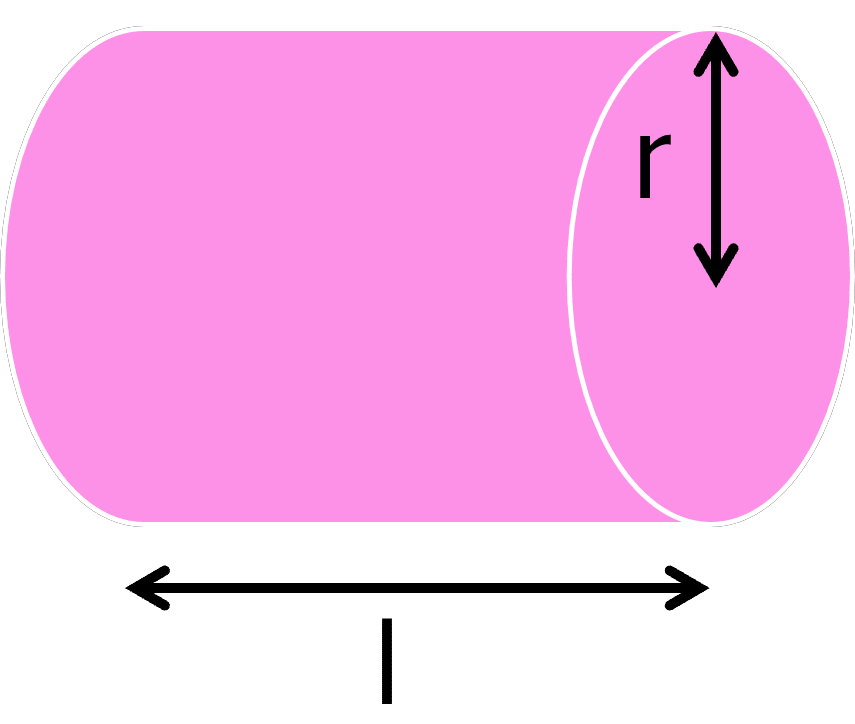

Cylinders
V=\pi r^2 l
- r= radius
- l= length
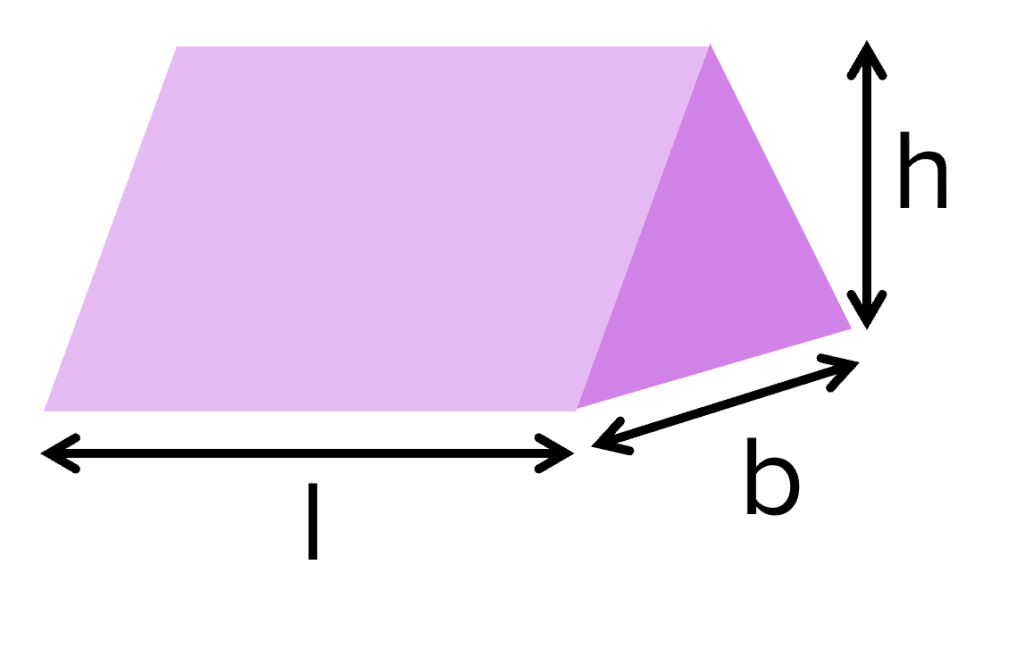

