Components of the Blood
Components of the Blood Revision
Components of the Blood
The blood is a tissue that plays an important role in the circulatory system. It has 4 main components (red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets and plasma) that all have their own specific functions.
Red Blood Cells
Red blood cells carry oxygen from the lungs to cells around the body for aerobic respiration.
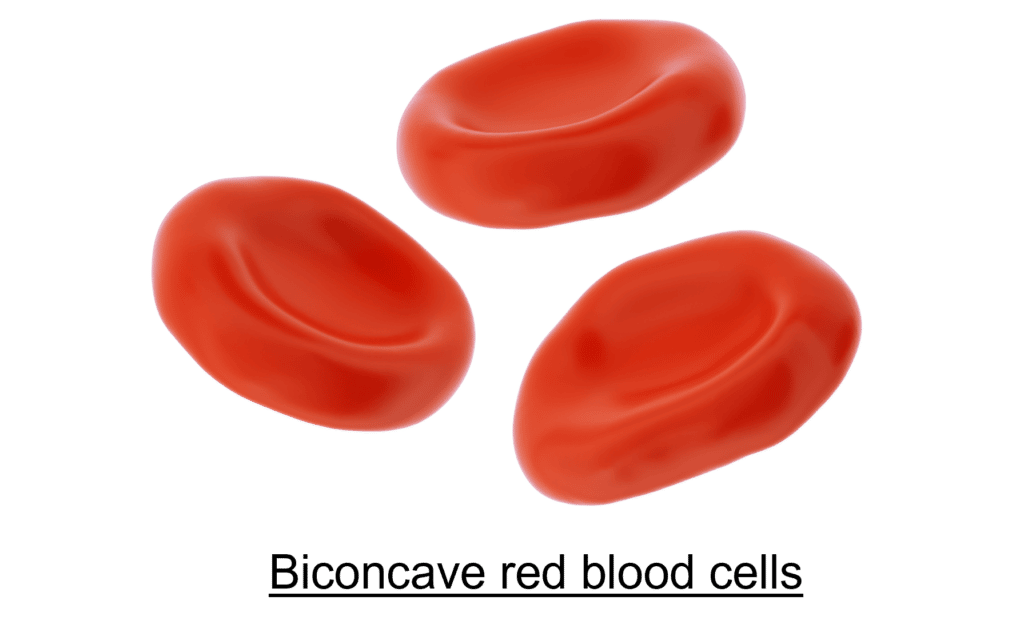
They contain a protein called haemoglobin which binds to the oxygen to form oxyhaemoglobin. When arriving at a cell that requires oxygen, oxyhaemoglobin splits back into haemoglobin and oxygen so the oxygen can diffuse into the cell.
Red blood cells are adapted for efficient gas exchange because:
- They have a biconcave shape which increases the surface area for increased diffusion.
- They are really small so can fit through small capillaries.
- They have no nucleus to make room for lots of haemoglobin.
- They have lots of haemoglobin to bind and carry lots of oxygen.
White Blood Cells
White blood cells are an important part of the immune system as they are responsible for identifying and destroying pathogens. They do contain a nucleus.
There are two different types of white blood cell:
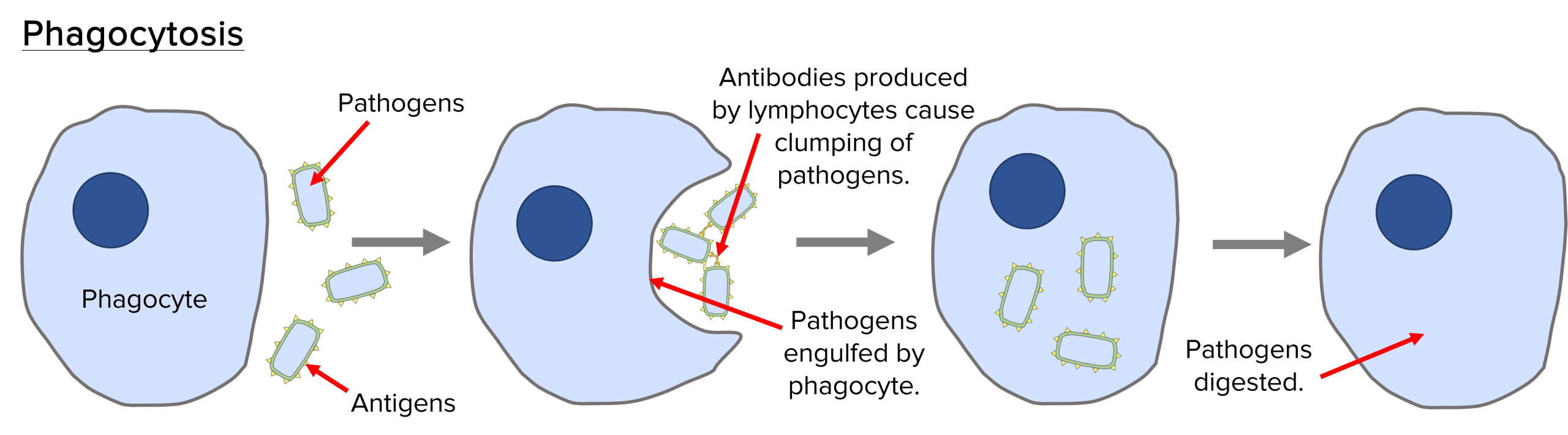
- Phagocytes engulf and digest pathogens through phagocytosis.
