Coordinates and Ratios
Coordinates and Ratios Revision
Coordinates and Ratios
Coordinates, denoted by \textcolor{red}{(x, y)}, are what we use to communicate where a particular point is located on a pair of coordinate axes.
There are 3 key skills you need to know involving coordinates and ratios for GCSE Maths.
Make sure you are happy with the following topics before continuing:
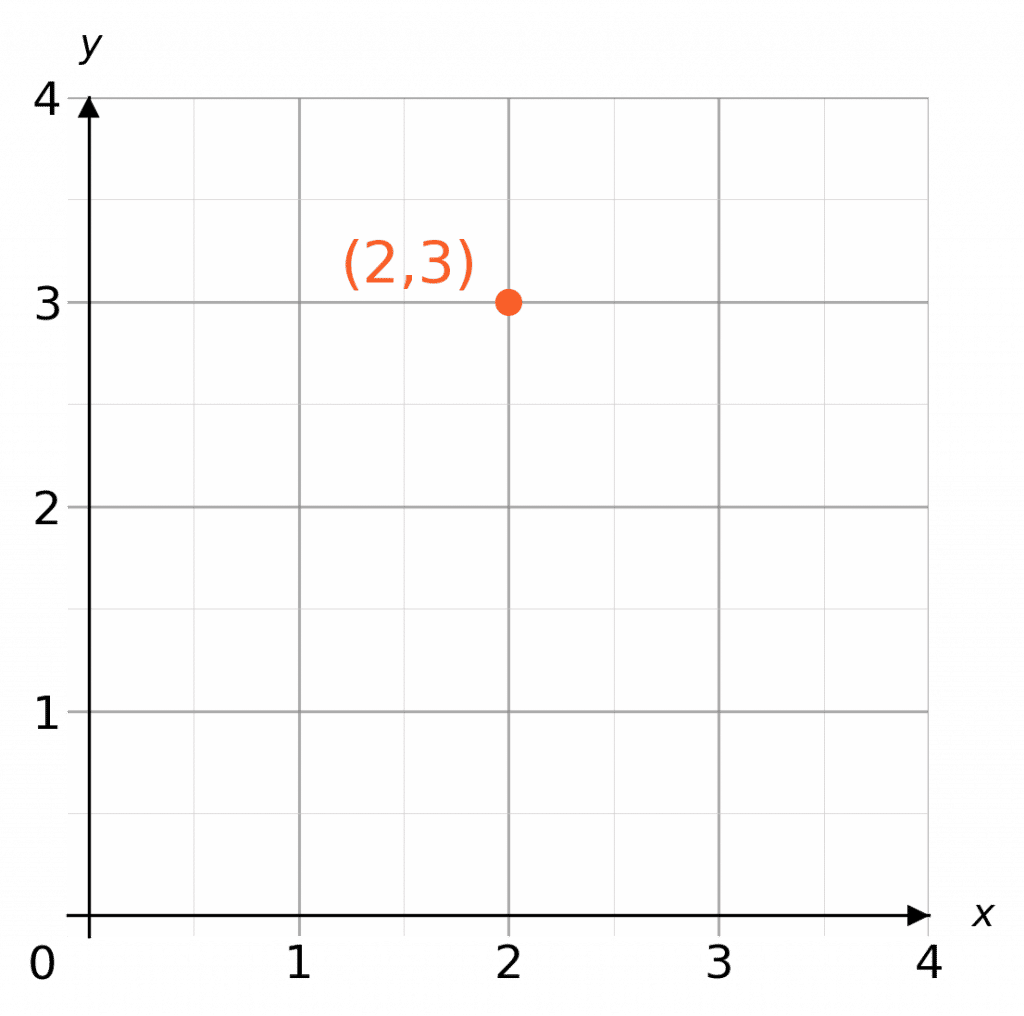
Skill 1: Plotting Coordinates
Plot the point (\textcolor{red}{2},\textcolor{blue}{3})
On the x-axes we find 2, and on the y axes we find 3 and mark the point with a dot or a cross.
