Sine Rule
Sine Rule Revision
The Sine Rule
When we first learn the sine function, we learn how to use it to find missing side-lengths & angles in right-angled triangles. The sine rule is an equation that can help us find missing side-lengths and angles in any triangle.
Make sure you are happy with the following topics before continuing:
The Sine Rule Formula
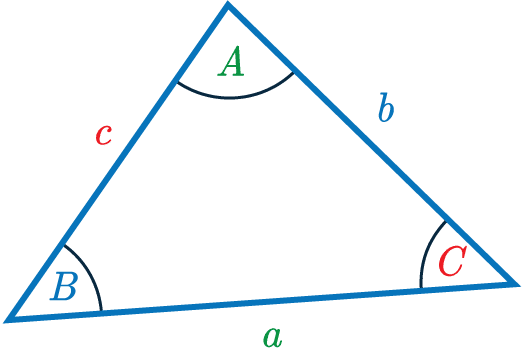
Looking at the triangle below, the sine rule is:
\dfrac{\textcolor{limegreen}{a}}{\sin \textcolor{limegreen}{A}}=\dfrac{\textcolor{blue}{b}}{\sin \textcolor{blue}{B}}=\dfrac{\textcolor{red}{c}}{\sin \textcolor{red}{C}}
In this topic, we’ll go through examples of how to use the sine rule to find missing angles and missing sides.

Example 1: Sine Rule to Find a Length
Use the sine rule to find the side-length marked x to 3 s.f.
[2 marks]
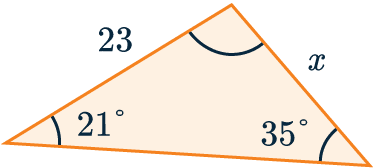
First we need to match up the letters in the formula with the sides we want, here:
a=x, A=21\degree, b = 23 and B = 35\degree
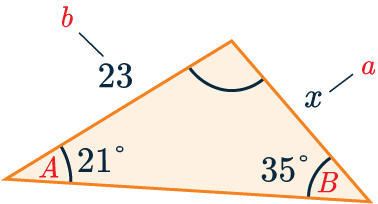
Next we’re ready to substitute the values into the formula. Doing so gives us:
\dfrac{x}{\sin(21°)}=\dfrac{23}{\sin(35°)}
Multiplying both sides by \sin(21°):
x=\dfrac{23}{\sin(35°)}\times\sin(21°)
Putting this into a calculator we get:
x=14.37029543...
x=14.4 (3 sf)
As in previous topics, there is no need to evaluate the sine functions until the final step.
Example 2: Sine Rule to Find an Angle
Use the sine rule to find the obtuse angle marked x to 2 s.f.
[2 marks]
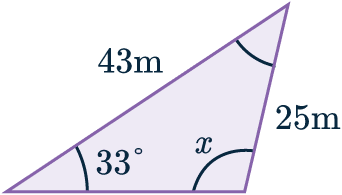
As we have been asked to find a missing angle, we can use another version of the sine rule:
\dfrac{\sin A}{a}=\dfrac{\sin B}{b}=\dfrac{\sin C}{c}
A=x, a=43, B=33\degree, b=25.
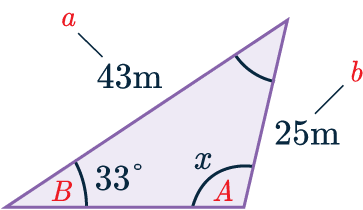
Substituting these values into the formula, we get:
\dfrac{\sin x}{43}=\dfrac{\sin(33°)}{25}
Multiply both sides by 43 to get:
\sin x=\dfrac{43\sin(33°)}{25}
Then, taking \sin^{-1} of both sides, we get:
x= \sin^{-1}\bigg(\dfrac{43\sin(33°)}{25}\bigg)
x=69.5175049...°
However, the question asked for an obtuse angle, but we got an acute answer – why?
It’s because we can draw two different (but both correct) triangles using the information we were given at the start.
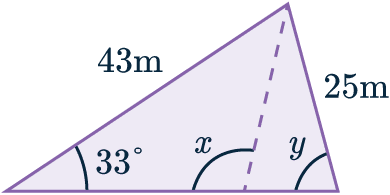
This is the ambiguous case of the sine rule, and it occurs when you have 2 sides and an angle that doesn’t lie between them.
To find the obtuse angle, simply subtract the acute angle from 180:
180-69.5175049=110.4824951
x=110\degree (2 sf)
Sine Rule Example Questions
Question 1: Use the sine rule to find the side-length marked x in the below triangle to 3 significant figures.
