Effect of Human Activity on Biodiversity
Effect of Human Activity on Biodiversity Revision
Effect of Human Activity on Biodiversity
Biodiversity is the variety of different species that live in an ecosystem or on the earth. Biodiversity is often reduced by human activities such as incorrect waste disposal, deforestation and destruction of peat bogs. These activities also contribute to global warming which can worsen the problem. Humans should be mindful of these issues and aim to minimise the effects on ecosystems and restore biodiversity.
Human Impact on Biodiversity
Biodiversity is the term used to describe the variety of species in an ecosystem or on earth. Great biodiversity ensures ecosystems are stable as species are less dependent on each other for food, shelter and maintenance of the environment. Human activities such as incorrect disposal of waste , deforestation and destruction of peat bogs can have damaging consequences for certain species and can ultimately reduce biodiversity. It is very important for humans to put measures in place to reduce their impact on natural ecosystems and maintain good biodiversity, particularly due to the rapidly growing human population.
People now live a lot longer due to advancements in medicine and farming techniques which is causing the population to grow exponentially. Whilst this is obviously good for humans, other organisms suffer as a consequence. The greater the human population the more of the earth’s resources that are used up and the more waste produced. People are also using more resources from the earth than ever before due to an increase in the standard of living. These factors can all lead to a reduction in biodiversity.
Waste Management
Humans produce lots of waste materials like chemicals that can pollute land, water and air if not handled and disposed of carefully.
- Toxic chemicals from industrial processes and farming (herbicides and pesticides) and household waste that get buried in landfill sites pollute land .
- Sewage and toxic chemicals from industrial processes and farming pollute water.
- When fossil fuels are combusted, the air is polluted with smoke and acidic gases that can cause acid rain.
Pollution in all its forms can ultimately cause the death of organisms and reduce biodiversity.
Deforestation
Humans use land for lots of different things: building, farming, mining, dumping waste and much more. The more land that is used, the less land is available for other organisms. In order to use areas of land, humans may have to destroy the environment and habitats that are currently occupying the space.
Deforestation is the act of humans chopping down lots of trees, often to create space for farming animals and growing crops for consumption or biofuels. Humans chop down more trees than they plant which makes deforestation unsustainable.
Deforestation causes many problems:
- It destroys animal habitats causing migrations, extinctions and a reduction in biodiversity.
- Tree roots hold soil together, making it more stable and less prone to erosion by rain. Without trees, soil is lost, reducing available nutrients.
- The land cleared will also be more prone to flooding due to the loose soil being washed away.
- Less trees mean less carbon dioxide is removed from atmosphere through photosynthesis.
- Trees store a large amount of carbon. When wood is burnt to clear the land, even more carbon dioxide is added to atmosphere.
The increase in carbon dioxide in the atmosphere causes global warming.
Destruction of Peat Bogs
Bogs are waterlogged and acidic areas of land. This means that there is very little oxygen so when plants die, they do not fully decompose and instead form peat. Instead of being released into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide, carbon is stored in the peat. Peat bogs also provide important habitats for certain organisms.
Humans destroy peat bogs for a number of reasons.
- Bogs are drained so the land can be used for farming.
- Peat is dried and burnt as fuel.
- Peat is used to make compost that farmers use to increase food production.
Carbon is released into the atmosphere, in the form of carbon dioxide, when peat is burnt as fuel and when bogs are drained (the amount of oxygen increases so respiring microorganisms begin to decompose the peat). The increased carbon dioxide in the atmosphere increases global warming.
Peat takes many years to form and humans are using it faster than it forms meaning, like fossil fuels, peat is a non-renewable energy resource.
The destruction of peat bogs means habitats are destroyed leading to a reduction in biodiversity.
Global Warming
The earth is insulated by a layer of gases that help control global temperatures. These gases (known as greenhouse gases) absorb energy from the Sun and send some of it towards the earth (causing the temperature to increase) and reflect the rest of it back out into space. Some of this energy gets trapped inside the gas layer and causes the earth to be warm, even at night.
Levels of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane are rising rapidly due to human activities, e.g. burning fossil fuels, deforestation, increased cattle rearing. This means more of the Sun’s energy is getting trapped within the Earth’s atmosphere and the earth is getting increasingly warmer. This is called global warming.