x = \textcolor{red}{2}
y=\textcolor{blue}{3}

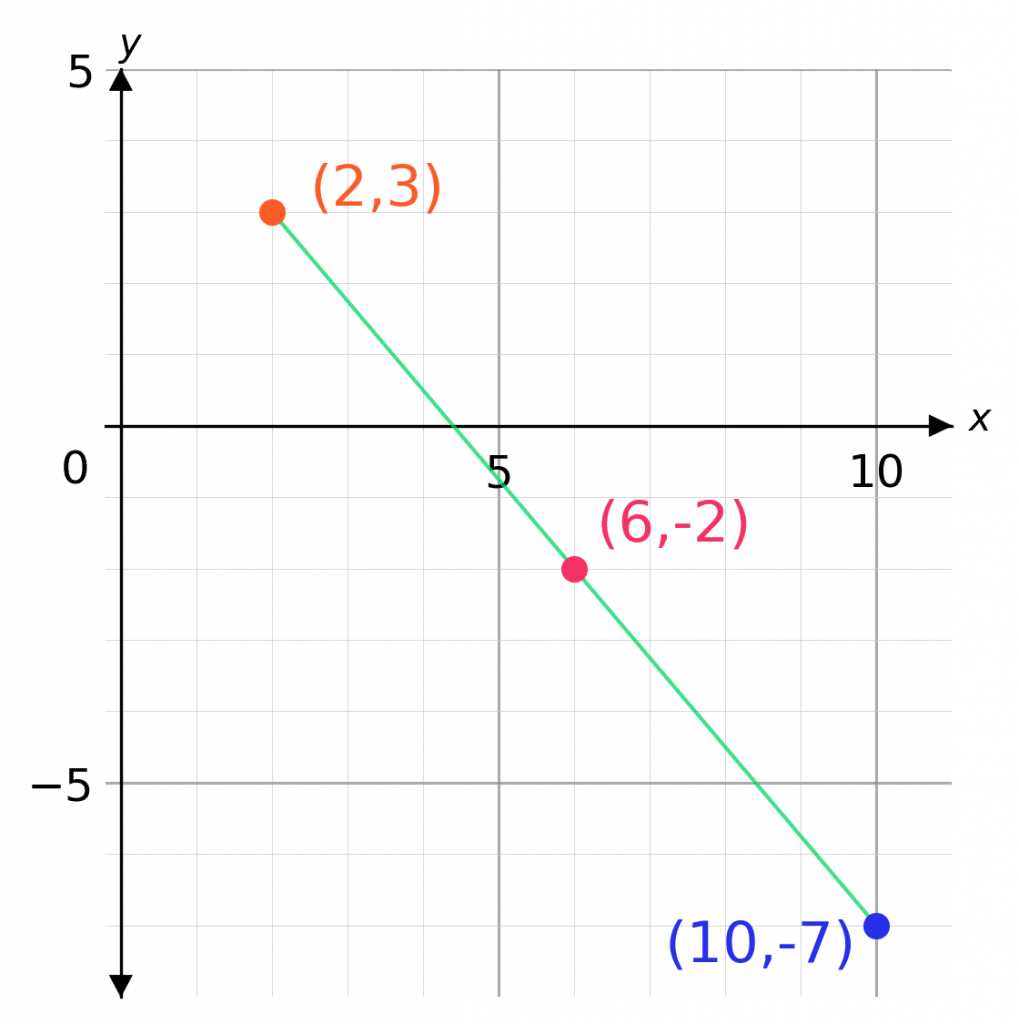
Skill 2: Finding the Midpoint of a Line
Find the midpoint of the line segment which joins points
\textcolor{Orange}{A:(2,3)} and \textcolor{blue}{B:(10,-7)}
The word midpoint refers to the point which is exactly halfway between the two points in question.
Step 1: Find the half way point of the x coordinates by adding them up and dividing by 2,
\text{Midpoint of }x\text{ coordinates } = (2 + 10) \div 2 = 6
Step 2: Repeat for the y coordinates,
\text{Midpoint of }y\text{ coordinates} = (-7 + 3) \div 2 = -2
Step 3: Write the values for the midpoint as a coordinate: \textcolor{red}{(6, -2)}
You can also find the midpoint of a line segment, if the two points at either end are drawn on a grid. , just by looking at it.

Skill 3: Ratios to find Coordinates
Finding a point a certain way between two points is the hardest part of this topic and involves a good knowledge of using ratios.
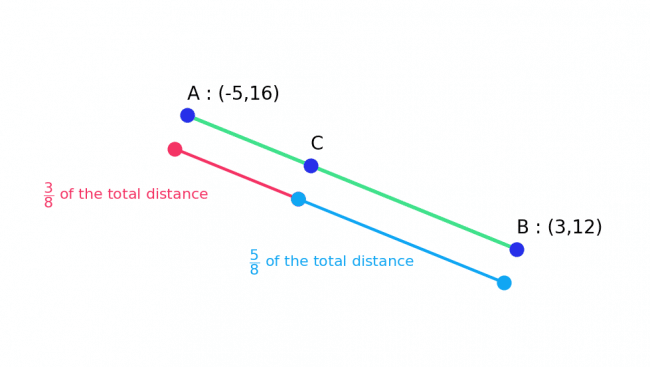
Example: Points A and B have coordinates (-5, 16) and (3, 12) respectively.
Point C lies on the line segment between points A and B such that AC:CB = \textcolor{red}{3}:\textcolor{blue}{5}.
Find the coordinates of point C.
Step 1: Find the total parts.
\textcolor{red}{3}:\textcolor{blue}{5} which means there are \textcolor{limegreen}{8} parts in total.
