The Heart
The Heart Revision
The Heart
The heart is a vital part of the circulatory system as it keeps blood flowing around the body. The structure of the heart allows blood to flow in the right direction and get where it needs to be in the body. The heart rate is controlled by a group of specialised cells that act as a pacemaker.
Functioning of the Heart
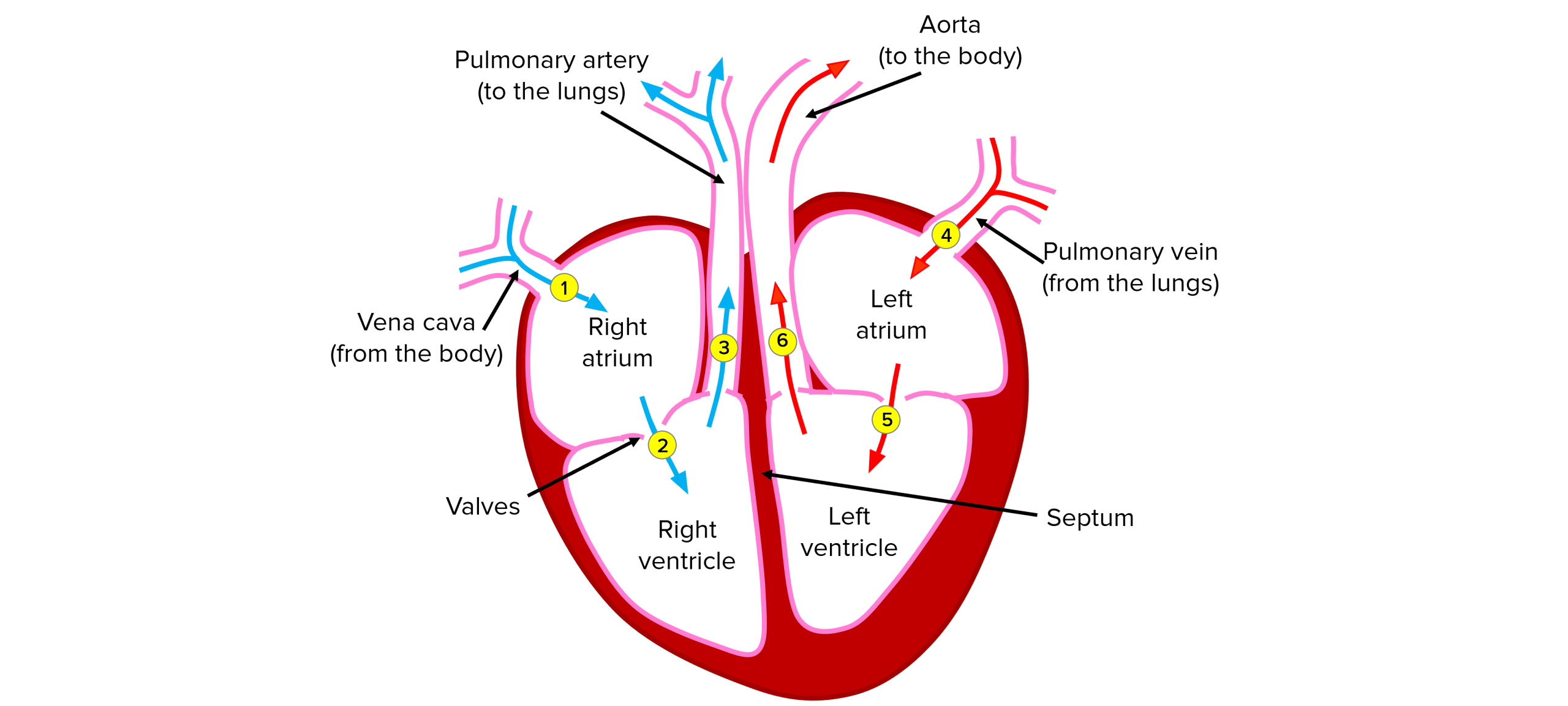
The heart has a left side and a right side, divided by the septum. Each side of the heart is split into an atrium and a ventricle.
Blood flows in very specific directions through the heart to ensure deoxygenated blood is sent to the lungs and oxygenated blood is sent around the body. The heart has valves that prevent blood flowing backwards, just like veins.
- Deoxygenated blood from the body enters the right atrium through the vena cava.
- The atria contract pushing the deoxygenated blood to the right ventricle.
- The ventricles contract pushing the deoxygenated blood through the pulmonary artery to the lungs to be oxygenated.
- Oxygenated blood from the lungs enters the left atrium through the pulmonary vein.
- The atria contract pushing the oxygenated blood to the left ventricle.
- The ventricles contract pushing the oxygenated blood through the aorta to the rest of the body, to supply respiring cells with oxygen.
The walls of the ventricles are much thicker than the walls of the atria because they have to push the blood further. Likewise, the walls of the left ventricle are thicker than the walls of the right ventricle because the right ventricle only has to push the blood to the lungs but the left ventricle pushes blood all around the body. The thicker the walls, the higher the blood pressure that can be created and the further the blood will be able to travel.
The heart is made of cardiac muscle and has a network of coronary arteries that supply the muscle cells with oxygen for respiration. The energy produced in respiration is needed for the contraction of the cardiac muscles and therefore the pumping of the heart.
Note:
Diagrams of the heart will have the right side of the heart on the left side of the page and vice versa. Don’t let this fool you when describing the flow of blood through the heart.
Pacemakers
Natural resting heart rate is controlled by specialised cells in the wall of the right atrium. They perform the role of a pacemaker which means they regulate the contraction of the heart by sending electrical impulses to the cardiac muscle cells.
Some people have faulty pacemakers and so have an irregular heartbeat. Artificial pacemakers can be implanted under the skin with wires that connect to the heart to produce currents that cause the heart muscles to contract and help the heart beat regularly.
The Heart Example Questions
Question 1: Describe how deoxygenated blood moves through the heart.
[3 marks]
- Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium via the vena cava.
- The right atrium contracts and pushes it into the right ventricle.
- The right ventricle contracts and pushes it to the lungs to be oxygenated.
Question 2: Explain why the walls of the left ventricle are thicker than the walls of the right ventricle.
[2 marks]
The left ventricle transports blood all around the body whereas the right ventricle only transports blood to the lungs.
The left ventricle needs more muscle to generate a higher blood pressure to push the blood further.
Question 3: Where would you find pacemaker cells in the heart and what do they do?
[2 marks]
Pacemaker cells are found in the wall of the right atrium and regulate heart rate by sending electrical impulses to the heart muscles.





