Column Vectors
Column Vectors Revision
Column Vectors
A vector is something that has both a magnitude and direction. On diagrams they are denoted by an arrow, where the length tells us the magnitude and the arrow tells us the direction.
Vectors are often split up into two parts, which we call components: An x component, which moves left or right, and a y component, which moves up or down.
Make sure you are happy with the following topics before continuing:
What are Column Vectors?
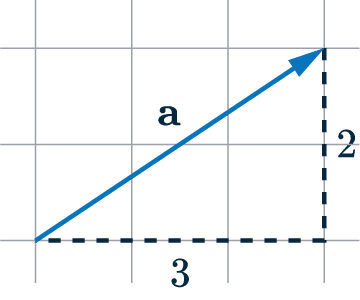
A column vector splits the x and the y direction up, with x on top and y on bottom.
\begin{pmatrix}x\\y \end{pmatrix}
e.g. the vector \mathbf{a} goes 3 spaces to the right and 2 spaces up, so would be expressed as \begin{pmatrix}3\\2 \end{pmatrix}.

Adding and Subtracting Column Vectors
To add/subtract column vectors, we add/subtract the x and y values separately.
\begin{pmatrix}a\\b \end{pmatrix} + \begin{pmatrix}c\\d \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix}a + c\\b + d \end{pmatrix}
For example:
\begin{pmatrix}-3\\4\end{pmatrix}+\begin{pmatrix}5\\2\end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}2\\6\end{pmatrix}
\begin{pmatrix}6\\3\end{pmatrix}-\begin{pmatrix}2\\1\end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}4\\2\end{pmatrix}
Multiplying Column Vectors
To multiply a column vector by a number, we multiply both values in the vector by that number, e.g.
5\times\begin{pmatrix}2\\-3\end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}10\\-15\end{pmatrix}
Example: Working with Column Vectors
Let \mathbf{a}=\begin{pmatrix}3\\8\end{pmatrix} and \mathbf{b}=\begin{pmatrix}-7\\2\end{pmatrix}
Write 2\mathbf{a}+\mathbf{b} as a column vector.
[2 marks]
2\mathbf{a}+\mathbf{b}=2\begin{pmatrix}3\\8\end{pmatrix}+\begin{pmatrix}-7\\2\end{pmatrix}
2\mathbf{a}+\mathbf{b}=\begin{pmatrix}6\\16\end{pmatrix}+\begin{pmatrix}-7\\2\end{pmatrix}
2\mathbf{a}+\mathbf{b}=\begin{pmatrix}-1\\18\end{pmatrix}
Column Vectors Example Questions
Question 1: Let \mathbf{a}=\begin{pmatrix}1\\5\end{pmatrix} and \mathbf{b}=\begin{pmatrix}2\\2\end{pmatrix} Write \mathbf{a}-\mathbf{b} as a column vector.
[2 marks]
\mathbf{a}-\mathbf{b}=\begin{pmatrix}1\\5\end{pmatrix}-\begin{pmatrix}2\\2\end{pmatrix}
\mathbf{a}-\mathbf{b}=\begin{pmatrix}-1\\3\end{pmatrix}
Question 2: Let \mathbf{a}=\begin{pmatrix}2\\7\end{pmatrix} and \mathbf{b}=\begin{pmatrix}-5\\3\end{pmatrix}. Write 3\mathbf{a}-2\mathbf{b} as a column vector.
[2 marks]
Firstly, to multiply \mathbf{a} by 3, we must multiply both of its components:
3\mathbf{a}=3\times\begin{pmatrix}2\\7\end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}6\\21\end{pmatrix}
Then, in order subtract 2\mathbf{b}, we must first multiply \mathbf{b} by 2.
2\mathbf{b}=2\times\begin{pmatrix}-5\\3\end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}-10\\6\end{pmatrix}
Thus the calculation is:
3\mathbf{a}-2\mathbf{b}=\begin{pmatrix}6\\21\end{pmatrix}-\begin{pmatrix}-10\\6\end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}16\\15\end{pmatrix}
Question 3: Let \mathbf{a}=\begin{pmatrix}6\\2\end{pmatrix} and \mathbf{b}=\begin{pmatrix}5\\-3\end{pmatrix} and \mathbf{c}=\begin{pmatrix}2\\1\end{pmatrix}. Write \mathbf{a}+2\mathbf{b}-\mathbf{c} as a column vector.
[2 marks]
Firstly, to multiply \mathbf{b} by 2, we must multiply both of its components:
2\mathbf{b}=2\times\begin{pmatrix}5\\-3\end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}10\\-6\end{pmatrix}
Then, we can add \mathbf{a} and 2\mathbf{b}:
\mathbf{a}+2\mathbf{b}=\begin{pmatrix}6\\2\end{pmatrix}+\begin{pmatrix}10\\-6\end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}16\\-4\end{pmatrix}
The final calculation is to subtract \mathbf{c}:
\mathbf{a}+2\mathbf{b}-\mathbf{c}=\begin{pmatrix}16\\-4\end{pmatrix}-\begin{pmatrix}2\\1\end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix}14\\-5\end{pmatrix}