DNA
DNA Revision
DNA
DNA is a chemical found in the nucleus of cells that holds all the genetic information for an organism. DNA is made up of a chain of nucleotides that form chromosomes. Each chromosome contains several genes that contain the information to create specific proteins via protein synthesis. All of the genes of an organism is called a genome and understanding the human genome has lead to several scientific and medical breakthroughs. Changes to the genetic information are called mutations and can sometimes be harmful.
Structure of DNA
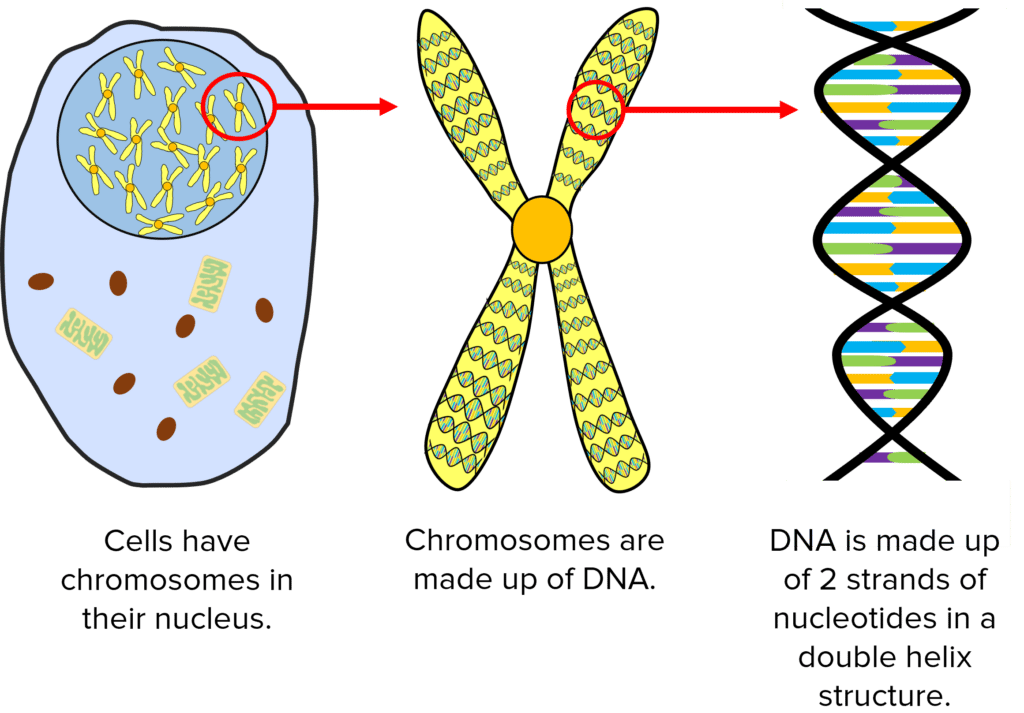
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is a chemical that holds all the genetic information of an organism and therefore controls growth and development. DNA is a polymer made from two strands of nucleotides that are coiled together in a double helix shape.
In the nucleus of plant and animal cells, DNA forms structures called chromosomes.
DNA in chromosomes is divided into smaller sections called genes that code for specific sequences of amino acids and create specific proteins.
Human Genome
The genome of an organism is all of its genetic information.
Studying the human genome can be very useful:
- Scientists study the human genome to identify genes that are linked to diseases and better understand inherited genetic disorders. This can help them identify people who are at risk of developing a disease and can help create effective treatments.
- Scientists also use the human genome to study migration patterns of our ancestors. They do this by studying the genomic differences between populations of people from around the world.
Nucleotides
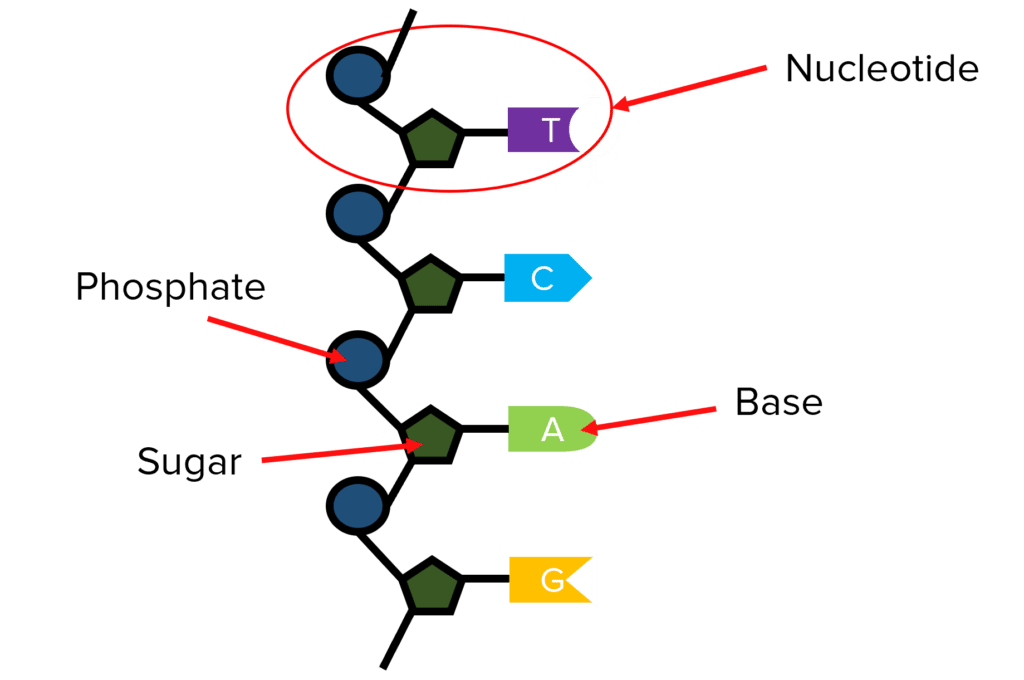
DNA is a polymer made from repeating nucleotides.