Triangular Prism
V=\dfrac{1}{2}bhl
- b= base
- h= height
- l= length
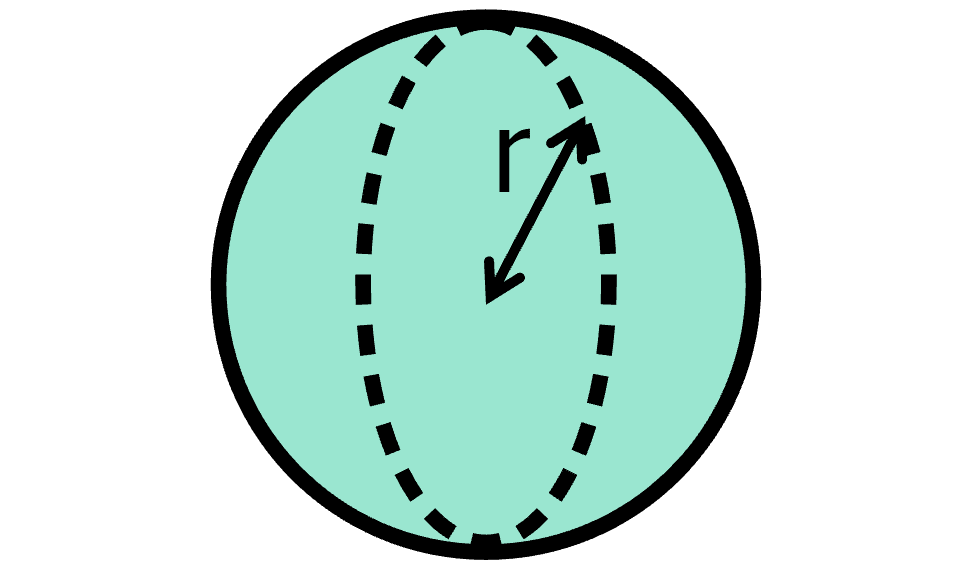

Sphere
V=\dfrac{4}{3} \pi r^3
- r= radius
Example 1: Calculating the Area of an Inhibition Zone.
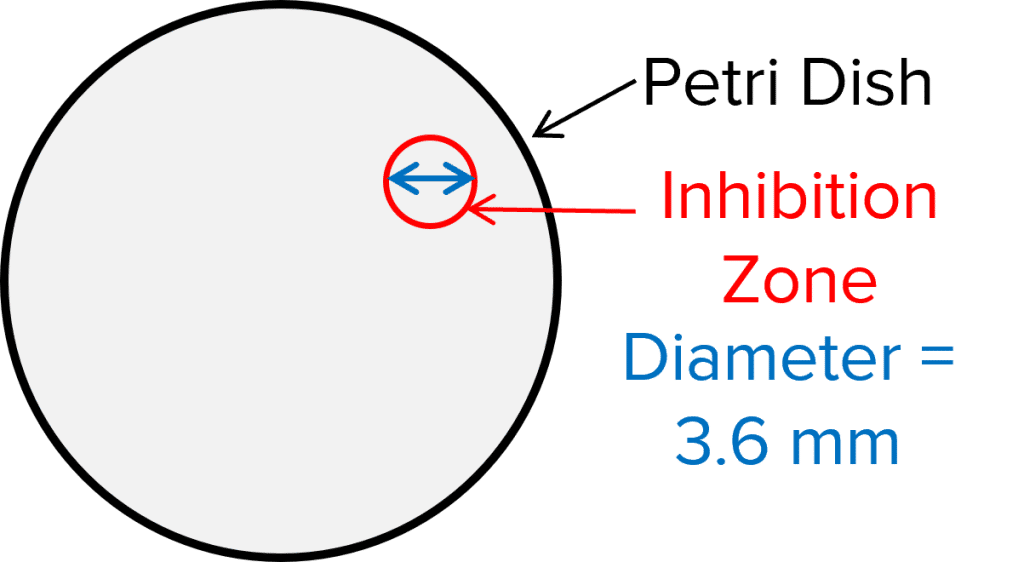

