Work Done by a Force
Work Done by a Force Revision
Work Done by a Force
Work done is the energy used by a force to move an object a certain distance.
What is Work Done?
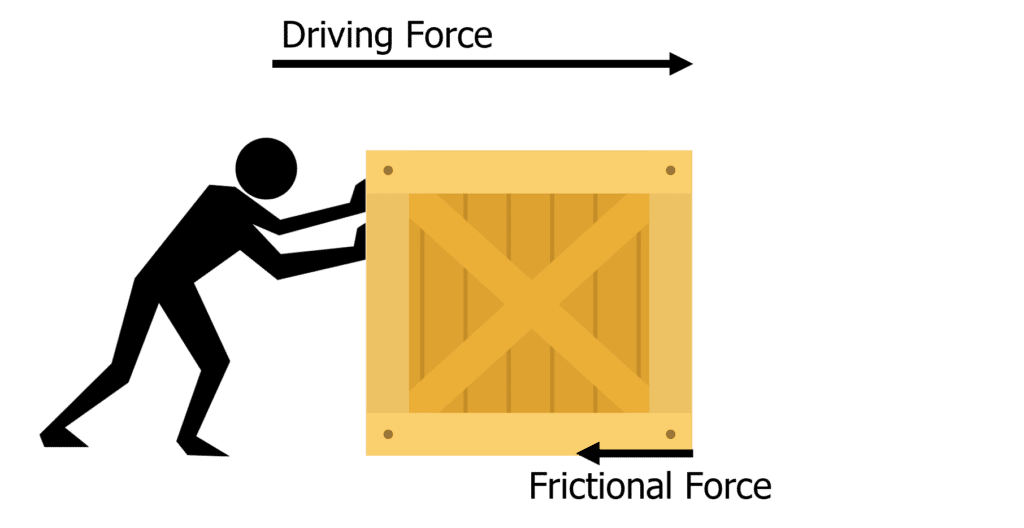
When an object is moved by a force through a distance, energy is transferred and there is work done on the object. This is because to move an object with mass, there must be a force. Whatever is applying this force (e.g a hand) requires energy to move the object. Therefore energy is transferred and the force does work on the object.
The energy is transferred to the kinetic energy store of the object, but if there is friction on the object then work is done against the frictional forces. This means there is a transfer to thermal energy and hence there is a temperature rise in the object.
An example where we can see this in action is a man pushing a heavy box on floor with lots of friction:
- Because the man is using force to push the box, he is doing work on the box, against the friction of the floor.
- Energy is being transferred to the kinetic energy store of the box.
- There is also some wasted energy transferred to thermal energy due to the friction between the box and the floor.
Calculating Work Done
The amount of work done on an object due to a force can be calculated using the following equation:
\textcolor{f21cc2}{W = Fs}
- \textcolor{f21cc2}{W} is work done in Joules \left(\text{J}\right)
- \textcolor{f21cc2}{F} is force in Newtons, \left(\text{N}\right)
- \textcolor{f21cc2}{s} is distance in metres \left(\text{m}\right).
1 \: \text{J} of work is done when a force of 1 \: \text{N} moves an object through a distance of 1 \: \text{m}.
Therefore \bold{\textcolor{f21cc2}{1}} Joule = \bold{\textcolor{f21cc2}{1}} Newton-meter.
Example: Calculating Work Done
A man pushes a box through a distance of \textcolor{f21cc2}{12 \: \text{m}}, and he exerts \textcolor{aa57ff}{14 \: \text{N}} of force on the box. Calculate the work done by the man. Ignore the frictional force.
[2 marks]
Using the work done equation:
W = Fs
Substitute in the values:
W = \textcolor{aa57ff}{14} \times \textcolor{f21cc2}{12}
Calculate the answer:
W = 168 \: \text{J or Nm}
Work Done by a Force Example Questions
Question 1: State what is meant by the term “work done”.
[2 marks]
Work done is the amount of energy transferred to an object when a force moves the object through a distance.
Question 2: A car drives 200 \: \text{m} and the engine effectively applies 150 \: \text{N} of force. Calculate the work done by the car’s engine and give the appropriate units.
[3 marks]
Using the work done equation:
\begin{aligned} \boldsymbol{W} &\boldsymbol{= Fs} \\ \boldsymbol{W} &\boldsymbol{= 150 }\: \textbf{N} \boldsymbol{\times \: 200 }\: \textbf{m} \\ \boldsymbol{W} &\boldsymbol{= 3000} \: \textbf{J} \: \text{or} \: \textbf{Nm} \end{aligned}
Question 3: A man pushes a box 4 \: \text{m}, and 100 \: \text{J} of energy is transferred to the kinetic energy store of the box. Calculate the force exerted by the man on the box.
[3 marks]
Using the work done equation:
W = Fs
Rearrange to get the force:
F = \dfrac{W}{s}
F = \dfrac{100 \: \text{J}}{4 \: \text{m}}
\bold{F = 25} \: \textbf{N}





