Plant Hormones
Plant Hormones Revision
Plant Hormones
Plants contain hormones that promote growth. Auxins control the growth of plants in the roots and shoots, allowing them to respond to light and gravity. This can be investigated in a simple practical using plant seedlings. Plant hormones and chemicals can be extracted or artificially copied and used to our advantage.
Auxins
Auxin is a plant hormone that causes the tips of roots and shoots to grow. They are produced at the tips and work backwards, elongating the cells just behind the tip.
Uneven distribution of auxins causes the tips of the roots and shoots to grow in different directions. Plants use auxins to their advantage, making the plant shoots grow towards light (phototropism) and roots grow in the direction of gravity (gravitropism or geotropism). This allows the shoot to absorb light for photosynthesis and the roots to absorb water and nutrients from the soil and anchor the plant to the ground.
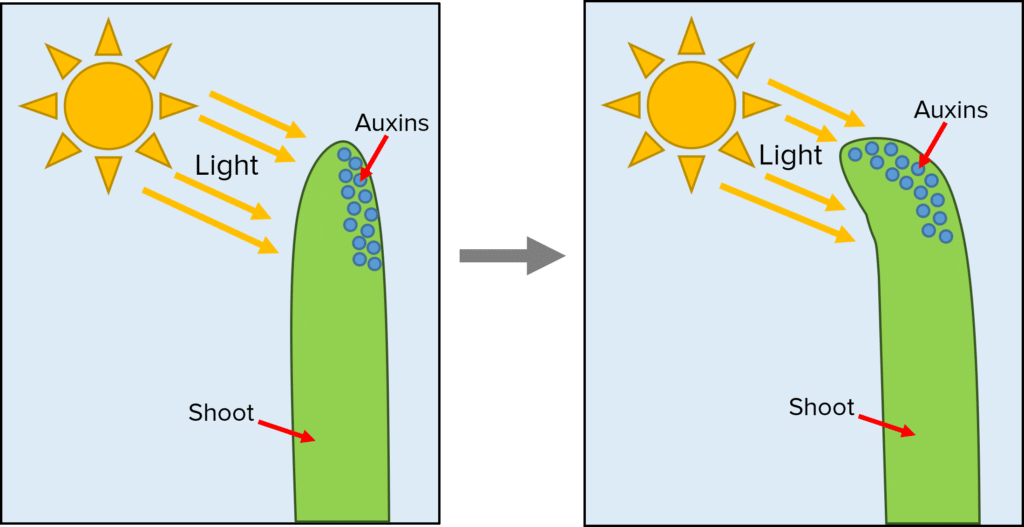
Phototropism (shoots):
In plant shoots, auxins promote growth. Auxins accumulate in the side of the shoot tip furthest away from the light source. Cells therefore grow and elongate more on the shady side of the plant, causing the shoot to bend towards the light.
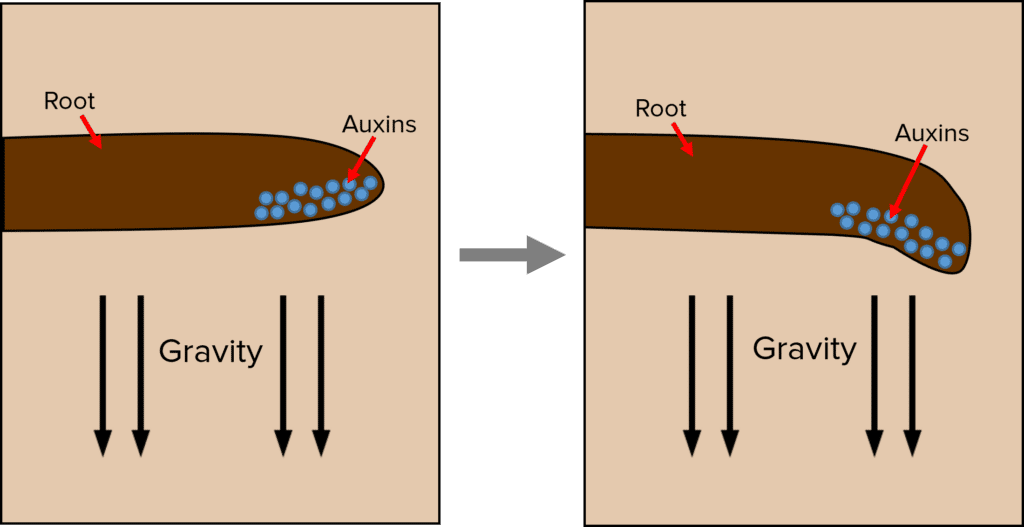
Geotropism (roots):
In plant roots, auxins inhibit growth. If a root is growing sideways, auxins will accumulate in the lower side of the root tip due to gravity. These cells therefore grow and elongate less than the cells on the upper side, causing the shoot to bend downwards, in the direction of gravity.