The distance from A to C is \textcolor{red}{3} parts of a total \textcolor{limegreen}{8}.
Step 2: Find the x value.
Total distance in the x coordinates:
3 - (-5) = 8
Next we find \dfrac{\textcolor{red}{3}}{\textcolor{limegreen}{8}}of this.
\dfrac{\textcolor{red}{3}}{\textcolor{green}{8}} \times 8 = 3
Adding this to the x coordinate of A, we get
x\text{ coordinate of C } = -5 + 3 = -2
Step 3: Repeat for y
Total distance in the y coordinates:
12 - 16 = -4
\dfrac{\textcolor{red}{3}}{\textcolor{green}{8}} \times -4 = -\dfrac{3}{2}
Adding this to the y coordinate of A, we get
y\text{ coordinate of C } = 16 + \left(-\dfrac{3}{2}\right) = \dfrac{29}{2}
Therefore, the coordinates of C are \left(-2, \dfrac{29}{2}\right).
You could also write this as \left(-2, 14.5\right).
Coordinates and Ratios Example Questions
Question 1: Write down the coordinates of points A, B, and C seen below.
[3 marks]
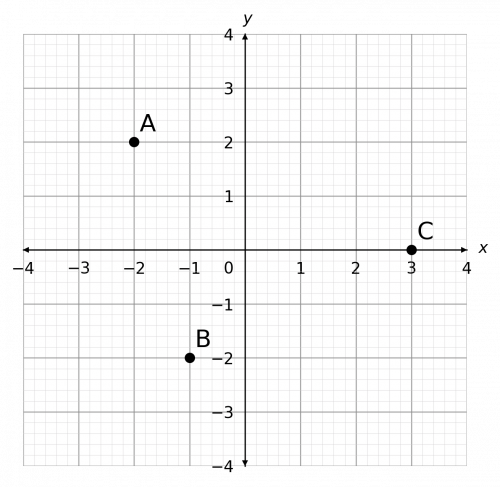
A is - 2 in the x direction and 2 in the y direction, so A = (-2, 2).
B is - 1 in the x direction and - 2 in the y direction, so B = (-1, -2).
C is 3 in the x direction and 0 in the y direction, so C = (3, 0).
Question 2: Find the midpoint of the line segment that joins points A and B as seen below.
[2 marks]
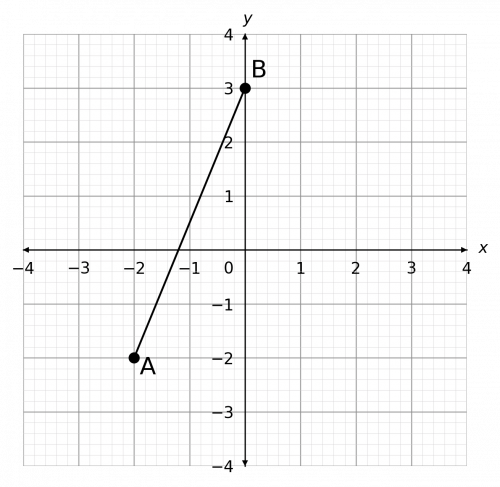
Point A has coordinates (-2, -2).
Point B has coordinates (0, 3).
By taking the average of the x coordinates of A and B, the x coordinate of the midpoint is
\dfrac{-2 + 0}{2} = -1.
By taking the average of the y coordinates of A and B, the y coordinate of the midpoint is
\dfrac{-2 + 3}{2} = \dfrac{1}{2}.
Therefore, the coordinates of the midpoint are \left(-1, \dfrac{1}{2}\right).
Note: it is often useful to check the graph to see if your answer looks correct.
Question 3: Points A and B have coordinates (-10, 37) and (-16, 1) respectively. Point C lies on the line segment between points A and B such that AC:CB = 2:7. Find the coordinates of point C.
[2 marks]
In a ratio of 2:7 there are 9 parts in total, and the distance from A to C constitutes 2 of those parts. Therefore, the distance from A to C counts for \dfrac{2}{9} of the total distance between A and B. So, we’re going to subtract the individual coordinates of A from B to find the distance in both x and y, and then we are going to add \dfrac{2}{9} of these respective distances to the coordinates of point A.
First, x coordinates: -16 -(-10) = -6, then
\dfrac{2}{9} \times (-6) = -\dfrac{12}{9} = -\dfrac{4}{3}
Adding this to the x coordinate of A, we get
x\text{ coordinate of C } = -10 + \left(-\dfrac{4}{3}\right) = -\dfrac{34}{3}
Second, y coordinates: 1 - 37 = -36, then
\dfrac{2}{9} \times (-36) = -\dfrac{72}{9} = -8
Adding this to the y coordinate of A, we get
y\text{ coordinate of C } = 37 + (-8) = 29
Therefore, the coordinates of C are \left(-\dfrac{34}{3}, 29\right).