GCSE Maths Equations
GCSE Maths Equations Revision
GCSE Maths Formula Sheet
The GCSE maths formula sheet Z-card includes the formulae you will need to learn for your GCSE maths exam. Whether you are doing AQA, Edexcel or OCR, the following list of maths equations are relevant to you.
Click here to see our Equations To Memorise Z-Card
or
Download free B&W free PDF Version
Algebra
| Higher Only |
|
The quadratic equation:
|
\textcolor{blue}{a}x^2+\textcolor{red}{b}x+\textcolor{Orange}{c}=0 |
| Its solutions are found using the quadratic formula: | x=\dfrac{-\textcolor{red}{b}\pm\sqrt{\textcolor{red}{b}^2-4\textcolor{blue}{a}\textcolor{Orange}{c}}}{2\textcolor{blue}{a}} |
| Direct proportionality: (y is proportional to x, x^2) |
y \propto x \rightarrow y = \textcolor{limegreen}{k}x y \propto x^2 \rightarrow y = \textcolor{limegreen}{k}x^2 |
| Inverse proportionality: (y is inversely proportional to x, x^2) |
y \propto \dfrac{1}{x} \rightarrow y = \dfrac{\textcolor{limegreen}{k}}{x} y \propto \dfrac{1}{x^2} \rightarrow y = \dfrac{\textcolor{limegreen}{k}}{x^2} |
Compound measures
| \text{Speed (s)} = \dfrac{\text{distance (d)}}{\text{time (t)}} | 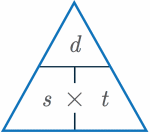 |
| \text{Density (d)} = \dfrac{\text{mass (m)}}{\text{volume (V)}} | 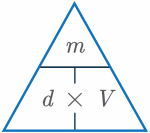 |
| \text{Pressure (p)} = \dfrac{\text{force (F)}}{\text{area (A)}} | 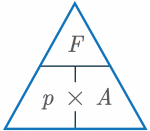 |
Geometry
| Area of a rectangle =l \times w |  |
| Area of a triangle =\dfrac{1}{2} b \times h | 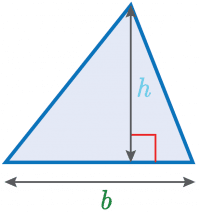 |
