Transformers
Transformers Revision
Transformers
Transformers change the voltage of alternating currents. They do this using electromagnetic induction, and are used in the national grid to change the voltage we use in our homes.
Transformers
Transformers can increase or decrease the voltage of alternating currents. They do not work with direct currents.
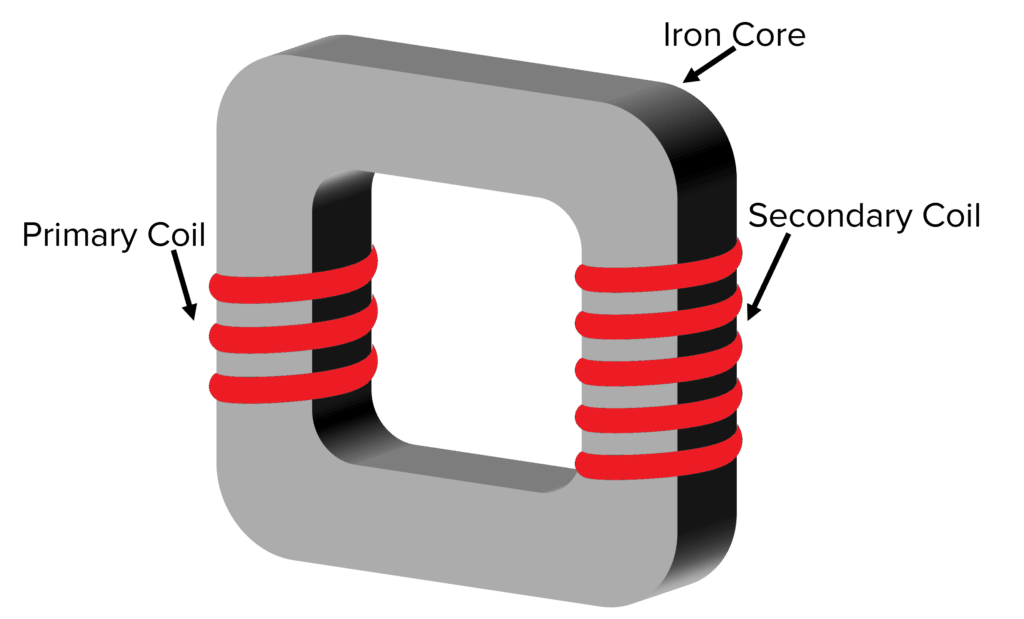
A transformer consists of two coils wound around an iron core. There is a primary coil and a secondary coil. The primary coil handles the input potential difference, and the secondary coil handles the output potential difference.
When an alternating potential difference is applied across the primary coil, the iron core will magnetise and then quickly demagnetise. An alternating potential difference is induced across the secondary coil due to this changing magnetic field. This is an example of electromagnetic induction.
- Step-up transformers have more turns on the secondary coil than the primary coil and therefore they increase the potential difference. A higher p.d means a lower current. This reduces energy loss via heat when the electricity is travelling through wires around the national grid.
- Step-down transformers have more turns on the primary coil than the secondary coil and they decrease the potential difference. They are used to reduce the voltage to a level that can be used in homes.
The Transformer Equation
The ratio of the potential differences across the primary and secondary coils is dependent on the ratio of the number of turns on each coil. The transformer equation allows us to calculate the output potential difference of a transformer as long as we know the number of turns on each coil and the input potential difference:
\textcolor{f21cc2}{\dfrac{V_p}{V_s} = \dfrac{n_p}{n_s}}
- \textcolor{f21cc2}{V_p} is the potential difference across the primary coil in volts \left(V\right)
- \textcolor{f21cc2}{V_s} is the potential difference across the secondary coil in volts \left(V\right)
- \textcolor{f21cc2}{n_p} is the number of turns on the primary coil
- \textcolor{f21cc2}{n_s} is the number of turns on the secondary coil
For step-up transformers, \textcolor{f21cc2}{V_s} > \textcolor{f21cc2}{V_p}.
For step-down transformers, \textcolor{f21cc2}{V_s} < \textcolor{f21cc2}{V_p}.
Transformers and Power
Transformers are not quite 100% efficient. However, they are very close. Therefore if we assume they are 100% efficient, then the electrical power output is equal to the electrical power input. This assumption allows us to use P = VI:
\textcolor{00bfa8}{\text{electric power output} = \text{electric power input}}
\textcolor{00bfa8}{V_s I_s = V_p I_p}
- \textcolor{00bfa8}{V_p} is the input potential difference across the primary coil in volts \left(V\right)
- \textcolor{00bfa8}{I_p} is the current through the primary coil in amps \left(A\right)
- \textcolor{00bfa8}{V_s} is the output potential difference across the secondary coil in volts \left(V\right)
- \textcolor{00bfa8}{I_s} is the current through the secondary coil in amps \left(A\right)
Example: Transformer Calculations
A transformer has a primary coil with \textcolor{bd0000}{50} turns and a secondary coil with \textcolor{2730e9}{100} turns. The input potential difference is \textcolor{00bfa8}{10 \: \text{V}}.
Calculate the output potential difference in volts.
[3 marks]
We know the transformer equation is:
\dfrac{V_p}{V_s} = \dfrac{n_p}{n_s}
We want to find the output potential difference V_s. We can write the equation as:
V_s = \dfrac{n_s \times V_p}{n_p}
We know that n_s = \textcolor{2730e9}{100}, n_p = \textcolor{bd0000}{50} and V_p = \textcolor{00bfa8}{10 \: \text{V}}, so we can substitute in the values:
V_s = \dfrac{\textcolor{2730e9}{100} \times \textcolor{00bfa8}{10 \: \text{V}}}{\textcolor{bd0000}{50}}
V_s = 20 \: \text{V}
Transformers Example Questions
Question 1: Explain the differences between step-up and step-down transformers.
[2 marks]
Step-up transformers are used to increase potential difference and step-down transformers are used to decrease the potential difference.
Step-up transformers have more turns on the secondary coil, whereas step-down transformers have more turns on the primary coil.
Question 2: The output potential difference of a transformer at a substation is 110 \: \text{V}. The primary coil of the transformer has 6000 turns, and the secondary coil has 2 turns. Calculate the input potential difference of the transformer.
[3 marks]
Question 3: The primary coil of a transformer has a potential difference of 10\: \text{V}and a current of 2\: \text{A}. The secondary coil of the transformer has a current of 4\: \text{A}. Calculate the output potential difference of the transformer.
[3 marks]
Transformers Worksheet and Example Questions
Induced pd, Transformers and the National Grid Questions
GCSEOfficial MME
MME Premium Membership
£19.99
/monthLearn an entire GCSE course for maths, English and science on the most comprehensive online learning platform. With revision explainer videos & notes, practice questions, topic tests and full mock exams for each topic on every course, it’s easy to Learn and Revise with the MME Learning Portal.
Sign Up Now




