Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis Revision
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis the process by which plants make their own food in the form of glucose. Glucose is then either stored within the plant, used for respiration or used to build new molecules. Many factors affect the rate of photosynthesis and being able to control these factors enables farmers and gardeners to efficiently produce lots of healthy plants.
What is Photosynthesis?
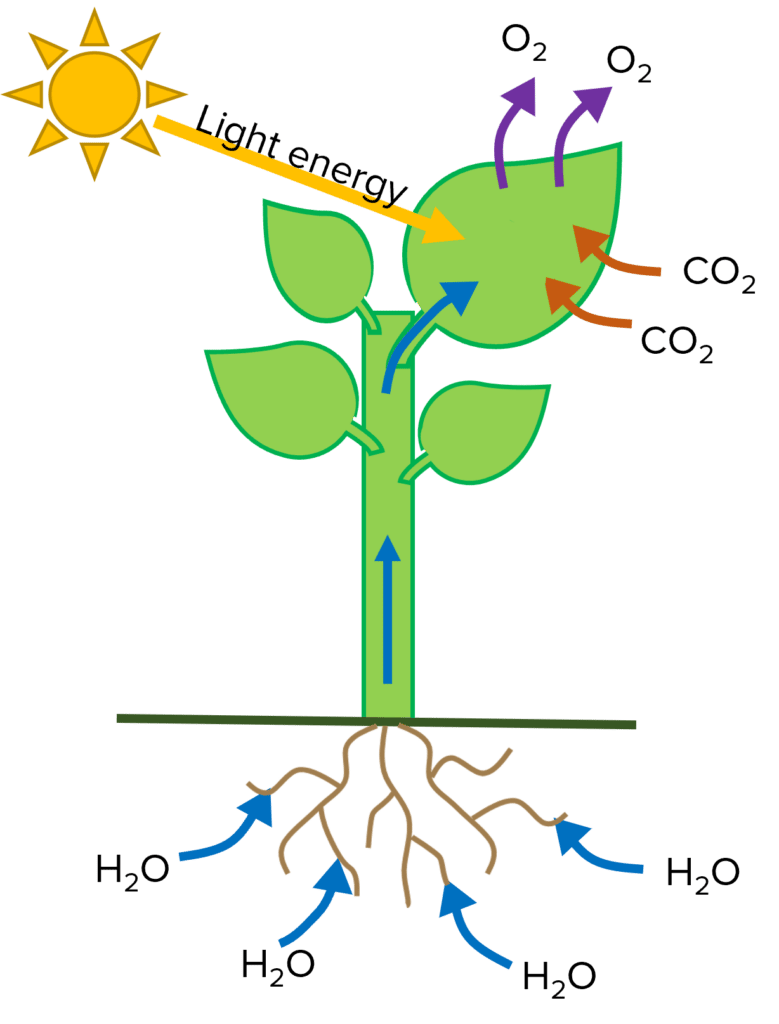
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants (and some algae) use light energy to create their own food, in the form of glucose, from carbon dioxide and water. Oxygen is also made which can be released into the atmosphere or used for aerobic respiration.
Word equation:
Carbon dioxide + Water ——Light——> Glucose + Oxygen
Chemical equation:
6CO2 + 6H2O ——Light——> C6H12O6 + 6O2
Plant cells have chloroplasts which contain a green pigment called chlorophyll which absorbs the light needed for photosynthesis.
Most photosynthesis happens in the leaves as they are specifically adapted for this function.
Photosynthesis is an endothermic reaction which because energy is transferred to the chloroplasts from the environment, in the form of light.
Uses of Glucose in Plants
The glucose made in photosynthesis is used by the plant in many ways.
- Glucose is used to produce energy in respiration.
- Lots of glucose molecules are joined together to form cellulose which provides strength to cell walls.
- Glucose can be combined with nitrate ions that are absorbed from the soil to produce amino acids. Amino acids join together to make proteins in a process called protein synthesis.
- Glucose can be stored as insoluble starch in the plants leaves, stems and roots. This means the plant will have glucose available in times where it cannot photosynthesise such as during winter.
- Glucose can also be stored in seeds as fats and oils.
Limiting Factors of Photosynthesis
Light intensity, carbon dioxide (CO2) concentration, temperature and amount of chlorophyll have a combined affect on the rate of photosynthesis.
If there is a shortage of these factors, they can limit the rate of photosynthesis – they become the limiting factor:
- At night, it is dark, so light becomes the limiting factor. If there was more light, photosynthesis would happen quicker.
- In winter, it is cold, so temperature becomes the limiting factor. If the temperature was warmer, photosynthesis would happen quicker.
- On sunny and warm days, light intensity and temperature levels are both high so CO2 concentration becomes the limiting factor. Increasing CO2 concentration would increase the rate of photosynthesis.
- Diseased plants may have less chlorophyll so will not be able to absorb as much light for photosynthesis. This means the amount of chlorophyll is the limiting factor.
Creating an Ideal Environment for Plant Growth
An ideal environment for plant growth can be created artificially in a greenhouse. Factors that affect photosynthesis can be controlled easily and prevented from being limited:
Heat:
- Glass structure traps heat from the sun to keep the plants warm.
- Windows can be opened to provide ventilation if it gets too hot.
- Heaters can be used in winter to keep the inside of the greenhouse warm.
Light:
- Glass panes allow lots of light in for photosynthesis.
- At night, artificial lamps can be used to enable plants to continue photosynthesising when there is no natural light.
Carbon dioxide concentration:
- Paraffin heaters can be used that increase the temperature and the amount of carbon dioxide.
Keeping plants in a greenhouse prevents diseases and pest infestations and therefore promotes healthy growth.
Water and fertiliser can be controlled more easily in a greenhouse so plants can receive everything they need to grow.
Farmers use these techniques to make their crops grow faster and stronger, increasing their crop yields and making more money. However, controlling all of the factors on a large scale can be very expensive. It is important that the increase in crop yield is enough cover the costs of the greenhouse while also making a profit. Farmers will provide their crops with the optimum amounts of heat, light etc. but no more than that, as this would be wasting money.
Photosynthesis Example Questions
Question 1: What is the balanced chemical equation for photosynthesis?
[4 marks]
6CO2+6H2O——Light——>C6H12O6+6O2
1 mark for products.
1 mark for reactants.
1 mark for stating light/ light energy required.
1 mark for correct balancing.
Question 2: Explain why plants can’t photosynthesise at night.
[2 marks]
At night it is dark and plants need light energy to photosynthesise.
Light becomes the limiting factor.
Question 3: Describe one way that carbon dioxide concentration can be controlled in a greenhouse.
[1 mark]
Paraffin heaters can be used to increase the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Photosynthesis Worksheet and Example Questions
Photosynthesis Reaction Questions
GCSEOfficial MMEUse of Glucose Questions
GCSEOfficial MME
MME Premium Membership
£19.99
/monthLearn an entire GCSE course for maths, English and science on the most comprehensive online learning platform. With revision explainer videos & notes, practice questions, topic tests and full mock exams for each topic on every course, it’s easy to Learn and Revise with the MME Learning Portal.
Sign Up Now




