Biological Methods of Extracting Metals
Biological Methods of Extracting Metals Revision
Biological Methods of Extracting Metals
Copper is a wildly used resource that can be found throughout modern society. Copper has traditionally been extracted from high grade ores using large scale mining projects. Due to pressures on copper reserves, industries are driven to extract copper from lower grade ores. This has spurred the development of new ways of extracting copper, including phytomining and bioleaching.
Copper and its Ores

Copper is one of the most widely used metal on Earth. Copper is used in electronics to conduct electricity, in alloys to produce other metals with desirable properties, in construction for roofs, and in the arts as brass and bronze. The global demand for copper has increased dramatically over the last century as human civilization has become more and more developed. This sky rocketing demand has lead to increasing concerns about the amount of copper that remains in the Earth’s crust.
Copper is a finite natural resource. That means that once we have used it all up, it will be gone. Already, human consumption is depleting the supply of copper rich ores (ores that have contain a high percentage of copper). This makes it harder to meet the demand for copper in a sustainable way and is driving a move towards extraction of cooper from low grade ores (ores in which the percentage of copper is relatively low).
The desire to extract copper from lower grade ores has lead to the development of novel techniques. These techniques include phytomining, where plants are used to extract copper in the ground, and bioleaching, where bacteria drive chemical reactions.
Phytomining
Phytomining is the process of using plants to extract copper from low grade ores in the ground. Firstly, areas of land must be found that contain a high concentration of low grade copper ores. Once found, plants are planted on this land and allowed to grow.
As the plants grow they absorb minerals from the ground in which they are growing. This process causes copper compounds to be taken up into these plants and stored within them.
Once the plants have grown, they are harvested and burnt. The ash left behind will contain a relatively high concentration of copper compounds. Copper can then be extracted from these compounds.
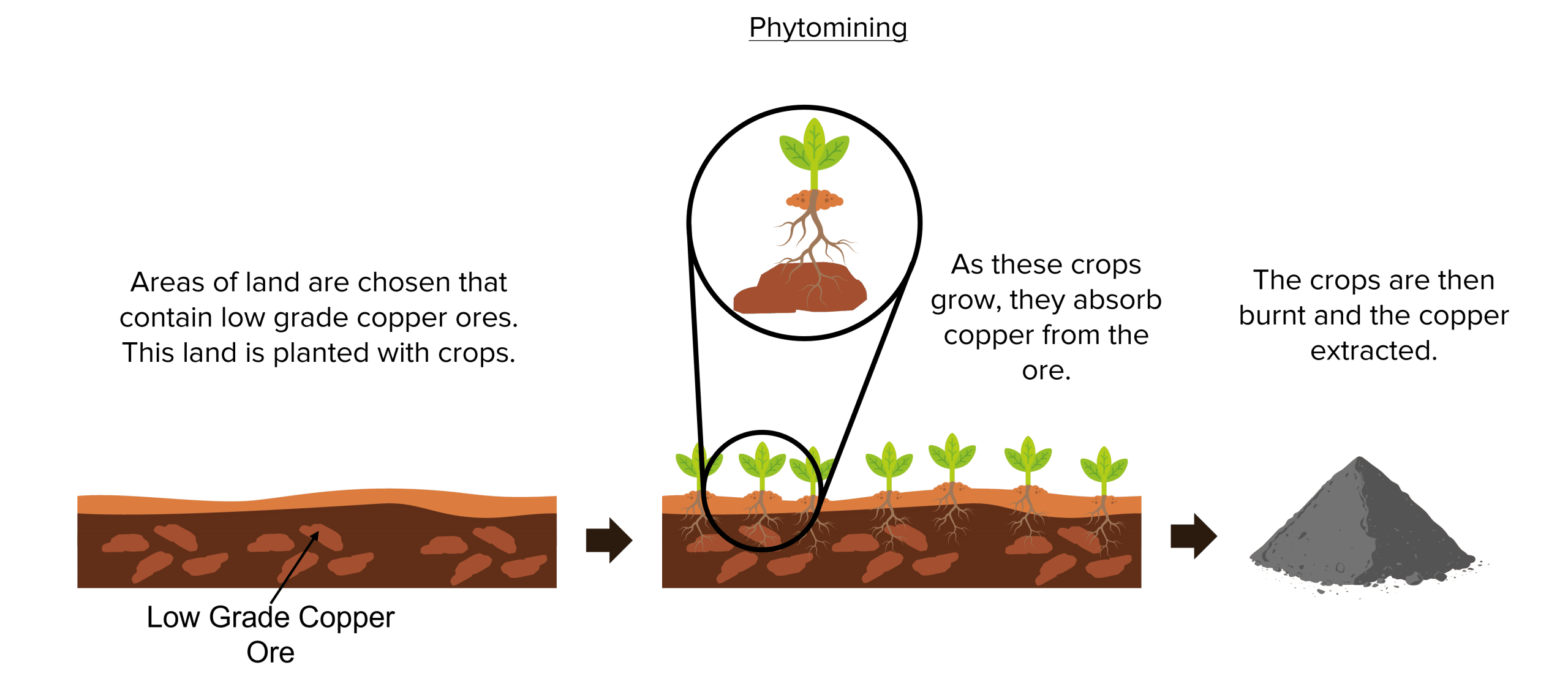
This process has the advantage of being much less damaging to the environment than traditional methods of copper extraction. Phytomining does not require large scale mining operations, which destroy land and often produce large amounts of carbon emissions. Phytomining produces much less carbon as the emissions created by burning plants is off set by the carbon absorbed by them during photosynthesis.
However, phytomining is a slow process. It is necessary to allow the plants grow to a size large enough to contain useful amounts of copper compounds. It may also require the clearance of land in the natural environment to make space for the growing of the plants.