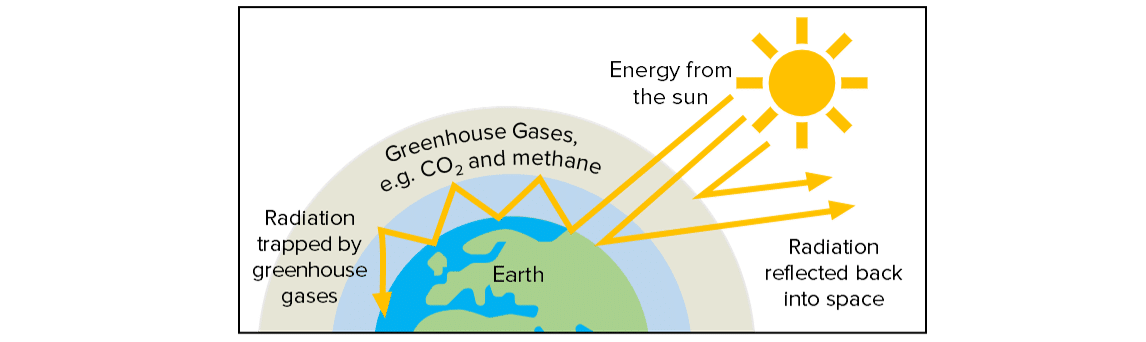
Global warming can have very serious consequences for the Earth. The hotter temperatures cause ice caps to melt, sea levels to rise and flooding. Extreme weather conditions, e.g. hurricanes, droughts, are also more likely due to the increased temperatures. These physical effects on the earth can have a large impact on wildlife.
- Habitats may be destroyed causing extinctions and reduction in biodiversity.
- Food chains may be disrupted which can affect whole communities (due to interdependence) and decrease biodiversity.
- Organisms may have to migrate due to extreme weather conditions or changes in temperature. This can increase the spread of certain pests and diseases.
Maintaining Biodiversity
Thanks to scientific research, humans are now beginning to realise the extent of the damage they have caused to the earth. Some people and organisations are putting systems into place to try and minimise the negative effects of humans and restore biodiversity. This includes:
- Setting up specialised breeding programmes to save endangered species from extinction.
- Protecting and often regenerating rare habitats to protect species that live there, e.g. rainforests and coral reefs.
- Crops fields often only contain one type of crop meaning there is very low biodiversity. Farmers have begun reintroducing field margins and hedgerows between crop fields to increase biodiversity.
- Some governments have put laws and programmes in place to reduce the amount of deforestation and reduce greenhouse gas emissions from big businesses. This is with the aims of limiting global warming.
- Waste is recycled instead of being sent to landfill, limiting the amount of land used for landfill and keeping ecosystems intact.
However, these methods are not always ideal:
- They can be very expensive.
- Schemes that aim to increase biodiversity may decrease food production.
- Land is needed to sustain the increasing population. This often includes using land with high biodiversity and thriving ecosystems.
Effect of Human Activity on Biodiversity Example Questions
Question 1: Explain how deforestation contributes to global warming.
[3 marks]
- The fewer trees there are the less carbon dioxide removed from the atmosphere for photosynthesis.
- Trees are burnt to clear the land which releases more carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
- Carbon dioxide traps the suns radiation/energy and causes global warming.
Question 2: Name 2 human uses of peat.
[2 marks]
- Burnt as a fuel.
- Used to make compost / increase crop production.
Question 3: Name 2 consequences of global warming.
[2 marks]
Any 2 from:
- Drought
- Storms
- Hurricanes
- Heat waves / hotter
- Melting ice caps
- Flooding
- Rising seas levels
- Habitat loss
- Food chain disrupted
- Migration
- Extinction
Effect of Human Activity on Biodiversity Worksheet and Example Questions
Biodiversity Questions
GCSEOfficial MMEMaintaining Biodiversity Questions
GCSEOfficial MMEDeforestation Questions
GCSEOfficial MMEGlobal Warming Questions
GCSEOfficial MMEPollution of Land and Water Questions
GCSEOfficial MME
MME Premium Membership
£19.99
/monthLearn an entire GCSE course for maths, English and science on the most comprehensive online learning platform. With revision explainer videos & notes, practice questions, topic tests and full mock exams for each topic on every course, it’s easy to Learn and Revise with the MME Learning Portal.
Sign Up Now




