Vaccinations and Drugs
Vaccinations and Drugs Revision
Vaccinations and Drugs
Vaccinations prevent disease in individuals and can reduce the spread of a disease if given to enough people. Different types of drugs are available to treat infections of different pathogens and cure specific symptoms. Antibiotics are drugs that can cure bacterial diseases but strains of bacteria have become resistant to them.
Vaccines
Vaccines contain dead or weak forms of the pathogen, including its antigens. When injected into the body, it triggers an immune response and lymphocytes produce antibodies to destroy it.
As the pathogen is weakened, the person will destroy it easily and not get symptoms of the disease. However, it will leave behind memory cells that will be able to quickly produce the correct antibodies to destroy the pathogen if infected again.
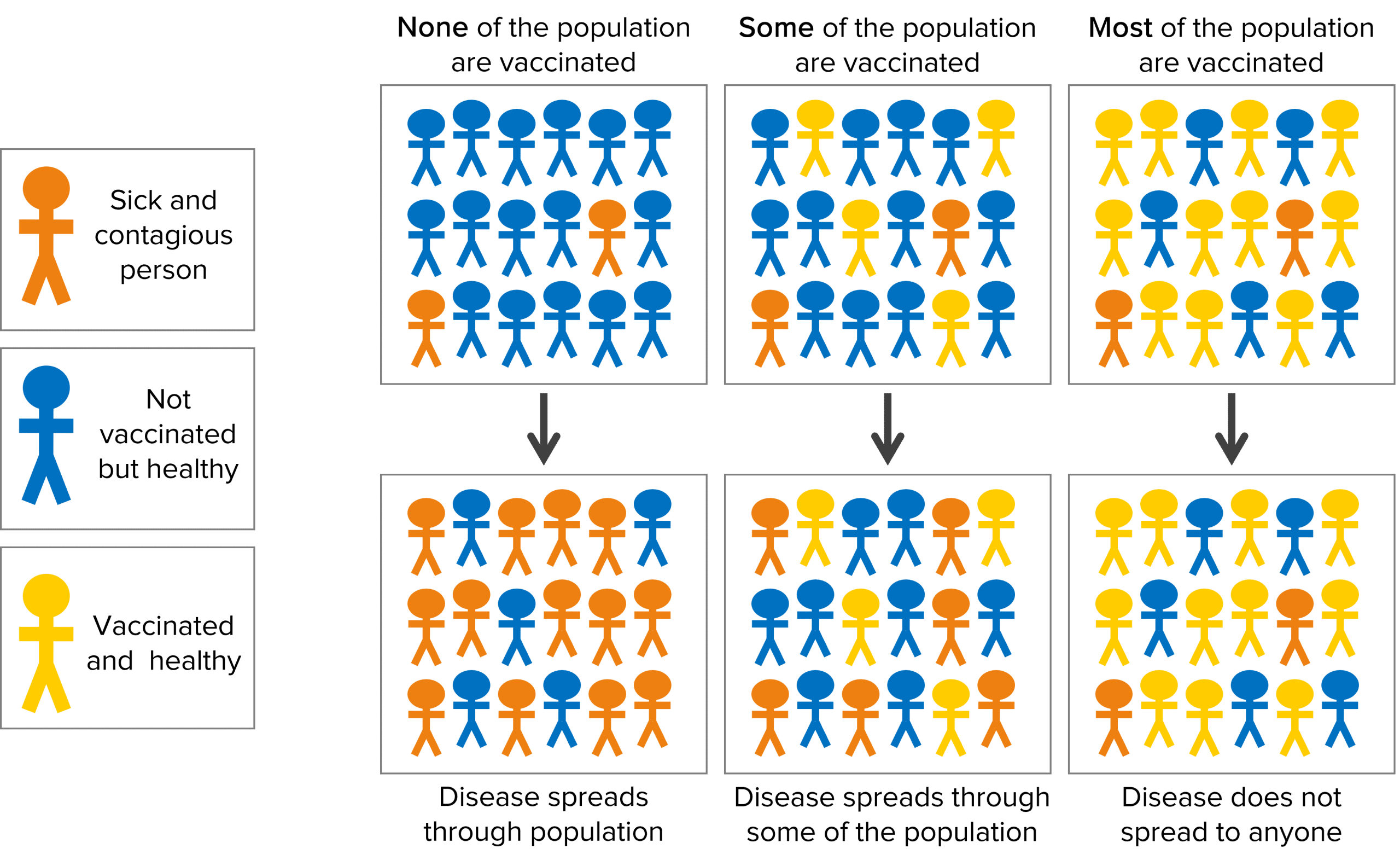
Vaccinated people are able to destroy the pathogen before it becomes infectious so are less likely to spread the disease to others. If enough of the population are vaccinated the spread of the disease can be significantly reduced, even to those who are unvaccinated. This principle is called herd immunity.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Vaccines
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|
|
|
|
Antibiotics vs. Painkillers
Disease treatments either target the cause of the disease (e.g. antibiotics) or treat the symptoms (e.g. painkillers).
Painkillers such as paracetamol and aspirin are used to treat symptoms like headaches and sore throats. They do not cure the disease itself so the body’s immune response must step in and destroy the pathogen.
Antibiotics, such as penicillin, slow or stop the growth of harmful/ infectious bacteria in the body, curing the person of the disease. Specific antibiotics are used to treat specific bacterial infections.
Antibiotics only work on bacteria, they do not kill viruses. This is because viruses reproduce inside host cells so it is extremely difficult to destroy it without also destroying the host cells.
Since their discovery and development, antibiotics have been incredibly successful and have significantly reduced the amount of deaths from bacterial diseases. However, they have been overused and some strains have become resistant to the antibiotics which can be very worrying.
Antibiotic Resistance
Antibiotic resistance evolves at random:
- A random mutation happens in the genetic material of a bacterial cell that makes it resistant to a certain type of antibiotic.
- These bacteria will survive any treatments with this antibiotic and reproduce in the body, causing an increase in numbers of the resistant bacterial strain.
When a bacterial strain becomes resistant to an antibiotic, scientists must work to find another type of antibiotic to treat the disease.
Antibiotic resistance can evolve very quickly because bacteria reproduce at a fast rate (usually by binary fission).
To slow the rate of development of resistant bacterial strains, it is important to limit the use of antibiotics to more serious infections.
Vaccinations and Drugs Example Questions
Question 1: Explain the concept of herd immunity.
[4 marks]
- Vaccinated people can destroy the pathogen.
- So they are less likely to spread the disease to others.
- If enough of the population are vaccinated, the spread of the disease will be prevented.
- Those who are unvaccinated also get protection from the disease.
Question 2: What is the main difference between the functioning of antibiotics and painkillers?
[2 marks]
Painkillers treat the symptoms of a disease, antibiotics target the cause/stop the growth of the infectious bacteria.
Question 3: How do antibiotic resistant bacterial strains arise?
[2 marks]
- Random mutation in the genetic material that causes resistance to an antibiotic.
- These bacteria survive treatments with antibiotics and reproduce.
Vaccinations and Drugs Worksheet and Example Questions
Vaccination Questions
GCSEOfficial MMEAntibiotics and Painkillers Questions
GCSEOfficial MME
MME Premium Membership
£19.99
/monthLearn an entire GCSE course for maths, English and science on the most comprehensive online learning platform. With revision explainer videos & notes, practice questions, topic tests and full mock exams for each topic on every course, it’s easy to Learn and Revise with the MME Learning Portal.
Sign Up Now