| Area of a Parallelogram = b \times h | 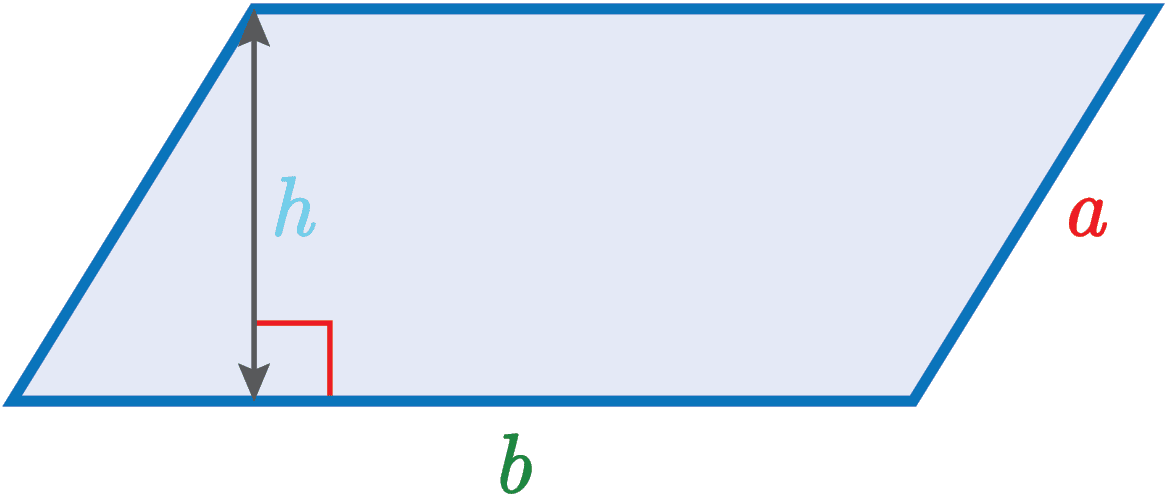 |
| Area of a Trapezium = \dfrac{1}{2}(a + b) \times h | 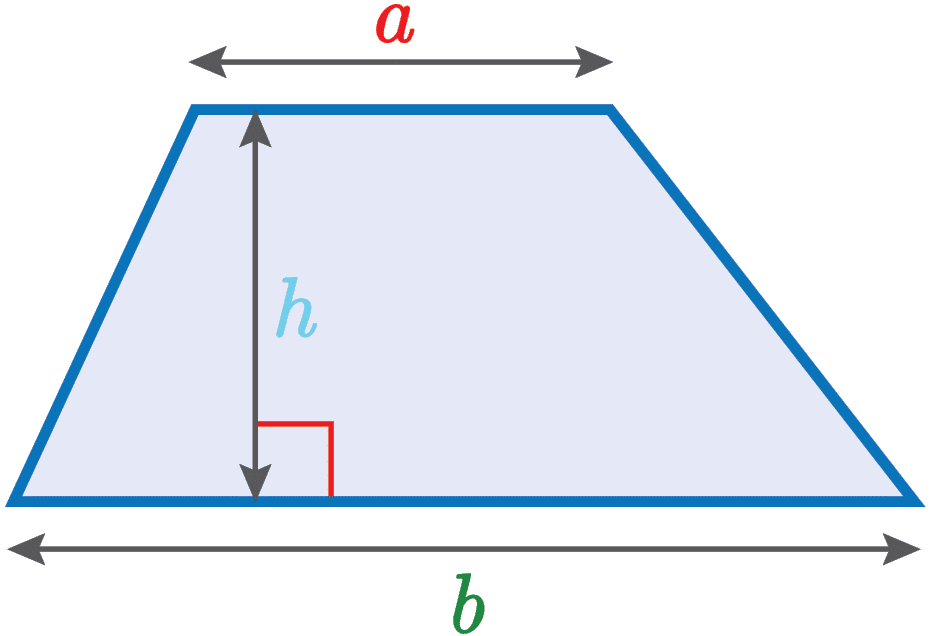 |
| Sum of interior angles for a regular polygon = (\text{number of sides } – \, 2) × 180 | |
| Interior angle of a regular polygon =\dfrac{(\text{number of sides } – \, 2) \times 180}{\text{number of sides}} | |
| Exterior angle of a regular polygon =\dfrac{360}{\text{number of sides}} | |
Circles
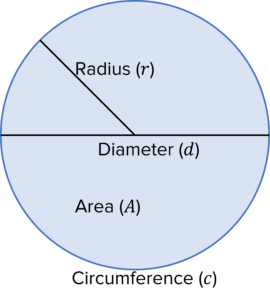
|
Circumference =c=2\pi r=\pi d
Area =A=\pi r^{2} |
 |
GCSE Maths Equations to memorise
Click here to see our Equations To Memorise Z-Card
 |
 |
 |
 |
Volumes
| Higher Only |
| Volume of a cuboid =\text{ length }\times\text{ width }\times\text{ height} |  |
| Volume of a prism =\text{ area of cross section }\times{ \text{length}} | 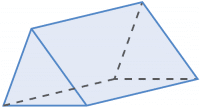 |
| Volume of a cylinder =\pi r^2 h | 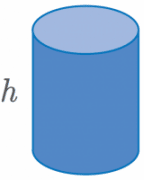 |
|
Volume of a pyramid =\dfrac{1}{3}\times\text{ area of base }\times\text{ vertical height }
|
 |
|
Volume of sphere =\dfrac{4}{3}\pi r^{3} Surface area of sphere =4\pi r^{2} |
 |
|
Volume of cone =\dfrac{1}{3}\pi r^{2}h Curved surface area of cone =\pi rl where l is the slant height |
 |
Pythagoras and Trigonometry
| Higher Only |
| Pythagoras’ theorem: a^2 +b^2 = c^2 | 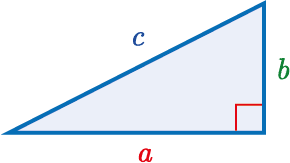 |
|
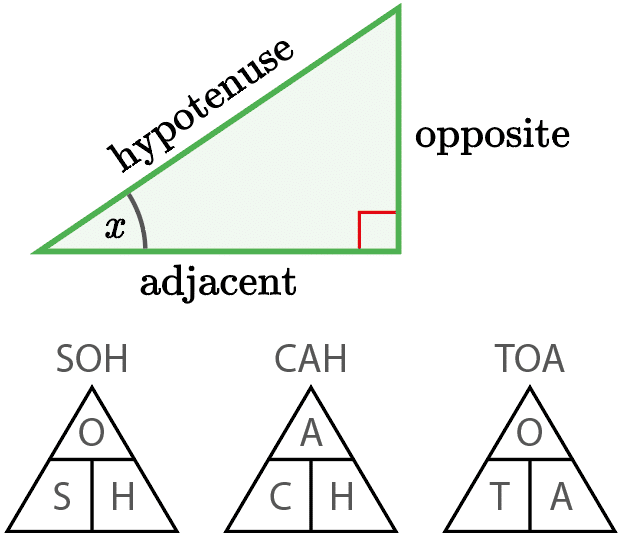
\sin(x) = \dfrac{\text{opp}}{\text{hyp}}\,\,\,\, \cos(x) = \dfrac{\text{adj}}{\text{hyp}}\,\,\,\, \tan(x) = \dfrac{\text{opp}}{\text{adj}}
|
 |