All the nucleotides contain a sugar and a phosphate group but will have one of 4 different bases, A, T, G and C.
Every group of 3 bases in the sequence codes for a different amino acid. The order of the bases determines the order of amino acids produced and therefore which specific protein is created.
Note:
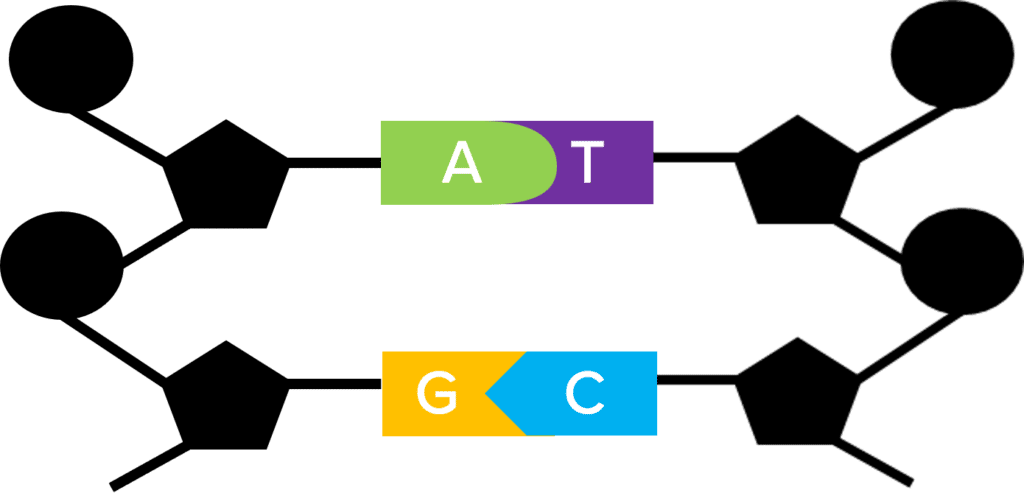
Higher biology students should also know that each base has a complementary base on the other stand of the DNA. The DNA strands are held together by the complementary base pairs:
A is always linked to a T and vice versa.
G is always linked to a C and vice versa.
Protein Synthesis
Proteins are built using DNA in a process called protein synthesis.
- A single-stranded copy of the DNA called mRNA is made in the nucleus.
- The mRNA travels out of the nucleus and to a ribosome which is situated in the cytoplasm.
- At the ribosome, carrier molecules bring specific amino acids in the right order based on the mRNA template and they form an amino acid chain. Every 3 bases codes for one amino acid.
- When the chain is complete, the amino acid chain folds into a unique shape, forming a specific protein. There are lots of different types of protein that are produced this way, including enzymes, hormones and structural proteins (like collagen).
The specific sequence of bases in the DNA creates a specific order of amino acids assembled at the ribosome. This will determine how the chain gets folded and which specific protein is made.
Not all parts of DNA code for proteins. Non-coding parts of DNA can control whether or not other genes are used to make a proteins. They can turn the expression of the genes on and off, changing the phenotype (characteristic) produced.
Mutations
Mutations are random changes in the sequence of an organisms DNA bases and happen continuously. They can be inherited, caused by exposure to certain substances and radiation or just occur spontaneously.
As DNA codes for specific amino acid sequences which create specific shaped proteins, some mutations can have detrimental effects on the organism:
- If the shape of an enzyme is altered, it will no longer be complementary to its substrate. They will not be able to bind and form an enzyme-substrate complex and it will not be able to catalyse the reaction.
- If structural proteins are altered, they could lose their strength and ability to provide support.
Most mutations have little to no effect on the protein created, e.g. changing its shape only slightly so it is still functional.
Mutations in non-coding sections of DNA can change how genes are expressed.