Required Practical
Investigating the affect of light on the growth of seedlings.
You can carry out simple experiments to investigate the effects of light or gravity on plant seedings. In this example we will vary the direction and intensity of light.
Doing the experiment
- Line 3 petri dishes with moist cotton wool or filter paper.
- Put 10 cress or mustard seeds into each petri dish and leave them in a warm place to germinate.
- Once germinated, measure the height of the seedlings using a ruler.
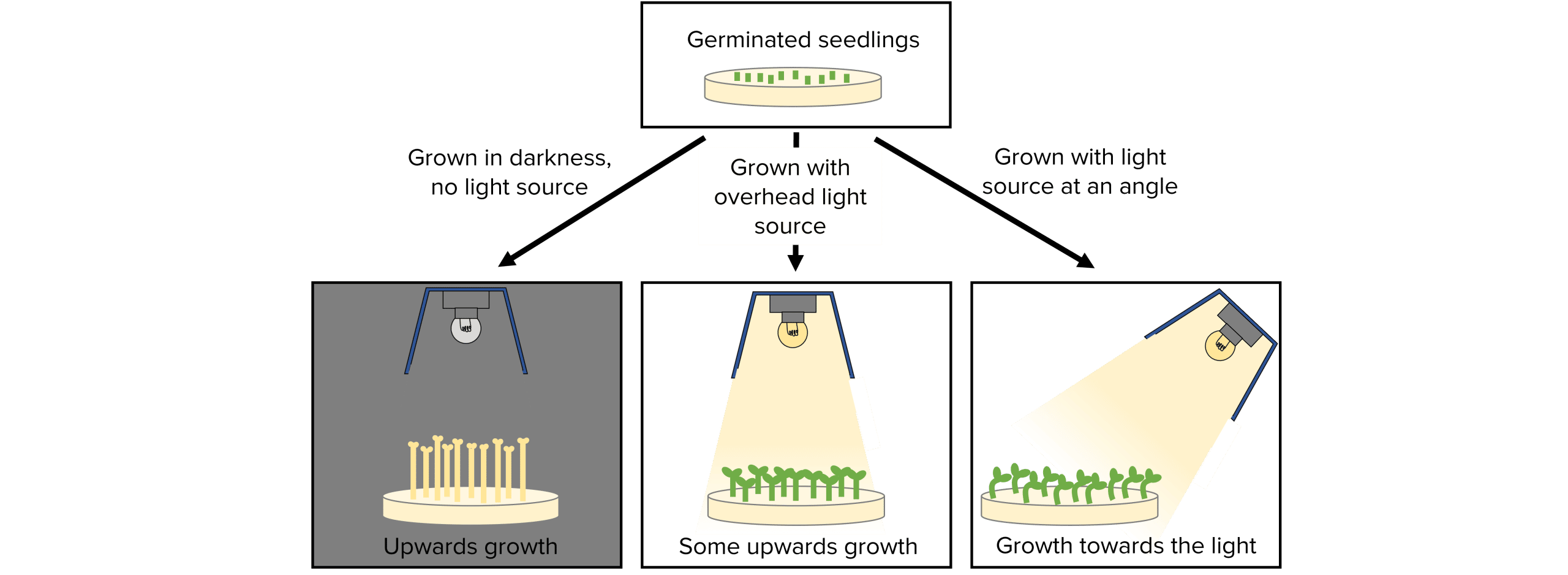
- Put one petri dish in a dark cupboard or room with no light source, one under an overhead light source and one under a light source at an angle and leave for a week.