| Sine Rule: \dfrac{\textcolor{red}{a}}{\sin \textcolor{red}{A}}=\dfrac{\textcolor{limegreen}{b}}{\sin \textcolor{limegreen}{B}}=\dfrac{\textcolor{blue}{c}}{\sin \textcolor{blue}{C}} | 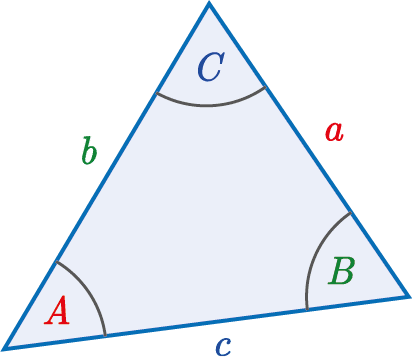 |
|
Cosine Rule: \textcolor{red}{a}^2=\textcolor{limegreen}{b}^2+\textcolor{blue}{c}^2-2\textcolor{limegreen}{b}\textcolor{blue}{c}\cos \textcolor{red}{A} or \cos(\textcolor{red}{A}) = \dfrac{\textcolor{limegreen}{b}^2+\textcolor{blue}{c}^2 - \textcolor{red}{a}^2}{2\textcolor{limegreen}{b}\textcolor{blue}{c}} |
|
| Area of a triangle: \dfrac{1}{2}ab\sin(C) |
| Trigonometry common values: | 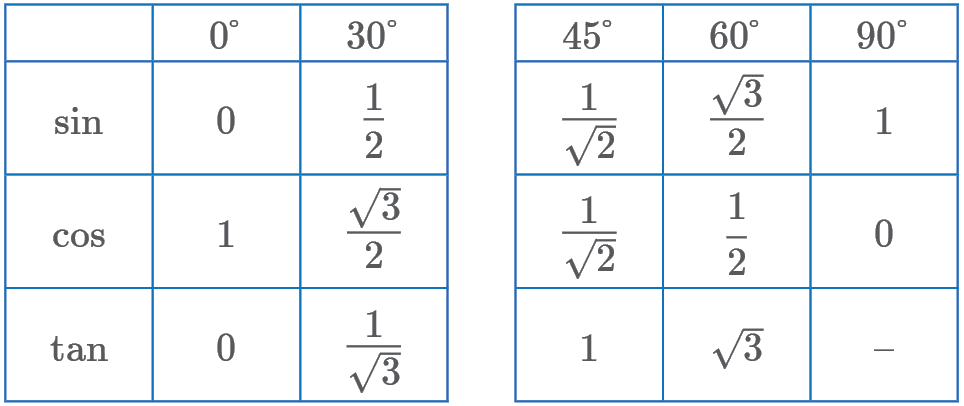 |
Probability and more
| Higher Only |
| Compound interest: |
\text{New value} = \text{original}\times \bigg(1 +\dfrac{\text{percentage}}{100} \bigg)^{\text{time}} |
| Depreciation: |
\text{New value} = \text{original}\times \bigg(1 -\dfrac{\text{percentage}}{100} \bigg)^{\text{time}}
|
| Percentage of amount: |
\dfrac{\text{percentage}}{100} \times \text{amount}
|
| Percentage change: |
\text{Percentage Change }= \dfrac{\text{new} - \text{original}}{\text{original}} \times 100
|
| Histograms: |
\text{Frequency Density }= \dfrac{\text{frequency}}{\text{class width}}
|
| Probability: |
\begin{aligned}P(A\text{ or }B)&=P(A)+P(B)-P(A\text{ and }B)\\P(A\text{ and }B)&=P(A\text{ given }B)P(B)\end{aligned} |
Kinematics
| Higher Only |
| \begin{aligned}v&=u+at\\s&=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}at^{2}\\v^{2}&=u^{2}+2as\end{aligned} |
s= distance u= start speed v= end speed a= acceleration t= time |