Bioleaching
In bioleaching, bacteria are used to extract copper ions from low grade copper ores. During this process, bacteria convert copper compounds within ores into solution. These copper compound solutions are called the leachate and can be separates using electrolysis or displacement reactions to form copper metal.
Bioleaching has the advantage of being a relatively green process. The process itself produces no carbon emissions as no fuels are burned. There is also less necessity for land clearance as land is not required to grow plants. It also doesn’t require land that already contains high concentrations of low grade ores.
The main disadvantage of this process is again the time taken for it to work. Bacteria require time to break down the low grade ore and form leachates. To produce useful quantities of copper compounds, a long enough amount of time must be allowed for the bacteria to do their job.
Extraction of Copper from Copper Compounds
Once copper compounds have been extracted using these methods, copper metal can be produced in a number of ways. The most common ways of doing this are electrolysis and displacement by scrap iron.
Electrolysis
In electrolysis, solutions containing copper are separated using a potential difference. Positive copper ions in the solution are attracted to negative electrode and are reduced. This produces solid copper metal which can then be collected for processing and further use.
Displacement with Iron
In displacement, scrap iron is used to displace copper ions from copper compounds. Iron is used to displace copper as it is a more reactive metal. Similar to electrolysis, this process is carried out in solution and produces neutral copper metal.
Biological Methods of Extracting Metals Example Questions
Question 1: State one advantage of phytomining over traditional copper mining.
[1 mark]
Any one from:
- Reduced carbon emissions.
- Reduced environmental destruction.
- Can use lower grade copper ores.
Question 2: Name a disadvantage of biological methods of extracting metals.
[1 mark]
Biological methods take a long time to work.
Question 3: Explain how electrolysis can be used to extract copper metal from a solution of copper containing compound.
[3 marks]
- The solution is exposed to a potential difference.
- Positive copper ions move towards the negative electrode and are reduced.
- Copper metal is formed.
Question 4: Why is iron used to extract copper in displacement reactions?
[1 mark]
Iron is more reactive than copper.
(Allow reverse)
MME Premium Membership
£19.99
/monthLearn an entire GCSE course for maths, English and science on the most comprehensive online learning platform. With revision explainer videos & notes, practice questions, topic tests and full mock exams for each topic on every course, it’s easy to Learn and Revise with the MME Learning Portal.
Sign Up Now




