Monoclonal Antibodies
Monoclonal Antibodies Revision
Monoclonal Antibodies
Monoclonal antibodies are identical copies of one type of antibody and are mass produced by creating hybridoma cells in a lab. They have many different uses, from treating and diagnosing all kinds of diseases to making pregnancy tests work. Whilst they are incredibly useful, there are limitations and ethical issues surrounding the use of monoclonal antibodies.
Production of Monoclonal Antibodies
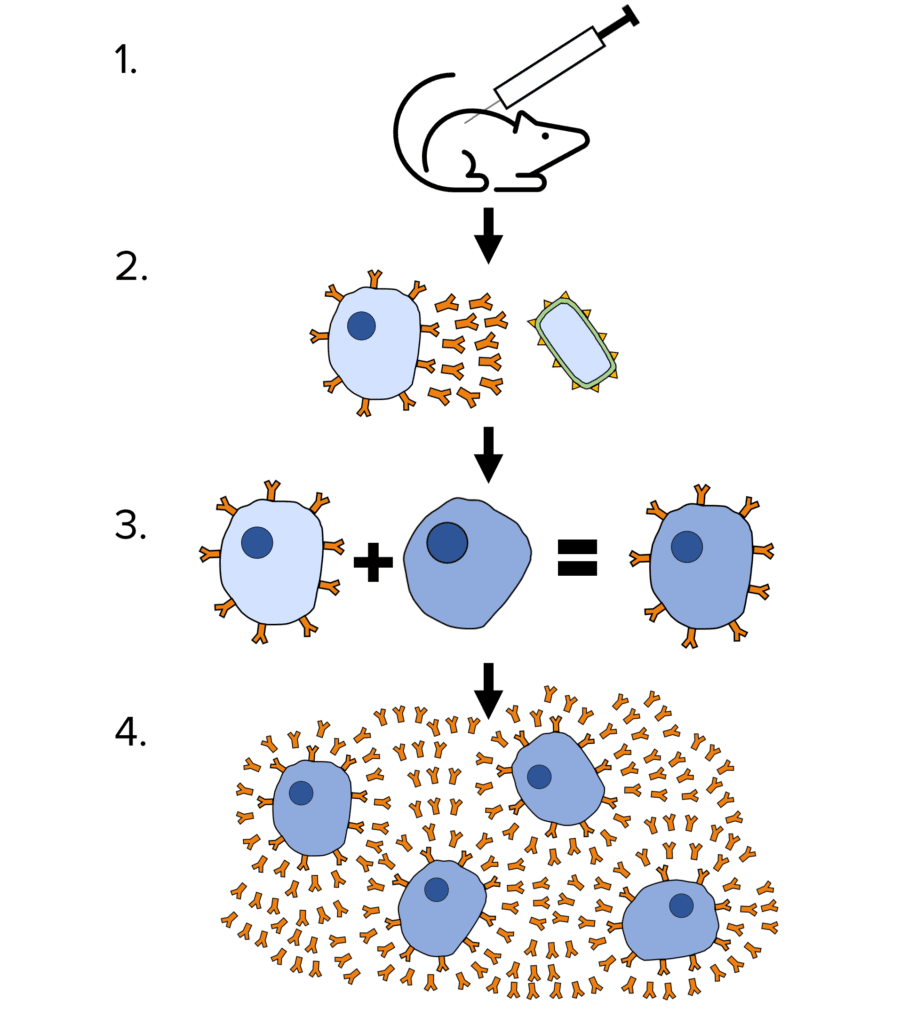
Monoclonal antibodies are simply copies of the same antibody because they come from a cloned lymphocyte.
- A mouse is injected with an antigen.
- This triggers an immune response in the mouse and its lymphocytes will begin producing antibodies specific to the injected antigen.
- These lymphocytes do not divide easily so are fused with tumour cells that divide rapidly. These new cells are called hybridomas.
- Hybridomas divide rapidly and create lots of cells that all create the same antibody. These antibodies can be collected, purified and used.
The antibodies made bind to one specific type of antigen which makes them extremely useful as they can target a specific chemical or specific group of cells.
Pregnancy Tests
Pregnancy tests use monoclonal antibodies to detect if a person is pregnant.
- Pregnant people produce the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) which is emitted in their urine.
- Monoclonal antibodies that are specific to the hCG hormone are attached to the pregnancy test stick.
- When urinated upon the urine travels up the stick, to the antibodies. If hCG hormone is present in the urine, it will bind to the monoclonal antibodies and cause a colour change, indicating that the person is pregnant.
Detecting and Treating Cancer
Monoclonal antibodies can help treat diseases such as cancer without damaging the other cells around it.
Cancers have specific antigens called tumour markers on their surface. Monoclonal antibodies specific to these antigens can be produced and adapted to detect and treat cancers all around the body.
- Monoclonal antibodies can bind to the cancerous cells and help doctors locate the cancer cells in the body so they can be treated and removed.
- Anticancer drugs can be attached to the monoclonal antibodies so they can bind specifically to the cancer cells and destroy them.
- Monoclonal antibodies can trigger the natural immune system to attack the cancerous cells.
- Monoclonal antibodies can also bind to the cancer cells and block chemicals that cause them to rapidly divide.
Laboratories and Research
Monoclonal antibodies can be produced to be able to target specific things in the blood, such as certain hormones, drugs and pathogens. Laboratories use them to run investigations about the levels of different substances in the blood so they can diagnose diseases and hormone imbalances and carry out drug tests.
Monoclonal antibodies can also be attached to fluorescent dyes to be able to identify the location of certain substances in the body for research and medical purposes.
Pros, Cons and Ethics
As previously discussed, the specificity of monoclonal antibodies means there this great potential for new disease treatments, diagnosis and research as they do not harm healthy cells. However, they are not as widely used as initially hoped when they were discovered. This is because there are lots of problems with them and opposition from people who think their use is unethical:
- There are more side effects than expected, caused by the use of mouse antibodies.
- It is more expensive and difficult to do than anticipated.
- Many people think it is unethical to use mice to produce antibodies.
Monoclonal Antibodies Example Questions
Question 1: Describe how monoclonal antibodies are produced.
[5 marks]
- A mouse is injected with an antigen.
- Mouse lymphocytes begin to produce antibodies specific to the antigen.
- Lymphocytes are fused with tumour cells to make them divide more rapidly. These are called hybridomas.
- Hybridomas divide rapidly and produce lots of cells that create lots of the same antibody.
- These antibodies are monoclonal antibodies and are collected and purified before use.
Question 2: Explain how pregnancy tests work.
[3 marks]
- hCG is a hormone found in the urine of pregnant people.
- Urine travels up the stick and over the hCG specific monoclonal antibodies.
- If hCG is present in the urine, it will bind to the antibodies and a colour change will occur indicating the person is pregnant.
Question 3: Give 2 ways that monoclonal antibodies can be used in the diagnosis or treatment of cancer.
[2 marks]
Any 2 from:
- Locates cancer cells so they can be treated and removed.
- Can attach anticancer drugs to target and destroy cancer cells.
- Can bind to cancer cells and trigger natural immune response.
- Can block chemicals that cause the cancer to divide.
Monoclonal Antibodies Worksheet and Example Questions
Producing Monoclonal Antibodies Questions
GCSEOfficial MMEUses of Monoclonal Antibodies
GCSEOfficial MME
MME Premium Membership
£19.99
/monthLearn an entire GCSE course for maths, English and science on the most comprehensive online learning platform. With revision explainer videos & notes, practice questions, topic tests and full mock exams for each topic on every course, it’s easy to Learn and Revise with the MME Learning Portal.
Sign Up Now

