Evidence for Evolution
Evidence for Evolution Revision
Evidence for Evolution
Darwin’s theory of evolution was once very controversial but is now supported by a variety of evidence. Fossil records show how organisms have changed over time and the evolution of antibiotic resistance in bacteria supports our understanding of how advantageous traits are inherited by offspring.
Fossils
Fossils are the remains of ancient organisms that are found in rocks. They show what organisms looked like millions of years ago and can be used to work out how much they have changed and evolved.
Fossils can be formed in 3 different ways:
- Parts of organisms that will not decay easily, like bones, shells and teeth, eventually get replaced by minerals. The minerals will form rocks with the same original shape. The surrounding sediments also turn to rock but the fossil will still be distinct from the rest of the rock.
- Soft material like clay can harden around whole organisms, traces of organisms (e.g. footprints), burrows or rootlet traces, forming a cast.
- When certain conditions are lacking, decay cannot happen and organisms are preserved. Examples include ice, peatbogs, amber and tar pits.
Fossils found deeper in the soil are generally from more simple organisms. This supports Darwin’s theory of evolution that all organisms evolved from these simple life forms.
However, the fossil record is incomplete. This is because many early forms of life were soft-bodied so left very few traces behind and many of the fossils that were made have been destroyed by geological activity.
Evolutionary Trees
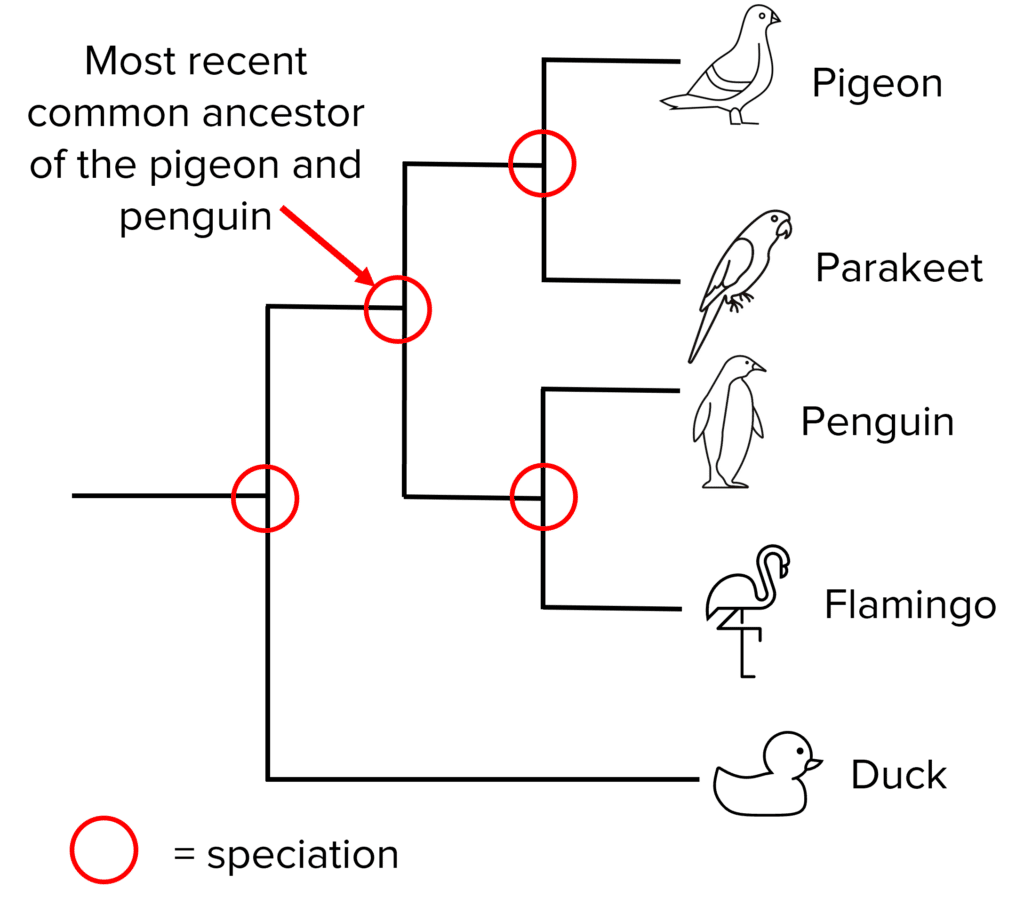
Evolutionary trees are a good way of representing the relationship between different species over evolutionary time. They show when speciation has occurred (when lines branch off).
They can be formed using data collected from fossil records and DNA sequences.
Example:
Out of all the species on the evolutionary tree, pigeons are most similar to parakeets because they share a more recent common ancestor.
Out of all the species on the evolutionary tree, pigeons are least similar to ducks because they share a more distant common ancestor.
Antibiotic Resistance in Bacteria
Bacteria reproduce very quickly in a process called by binary fission. This means that they evolve rapidly.
Mutations often occur in the DNA of bacterial pathogens. Some of these mutations lead to changes in characteristics of the bacteria and may even cause the bacteria to become resistant to certain antibiotics. Due to their high rate of reproduction, entire antibiotic-resistant strains can evolve very quickly.
Antibiotic resistance is very beneficial to the bacterial pathogen as it will not be killed by antibiotics, can reproduce a lot more and the population can grow. However, for humans or other hosts, antibiotic resistance cause big problems because the antibiotics that are used to treat people with bacterial infections will no longer work. This means infected people continue being ill and spread the disease to more people.
Scientists try to develop new antibiotics that bacterial strains are not resistant to but the process is expensive and slow. Also, some ‘superbugs‘ are resistant to all known antibiotics. MRSA is a ‘superbug‘ that usually affects vulnerable people in hospitals and can be fatal.
Preventing the evolution of antibiotic resistance:
- Overuse of antibiotics has caused antibiotic resistance to develop rapidly so doctors should avoid inappropriate prescribing of antibiotics e.g. in non-serious infections or viral infections.
- To make sure antibiotics definitely kill the bacterial pathogens so they do not mutate and develop resistance, patients must complete the full course of antibiotics.
- Antibiotics are often used in farming, to prevent illness and increase growth rate. Bacteria in the animals can also can develop resistance to the antibiotics if overused and these resistant strains can be passed to humans when meat is consumed. Using less antibiotics in farming will help to reduce the amount of antibiotic resistant bacterial strains.
Evidence for Evolution Example Questions
Question 1: Give two reasons why is the fossil record incomplete?
[1 mark]
Early life forms were soft-bodied so didn’t leave traces behind.
Fossils may have been destroyed by geological activity.
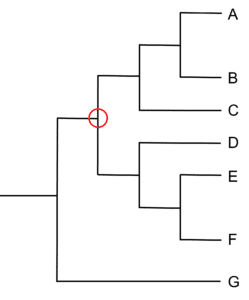
Question 2: Draw a circle around the most recent common ancestor between species A and D.
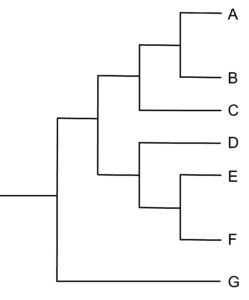
[1 mark]
Question 3: Give two ways that the evolution of antibiotic resistance in bacteria can be prevented.
[2 marks]
Any two from:
- Doctors should not prescribe antibiotics unnecessarily.
- Patients should complete the full course of antibiotics if prescribed.
- Limit the use of antibiotics in farming.





