Water and Nutrient Cycles
Water and Nutrient Cycles Revision
Water and Nutrient Cycles
All living things require water and nutrients (such as carbon and nitrogen) to survive, grow and reproduce. Nutrients and water are constantly being recycled through abiotic and biotic parts of the ecosystem so they can be used to create future organisms. The water cycle moves water from liquid to gaseous form and back again, providing land animals and plants with fresh water for them to survive. The carbon cycle moves carbon between different organisms and the atmosphere.
Water Cycle
The water cycle recycles all the water on the earth so organisms continue to receive the water they need to live.
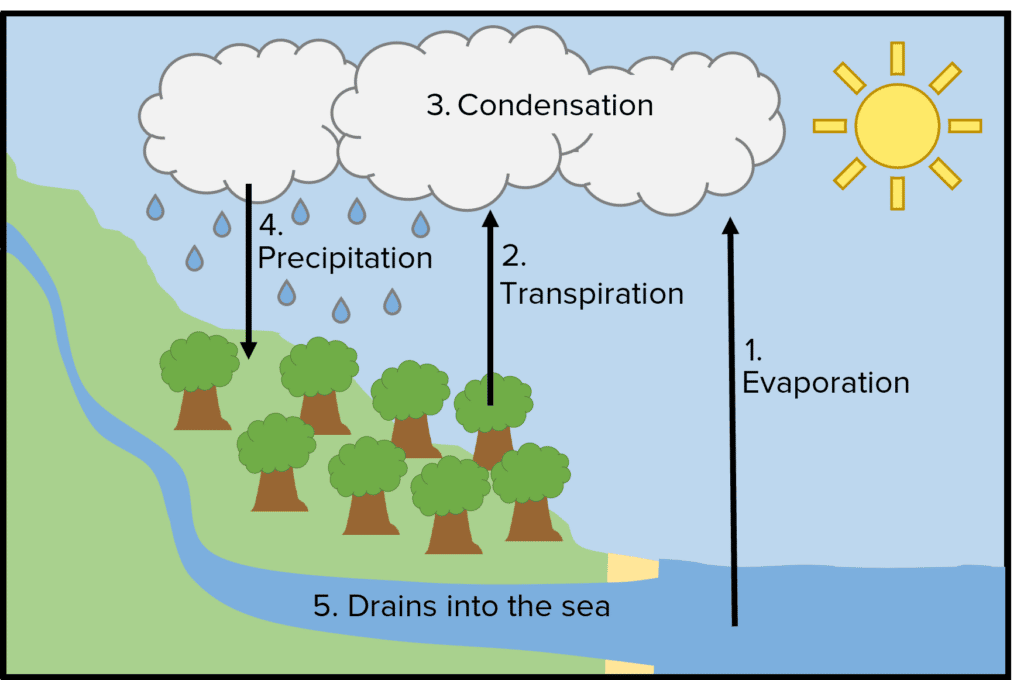
- Water is evaporated (turned into water vapour) using energy from the sun. This water comes from seas, lakes, rivers etc.
- Water also evaporates from plant leaves via transpiration.
- The water vapour is carried upwards until it cools and condenses into clouds.
- The water falls to the ground as precipitation (rain, hail, snow etc.) where it provides land organisms with fresh water.
- The water then drains into the sea via streams and rivers and the process begins again.
Carbon Cycle
Carbon is needed by all living organisms as it is a major component of biological molecules such as carbohydrates, lipids and proteins.
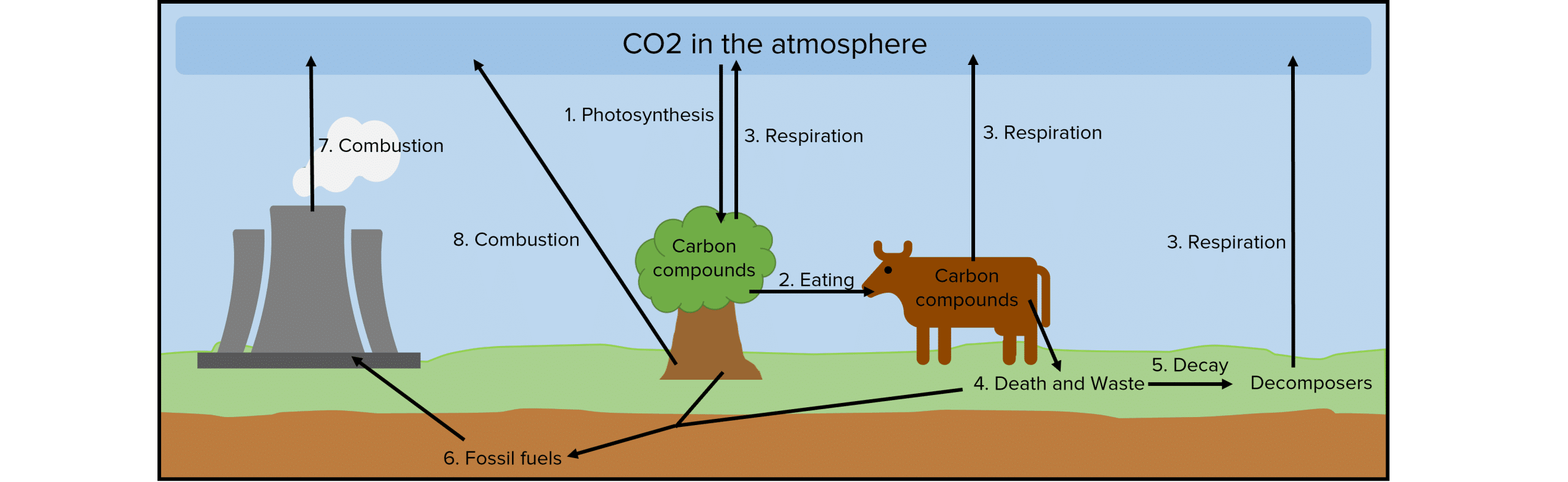
The carbon cycle allows carbon to move from organisms into the atmosphere so it can be reabsorbed by plants and used in photosynthesis.
- Carbon, in the form of carbon dioxide, is taken in by photosynthesising plants and is converted into glucose and other carbon compounds.
- Animals feed on the plants, passing the along the carbon. This carbon can pass all the way down the food chain, as animals feed on each other.
- Carbon is released back into the atmosphere in the form of carbon dioxide by all living organisms when they respire.
- Carbon returns to the environment via waste products or when the organisms die.
- When there is lots of oxygen and it is warm and moist, the waste materials and animal remains get digested by microorganisms called decomposers in the soil. This process releases carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere and puts mineral ions back into the soil.
- In certain conditions and over many years, animal and plant remains are compressed into fossil fuels such as oil, natural gas and coal.
- Fossils fuels are burnt (combustion) by humans to produce energy which releases carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere.
- Humans also burn (combustion) wood and other carbon containing compounds to produce energy which releases carbon back into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide.
Water and Nutrient Cycles Example Questions
Question 1: Name the process that makes liquid water turn to water vapour.
[1 mark]
Evaporation.
Question 2: How is carbon removed from the air?
[2 marks]
Plants take in carbon in the form of carbon dioxide for photosynthesis.
Question 3: How are animal and plant remains broken down?
[1 mark]
They are digested by microorganisms in the soil/ decomposers.