A biologist is performing an experiment on a new antibiotic drug. They measure a circular inhibition zone and find the diameter is 3.6 \text{ mm}.
Calculate the area of this inhibition zone.
[3 marks]
r=\dfrac{d}{2} = \dfrac{\textcolor{1c63ba}{3.6 \text{ mm}}}{2} = \textcolor{aa57ff}{\bold{1.8} \textbf{ mm}} \\ \bold{A=\pi r^2} = \pi \times (\textcolor{aa57ff}{1.8})^2 = \bold{10.2} \textbf{ mm}^2
Example 2: Calculating the Volume of Water Displaced
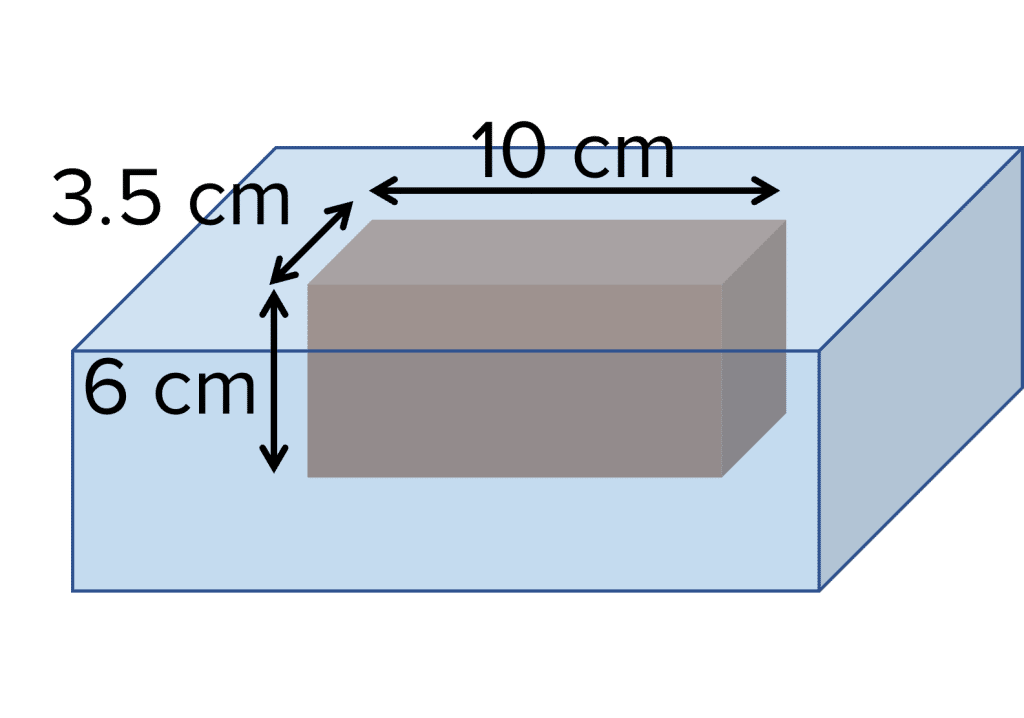

A wooden block with dimensions \textcolor{f95d27}{10 \text{ cm}} \times \textcolor{f43364}{6 \text{ cm}} \times \textcolor{10a6f3}{3.5 \text{ cm}} is dropped into a container of water. Calculate the volume of water displaced by the wooden block.
[2 marks]
Useful Formulae Example Questions
Question 1: Calculate the area of a square with sides of length 6 \text{ cm}.
[2 marks]
Question 2: Calculate the volume of a sphere with radius 40 \text{ mm}.
[2 marks]
Question 3: Calculate the circumference of a circle with a diameter of 2 \text{ m}.
[2 marks]

MME Premium Membership
£19.99
/monthLearn an entire GCSE course for maths, English and science on the most comprehensive online learning platform. With revision explainer videos & notes, practice questions, topic tests and full mock exams for each topic on every course, it’s easy to Learn and Revise with the MME Learning Portal.
Sign Up Now



