Series and Parallel Circuits
Series and Parallel Circuits Revision
Series and Parallel Circuits
Components can either be connected in series or parallel. The type of circuit can have an effect on the current, potential difference and resistance of the circuit.
Series Circuits
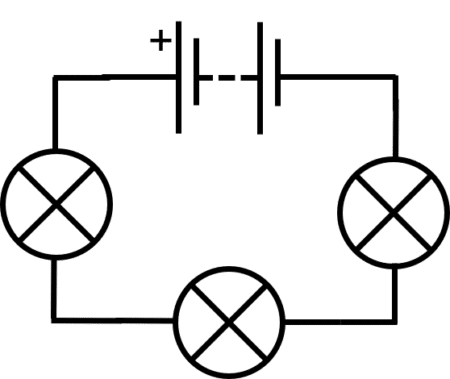
In a series circuit, circuit components are connected in a single loop, one after another.
The same flow of charge passes through each circuit component and so the current is the same in every component:
\textcolor{aa57ff}{\text{I}_{\text{total}}=\text{I}_1=\text{I}_2=\text{I}_3=\text{...}}
The battery or cell provides the supply of potential difference to the circuit. The potential difference is shared between the other components. So the total potential difference is equal to the potential difference of the battery:
\textcolor{aa57ff}{\text{V}_{\text{s}}=\text{V}_1+\text{V}_2+\text{V}_3+\text{...}}
Resistances in series adds up:
\textcolor{aa57ff}{\text{R}_{\text{total}}=\text{R}_1+\text{R}_2+\text{R}_3+\text{...}}
Parallel Circuits
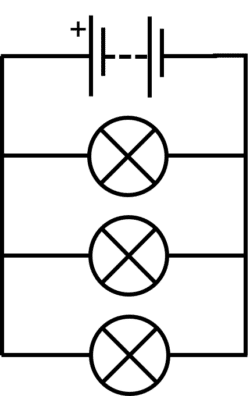
In parallel circuits, components are connected in separate loops.
Each charge can only flow through one of the loops and so current is shared between loops. So the supply current in the loop with battery is equal to the sum of the current in the other loops:
\textcolor{f21cc2}{\text{I}_s=\text{I}_1+\text{I}_2+\text{I}_3+\text{...}}
The potential difference is the same in every loop:
\textcolor{f21cc2}{\text{V}_1=\text{V}_2=\text{V}_3}
When resistors are connected in parallel, the supply current is shared between the resistors and so the overall resistance is reduced as the electrical charges may take many paths.
Example: Series and Parallel Circuit Rules
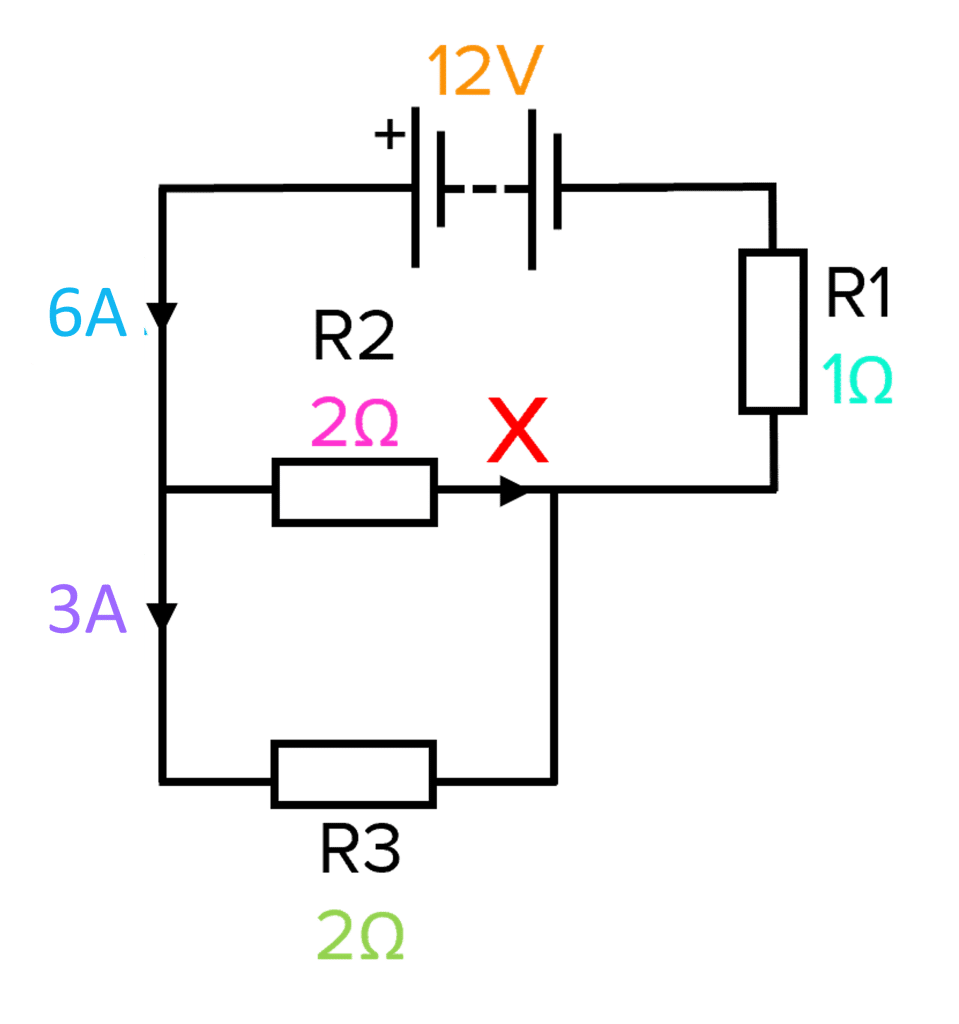
A student builds a circuit containing a battery and three resistors named \text{R}1, \text{R}2 and \text{R}3. A diagram showing their circuit is shown on the right.
a) Calculate the current at the arrow marked X on the circuit diagram.
[2 marks]
b) What is the potential difference across resistor \text{R}1?
[2 marks]
c) Suggest possible values for the potential difference across resistors \text{R}2 and \text{R}3. Explain your answer.
[2 marks]
Answer:
a) In parallel, current is shared between loops so:
\bold{\text{I}_{\text{s}}=\text{I}_1+\text{I}_2}.
Rearrange for I2 :