- Lymphocytes identify pathogens and produce antibodies that bind to the antigens on pathogens and cause them to clump together. This makes them easier to be engulfed by phagocytes. Some lymphocytes also release antitoxins that neutralise toxic substances produced by pathogens.
Platelets
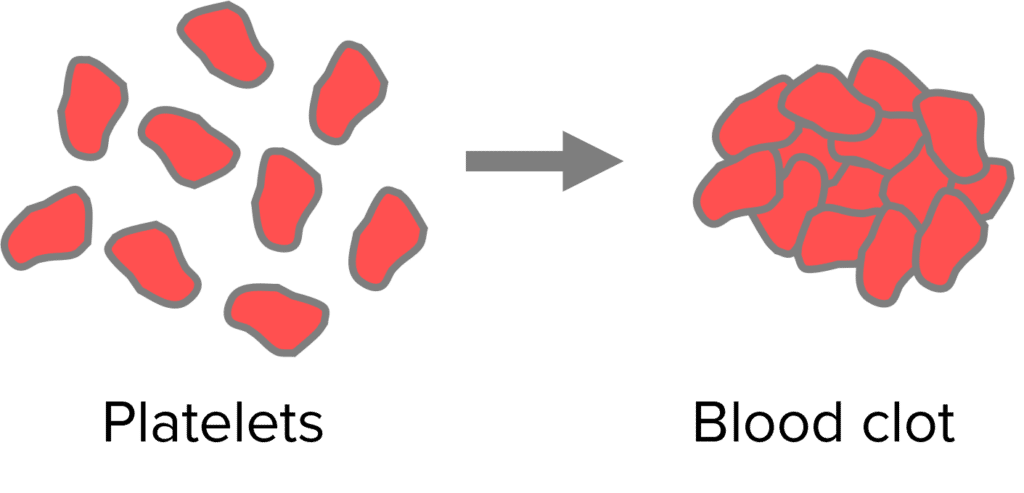
Platelets are fragments of cells produced in the bone marrow that cause the blood to clot. They do not have a nucleus.
They are particularly important when the organism has a wound as they stop blood from flowing out of the body and stop pathogens getting into the body.
They do this by forming blood clots and scabs.
People who have few platelets are prone to excessive bleeding and bruising.
Plasma
Plasma is a pale yellow liquid that transports everything in the blood:
- Red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets.
- Products from digestion of food such as glucose and amino acids.
- Waste products such as carbon dioxide and urea.
- Hormones, proteins, antibodies and antitoxins.
Components of the Blood Example Questions
Question 1: Explain 2 ways that red blood cells are adapted for efficient gas exchange.
[4 marks]
Any 2 from:
- Biconcave shape which increases surface area.
- Very small so can fit through narrow capillaries.
- No nucleus to make room for haemoglobin.
- Lots of haemoglobin to carry lots of oxygen.
Question 2: What is the main structural difference between a red blood cell and a white blood cell?
[1 mark]
Red blood cells do not contain a nucleus but white blood cells do contain a nucleus.
Question 3: What is the main function of platelets?
[2 marks]
Platelets cause blood to clot.
This stops blood pouring out of wounds and stops pathogens getting in.





