Our Solar System
Our Solar System Revision
Our Solar System
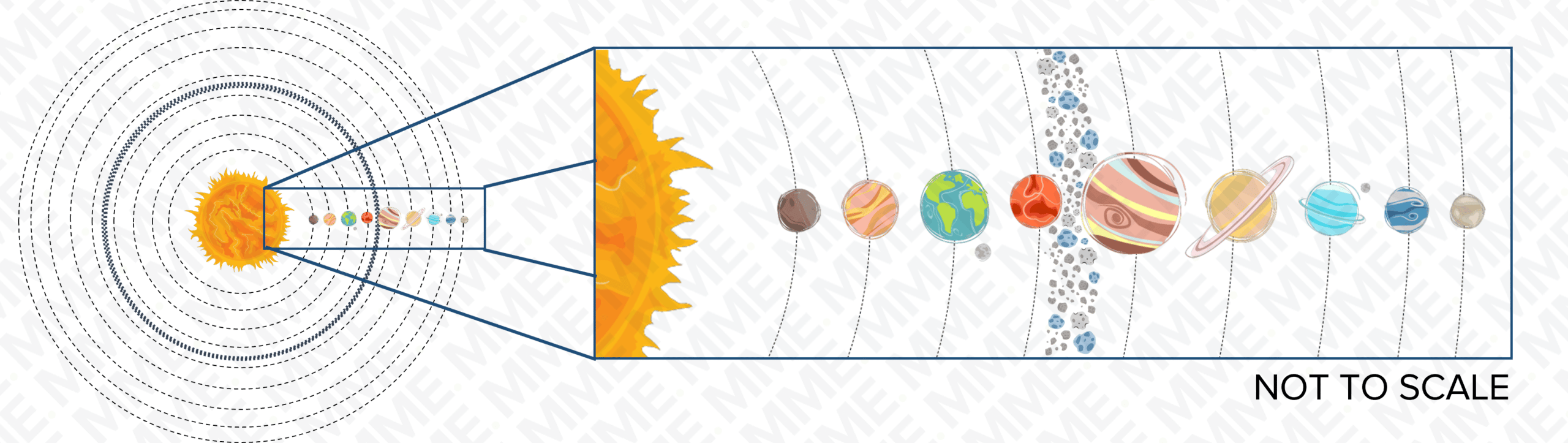
Our solar system is made up of the Sun and eight planets, including the Earth. The planets orbit the Sun.
The Solar System
The solar system contains the Sun, which is a star, and eight planets orbiting the Sun. The planets are kept in orbit by the Sun’s gravity. The planets are, in order of distance from the Sun:
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune.
There are also comets and asteroids orbiting the Sun. Comets are balls of dust and ice with highly elliptical (oval) orbits. Asteroids are lumps of rock and metal, the majority of which are orbiting the Sun in the asteroid belt, located between Mars and Jupiter.
Satellites are objects that orbit planets.
Some of the planets, such as the Earth, have one or many moons. Moons orbit planets and they are a type of natural satellite, meaning that they are not man-made.
Artificial satellites are man-made objects that orbit planets. These include satellites for communication, the International Space Station and space junk.

Our Solar System is on the edge of the Milky Way galaxy. Galaxies are collections of billions of stars that are held together by gravity. The Milky Way is one of billions of galaxies in the known universe.