- Measure the height of the seedings again and observe how they have grown under each light condition.
You must make sure to control other variables:
- Use the same number of seeds in each dish.
- Use the same type of seeds from the same packet.
- Keep the temperature the same for all the petri dishes.
- Give each petri dish the same amount of water.
Analysing the results
Observations from the petri dishes:
- Those grown in the dark will be the longest as they will keep trying to grow upwards in search of a light source. However their leaves will be small and yellow.
- Those with the overhead light source will grow directly upwards and will be healthy.
- Those with the light source at an angle will have grown in the direction of the light (phototropism) and will be healthy.
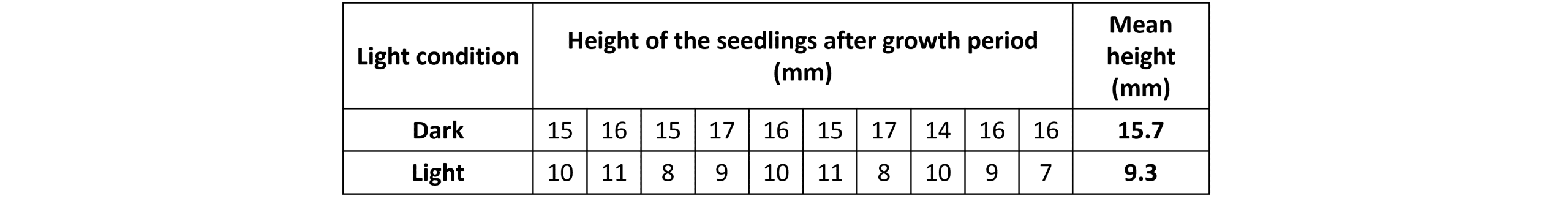
You can then calculate and compare the mean height of the seedlings grown under the overhead light and in the dark.
Conclusions
- The seedlings grow towards the light (phototropism).
- The seedlings grew taller in the dark than in the light.
Uses of Plant Hormones
Plant hormones can be extracted or artificially copied by humans and used in many ways.
Auxin– plant growth hormone in roots and shoots.
- Weed killers– Most weeds have broad leaves compared to the grasses and cereals that they grow next to. Selective weed killers use auxins to make the broad leaf plants grow too much and die. However, removing these unwanted plants with weed killers reduces biodiversity.
- Rooting powders– Auxins are used in rooting powders to grow full new plants from plant cuttings. They provide a very quick method to produce clones of the same plant.
- Tissue culture– To grow a full plant from just a few cells, scientists add auxins and nutrients to help the cells divide.
Gibberellin– plant growth hormone that stimulates germination, flowering and growth of stems.
- Dormancy– seeds may not germinate until they have gone through periods of cold and drought (the seeds are dormant). Adding gibberellins can cause these seeds to germinate at a time it wouldn’t usually and all at the same time.
- Flowering– adding gibberellins can cause plants to flower regardless of the weather and can make flowers grow bigger.
- Large fruit– gibberellins can make fruits grow larger. It is often used to make seedless fruits grow to the same size as regular fruits.
Ethene– speeds up ripening of fruits and controls cell division.
- Ripening– ethene is added to ripen fruits so they are ready to be sold in shops.
- Delaying ripening– ripening can be temporarily stopped by adding chemicals that stop the fruit producing ethene or remove ethene from the plant all together. This means that fruits can be transported when unripe and less easily damaged, then ripened when closer to the destination with artificially produced ethene.
Plant Hormones Example Questions
Question 1: Explain what causes plant roots to grow in the direction of gravity.
[3 marks]
- Gravity causes auxins to accumulate on the lower side of a root.
- Auxins inhibit growth in the root.
- Upper side grows more than lower side so root curves downwards in the direction of gravity.
Question 2: Name two variables you would need to keep the same when investigating the effect of direction of light on the growth of plant seedlings.
[2 marks]
Any two from:
- Number of seeds
- Type of seeds
- Temperature
- Amount of water
- Light intensity
Question 3: Give two ways that auxins are used by farmers and gardeners.
[2 marks]
- Weed killers
- Rooting powders


