Nuclear Fission and Fusion
Nuclear Fission and Fusion Revision
Nuclear Fission and Fusion
Nuclear fission and nuclear fusion are both ways of extracting energy from nuclei. They are both potentially very useful sources of energy however they can also be very dangerous.
Nuclear Fission
Nuclear fission occurs when an unstable nucleus splits into two or more pieces.
Nuclear fission rarely occurs spontaneously. In order to force a nucleus to split up, we can make it absorb a neutron. This makes the nucleus unstable and forces fission to occur.
When the nucleus splits, two smaller nuclei are produced. These will be of a different elements than the original nucleus. The new nuclei are also unlikely to be the same size as one another. All of the fission products have kinetic energy.
Two or three neutrons are also produced when fission occurs. These also have kinetic energy. If any of these neutrons are moving slow enough to be absorbed by another atom, they may cause that nucleus to undergo fission as well. This is called a chain reaction.
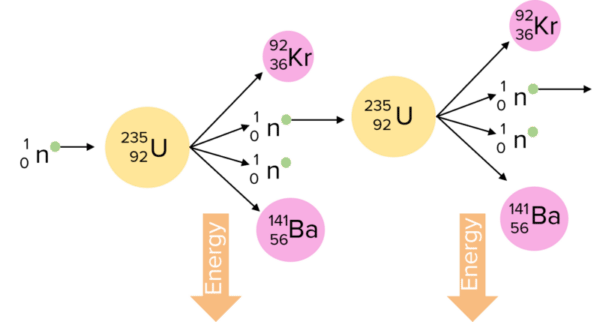
Energy that is not transferred to the smaller nuclei or the neutrons is released as gamma rays. In a nuclear power station, these gamma rays can be used to heat water, producing steam to turn turbines and generate electricity.
In nuclear power stations, the amount of energy produced is controlled by controlling how fast the chain reaction can occur. Control rods, which absorb neutrons, are lowered into the nuclear reactor to slow down the chain reaction and then lifted out of the reactor to speed up the chain reaction.
If an uncontrolled chain reaction occurs, a huge amount of energy may be released in an explosion. This is how nuclear weapons work.
Nuclear Fusion
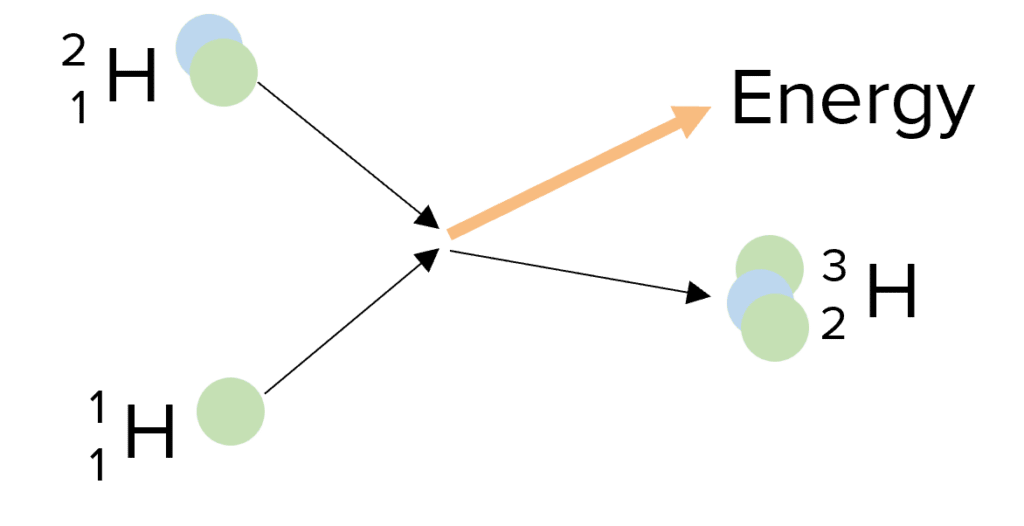
In nuclear fusion, two small nuclei collide and join together (fuse) to make a larger nucleus. The most common example is when two types of hydrogen fuse together to form helium. The bigger nucleus created has slightly less mass than the sum of the original two nuclei. This mass is converted to energy and released as gamma rays.
So far, scientists have not found a way to use nuclear fusion to generate electricity. This is because fusion requires very high temperatures and pressures and so a nuclear fusion reactor is very difficult and expensive to build.
Nuclear Fission and Fusion Example Questions
Question 1: Why do most nuclei need to absorb a neutron before undergoing nuclear fission?
[2 marks]
Nuclear fission rarely happens spontaneously. Absorbing a neutron makes the nucleus unstable, causing fission to occur.
Question 2: Explain what is meant by a “chain reaction” in nuclear fission.
[3 marks]
Neutrons are required to make a nucleus unstable and cause it to undergo fission. When the nucleus splits, two or three neutrons are produced. These neutrons go on to cause more fission reactions.
Question 3: What is the role of control rods in nuclear reactors and how do they do this?
[2 marks]
Control rods control the speed of the chain rection. When lowered into the reactor, the rods absorb neutrons and slow down the chain reaction. When lifted from the reactor, less neutrons are absorbed and the chain reaction speeds up.
Question 4: What is the difference between nuclear fission and nuclear fusion?
[2 marks]
In nuclear fission, a large nucleus splits into smaller nuclei and neutrons. In nuclear fusion, two small nuclei fuse together to make a bigger nucleus.
Nuclear Fission and Fusion Worksheet and Example Questions
Atoms and Nuclear Radiation Questions 1
GCSEOfficial MMEAtoms and Nuclear Radiation Questions 2
GCSEOfficial MMEHazards and Uses of Radiation Questions
GCSEOfficial MME
MME Premium Membership
£19.99
/monthLearn an entire GCSE course for maths, English and science on the most comprehensive online learning platform. With revision explainer videos & notes, practice questions, topic tests and full mock exams for each topic on every course, it’s easy to Learn and Revise with the MME Learning Portal.
Sign Up Now