Orbits
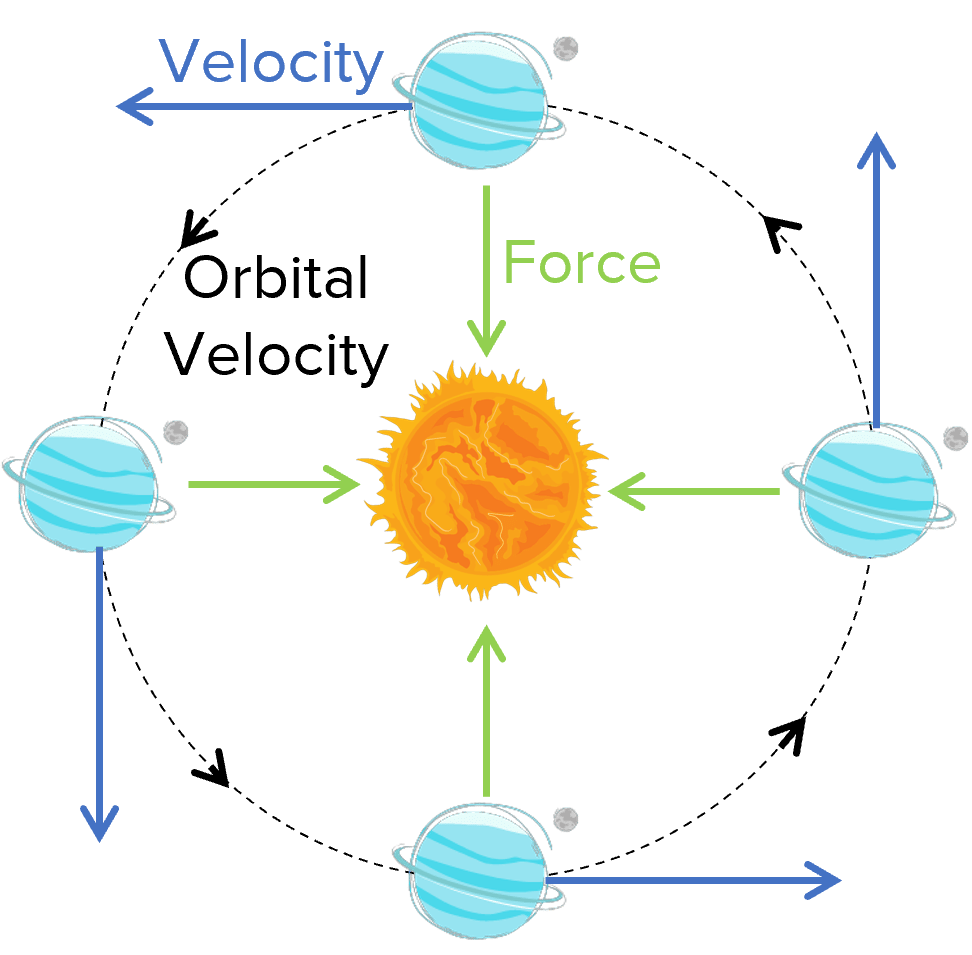
Planets orbit the Sun (and moons orbit planets) in approximately circular orbits. For an object to travel in a circle, it must constantly be accelerating towards the centre of the circle. Acceleration is always caused by a force, which in this case is gravity. Gravity acts towards the centre of the orbit and pulls that planet towards the Sun. This causes the planet to orbit the Sun in a circular motion.
The Speed of Orbits
During orbits, the planets have constant speed. This is despite the fact that they are constantly accelerating.
This is possible because the acceleration is always at a right angle to the velocity and so the acceleration changes the direction of the planet’s velocity but not the speed.
(Remember that speed is a scalar and velocity is a vector i.e. it has direction).
The closer you get to the planet, the stronger the gravitational force. Therefore, the acceleration is greater (because F=ma ) and so the velocity is faster.
If the speed of an object in orbit increases, to maintain a constant orbit, the radius of the orbit must decrease.
Our Solar System Example Questions
Question 1: For each of the following, state if it is a galaxy, a star, a planet, an artificial satellite or a natural satellite.
a. The Moon
b. The Milky Way
c. Jupiter
d. The International Space Station
[4 marks]
a. A natural satellite
b. A galaxy
c. A planet
d. An artificial satellite
Question 2: Describe the differences between comets and asteroids.
[4 marks]
Comets are balls of dust and ice whereas asteroids are made of rock and metal.
Comets orbit the Sun in highly elliptical orbits whereas asteroids orbit the sun in the asteroid belt, between Mars and Jupiter.
Question 3: Approximately how many stars are in the Milky Way galaxy?
[1 mark]
billions.
Question 4: Explain how gravity causes planets to travel in circular orbits.
[3 marks]
The gravitational force from the Sun acts always at right angles to the velocity of the planet.
This force causes the planet to accelerate towards the Sun.
The planet’s speed does not increase but it changes direction.
Resulting in circular motion around the Sun.
Question 5: Two identical radio satellites, are orbiting the Earth. Satellite A has an orbital radius of 5 \text{ km} and satellite B has an orbital radius of 10 \text{ km}. Which satellite has the fastest instantaneous speed? Explain your answer.
[2 marks]
Satellite A.
Closer to the Earth the satellite experiences a stronger gravitational force and so it travels faster.
MME Premium Membership
£19.99
/monthLearn an entire GCSE course for maths, English and science on the most comprehensive online learning platform. With revision explainer videos & notes, practice questions, topic tests and full mock exams for each topic on every course, it’s easy to Learn and Revise with the MME Learning Portal.
Sign Up Now