[3 marks]
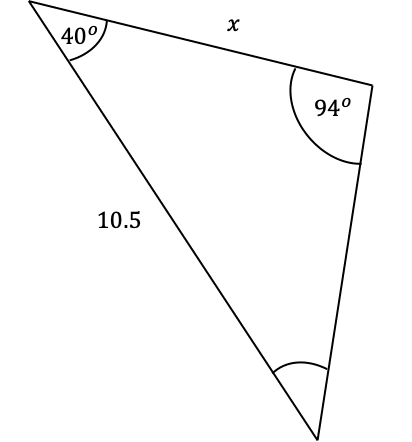
First, we need to find the angle opposite to the missing side as it is not given in the question. Using all the angles in a triangle add to 180 degrees we get that:
A=180\degree-40\degree-94\degree=46\degree
Now we have enough information to properly label the triangle and substitute values into the sine rule:
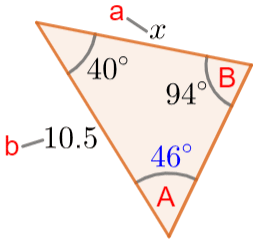
\dfrac{x}{\sin(46\degree)}=\dfrac{10.5}{\sin(94\degree)}
Solving for x we get:
x=\dfrac{10.5}{\sin(94\degree)}\times\sin(46\degree)=7.571511726...
x=7.57 (3 sf).
Question 2: Use the sine rule to find the side-length marked x in the below triangle to 3 significant figures.
[2 marks]
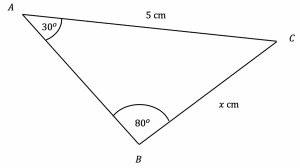
Here we are able to use the sine rule straightaway:
\dfrac{x}{\sin(30\degree)}=\dfrac{5}{\sin(80\degree)}
Multiplying both sides of the equation by \sin(30\degree):
x=\dfrac{5}{\sin(80\degree)}\times\sin(30\degree)=2.538566...
x=2.54 cm (3 sf).
Question 3: Use the sine rule to find the obtuse angle x on the diagram below to 3 significant figures.
[3 marks]
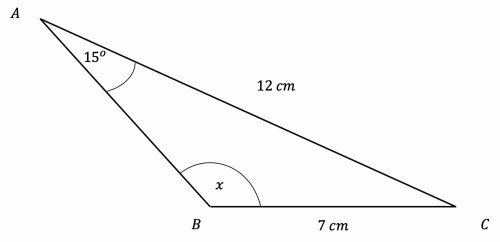
Here we are able to use the sine rule straightaway:
\dfrac{\sin(x\degree)}{12}=\dfrac{\sin(15\degree)}{7}
Multiplying both sides of the equation by 12 we find:
\sin(x)=\dfrac{12\times\sin(15\degree)}{7}=0.4436897916
Taking the inverse sine of both sides:
x=\sin^{-1}(0.4436897916)=26.33954244\degree
However considering the diagram, the angle is clearly obtuse (greater than 90 degrees). This is the ambiguous case of the sine rule and it occurs when you have 2 sides and an angle that doesn’t lie between them. To find the obtuse angle, simply subtract the acute angle from 180:
180\degree-26.33954244\degree =153.6604576
=154\degree (3 sf).
Instead of typing the full number into the calculator for each step of the calculation, you can use the ANS button to save time.
Question 4: Use the sine rule to find the angle CAB on the diagram below to 3 significant figures.
[2 marks]
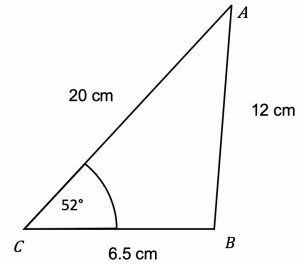
We are able to use the sine rule straightaway:
\dfrac{\sin(x\degree)}{6.5}=\dfrac{\sin(52\degree)}{12}
Multiplying both sides of the equation by 6.5 we find that:
\sin(x)=6.5 \times \dfrac{\sin(52\degree)}{12} =0.4268391582
Taking the inverse sine of both sides and keeping the answer from the previous step on our calculator, we get:
x=\sin^{-1}(ANS)=25.26713177
x=25.3 \degree (3 sf).
Question 5: Use the sine rule to find the side-length marked x below to 3 significant figures.
[2 marks]
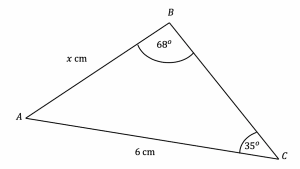
Applying the sine rule:
\dfrac{x}{\sin(35\degree)}=\dfrac{6}{\sin(68\degree)}
Multiplying both sides of the equation by \sin(35\degree), we find:
x=\dfrac{6}{\sin(68\degree)}\times\sin(35\degree)=3.711732685...
x=3.71 cm (3 sf).