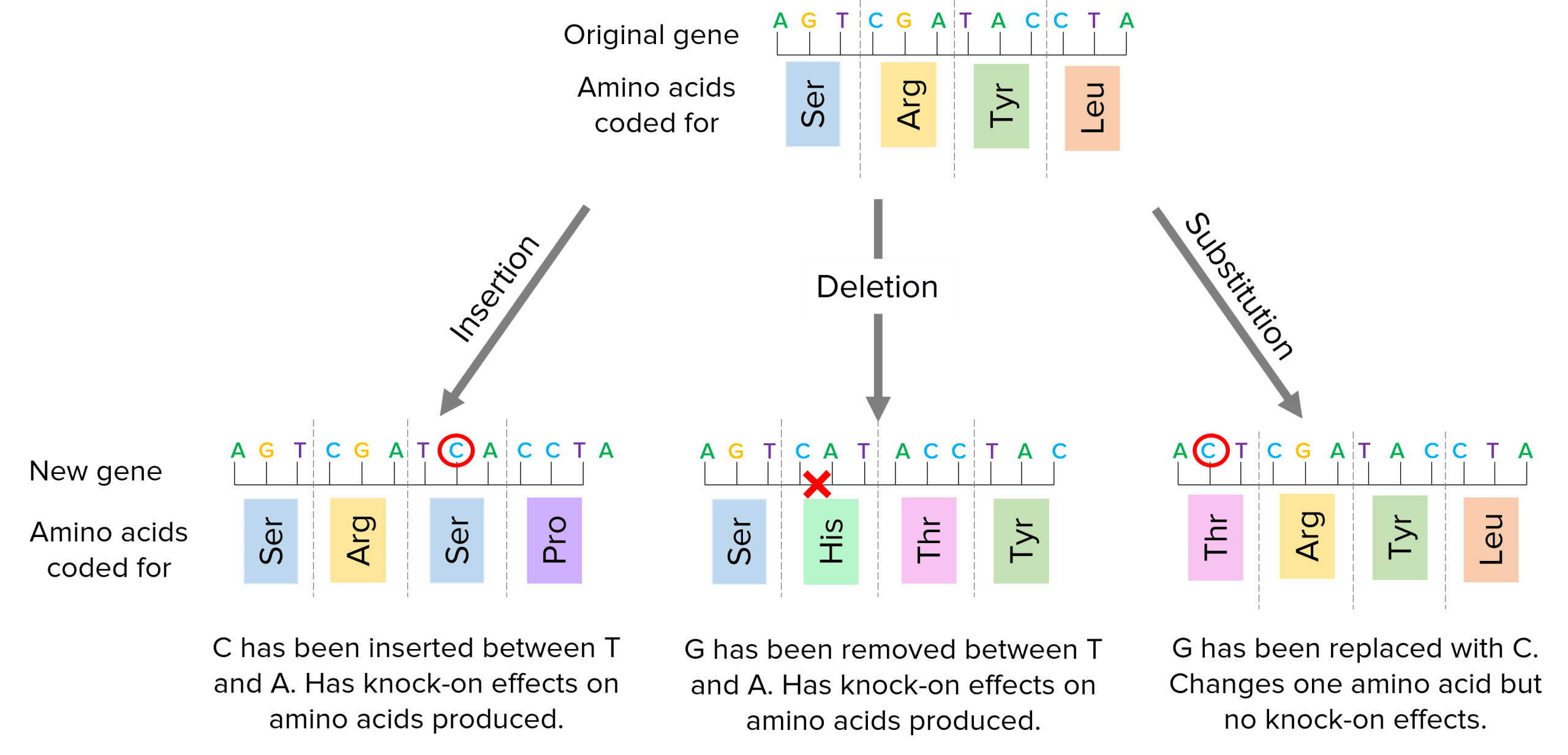
Types of mutations include:
- Insertions– A new base is inserted into the sequence where it is not supposed to be. As DNA is read in groups of 3 bases, this can cause knock-on effects further down the sequence and cause major changes to the amino acids coded for and the protein produced.
- Deletions– A base is removed from the sequence which will have knock-on effects further down the sequence and cause major changes to the amino acids coded for and the protein produced.
- Substitutions– A base is swapped for another base, which can be harmless or have more serious effects depending on the base that is changed.
DNA Example Questions
Question 1: Describe the structure of DNA.
[2 marks]
DNA is made up of 2 strands of nucleotides.
Coiled in a double helix shape.
Students studying biology only should know that:
- nucleotides are made up of a sugar, a phosphate and one of 4 bases.
- A, T, G and C.
Higher tier biology only students should also know that:
- Bases form complementary base pairs.
- A links to T
- G links to C
Question 2: Describe how proteins are made from DNA.
[6 marks]
- A single-stranded copy of the DNA if made.
- Called mRNA.
- mRNA travels out of the nucleus to the ribosome.
- Carrier molecules bring amino acids to the mRNA.
- Every 3 bases code for an amino acid.
- When the chain is complete, it folds into a specific protein.
Question 3: What is a mutation?
[2marks]
A mutation is a random change in the sequence of DNA bases in a gene or chromosome.