\text{I}_2=\text{I}_{\text{s}}-\text{I}_1=\textcolor{10a6f3}{6\text{ A}}-\textcolor{aa57ff}{3\text{ A}}=\bold{3\text{ A}}
b) \bold{\text{R}=\dfrac{\text{V}}{\text{I}}}
Rearrange to find V:
\text{V}=\text{IR}=\textcolor{10a6f3}{6\text{ A}}\times \textcolor{00bfa8}{1 \, \Omega}=\bold{6\text{ V}}
c) R2 and R3 have the same resistance so potential difference must be equal.
\text{V}_1 = \text{V}_2=\text{V}_3=6\text{ V}
Series and Parallel Circuits Example Questions
Question 1: State the difference between a series and parallel circuit.
[2 marks]
In a series circuit, circuit components are connected in a single loop whereas in a parallel circuit, components are connected in multiple, separate loops.
Question 2: Two lamps are connected in series. The current in one lamp is 5\text{ A}. What is the current in the other lamp.
[1 mark]
\bold{5\text{ A}}
In series, all components receive the same current.
Question 3: Two 3 \Omega resistors are connected in series. What is the total resistance of the circuit?
[1 mark]
Question 4: A student connects three resistors in a series circuit, and then in a parallel circuit. Which circuit has the least overall resistance? Explain your answer.
[3 marks]
The parallel circuit has the least overall resistance. This is because in series, each charge carrier must flow through each resistor and so the resistances add up. In parallel, the charge carriers have multiple possible paths and so resistance is less.
Question 5: Three lamps are connected in parallel to a battery that provides a current of 20\text{ A}. The current across two of the lamps is measured to be 5\text{ A} and 7\text{ A}. What current is measured across the third lamp?
[2 marks]
\bold{\text{I}_{\text{s}}=\text{I}_1+\text{I}_2+\text{I}_3} (current is shared between the lamps)
Rearrange for I3:
\text{I}_3=\text{I}_{\text{s}}-\text{I}_1-\text{I}_2=20\text{ A}-5\text{ A}-7\text{ A}=\bold{8\text{ A}}Series and Parallel Circuits Worksheet and Example Questions
Series and Parallel Circuits Questions
GCSEOfficial MME
MME Premium Membership
£19.99
/monthLearn an entire GCSE course for maths, English and science on the most comprehensive online learning platform. With revision explainer videos & notes, practice questions, topic tests and full mock exams for each topic on every course, it’s easy to Learn and Revise with the MME Learning Portal.
Sign Up Now




