Atmospheric Pollutants
Atmospheric Pollutants Revision
Atmospheric Pollutants
Atmospheric pollutants are released by the combustion of fossil fuels. Some atmospheric pollutants are harmful as they can act as greenhouse gasses. Others are harmful due to the damage they can do to human health or the environment. One damaging result of atmospheric pollutants is the production of acid rain. This damages both natural and man-made environments.
Fossil Fuel Pollutants
Fossil fuels are a major source of atmospheric pollutants. In 2021, 57 million tons of oil was burned in the UK alone. Fossil fuels are burned every day in power stations, homes, and vehicles, producing hundreds of millions of tons of atmospheric pollutants every year.
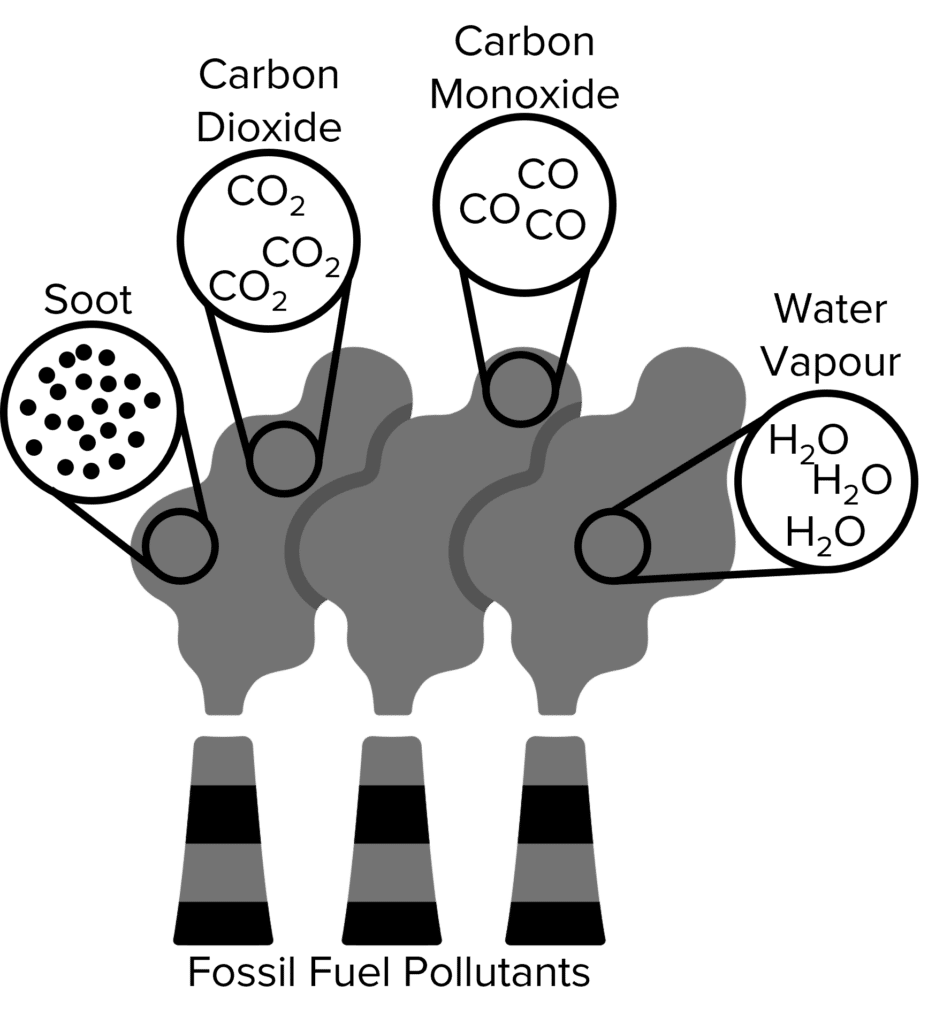
The two major pollutants released upon the complete combustion of fossil fuels are carbon dioxide \left(\text{CO}_2\right) and water vapour \left(\text{H}_2\text{O}\right). Fossil fuels are made up of hydrocarbons which are oxidised upon combustion. This processes breaks down the hydrocarbons, combining the carbon and hydrogen atoms with oxygen and releasing energy. These pollutants are both greenhouse gasses and will contribute to climate change by intensifying the greenhouse effect.
Fossil fuels may also undergo incomplete combustion. This happens when fuels burn without enough oxygen to oxidise all of their hydrocarbon molecules. When this happens, carbon monoxide \left(\text{CO}\right) is produced and released into the atmosphere. Carbon monoxide is a toxic gas. When inhaled, carbon monoxide will bind to red blood cells instead of oxygen. When inhaled in large quantities, carbon monoxide can prevent oxygen circulation, leading to fainting, coma, and, in the most extreme cases, death.
Incomplete combustion also produces solid carbon soot. Carbon soot is emitted a fine particles, known as particulate matter, and is another pollutant that is damaging to health. Particulate matter can be inhaled and become stuck in the lungs, leading to respiratory problems. It is also damaging to the environment. Small particles can create clouds in the atmosphere that reflect light from the sun back into space, leading to less light at the surface.
Sulfur and Nitrogen Dioxides
Fossil fuels also often contain impurities of sulfur. When fossil fuels are burned at high temperatures, this sulfur can become oxidised to form sulfur dioxide \left(\text{SO}_2\right). Nitrogen from the air may also react with oxygen at these temperatures to form nitrous oxides \left(\text{NO} + \text{NO}_2\right). Both sulfur dioxide and nitrous oxides are harmful to human health. They can cause respiratory problems when inhaled and may also contribute to heart disease in later life.
The most immediate problem caused by these oxides however is acid rain. When released into the air, sulfur and nitrous oxides will react with water in clouds. These reactions produce dilute sulfuric and nitric acid. This acid is carried in the clouds until it rains. They then fall back to the surface in the form of acid rain.

Acid rain does a lot of damage in the environment in the following ways:
- Killing plants by damaging their leaves and by rasing the acidity of the soil in which the plants are growing.
- Damaging aquatic environments by rasing the their acidity. This can be damaging to fish and aquatic plants.
- Damaging man-made structures. Statues and buildings made out of limestone are vulnerable to acid rain and will become corroded over time when exposed to it.
- Corroding metal, weakening the structures of buildings, making them less safe.
Atmospheric Pollutants Example Questions
Question 1: Name two pollutants associated with fossil fuels.
[2 marks]
Any two from:
- Carbon dioxide \left(\text{CO}_2\right)
- Water Vapour
- Carbon Monoxide \left(\text{CO}\right)
- Carbon soot (particulate matter)
Question 2: Explain why carbon monoxide is a toxic gas.
[2 marks]
Carbon monoxide will bind to red blood cells instead oxygen. This prevents oxygen from circulating in the body.
Question 3: Detail process by which acid rain is formed from fossil fuels.
[4 marks]
- Fossil fuels are burnt. This produces sulfur and nitrogen dioxide.
- These oxides are released into the air.
- They then react with water in clouds to form dilute acids.
- These fall to the surface as acid rain.





