Cloning
Cloning Revision
Cloning
Individuals that are genetically identical are called clones. Plant clones can be made using plant cuttings or in a process called tissue culture. Animals can be cloned using embryos or adult cells. There are benefits and risks to cloning organisms and some people believe it is unethical.
Cuttings and Tissue Culture
Plants can be cloned in 2 ways:
1. Cuttings from parent plants can be used to make genetically identical copies of the parent plant. This method is quick and simple and has been used by gardeners for many years.
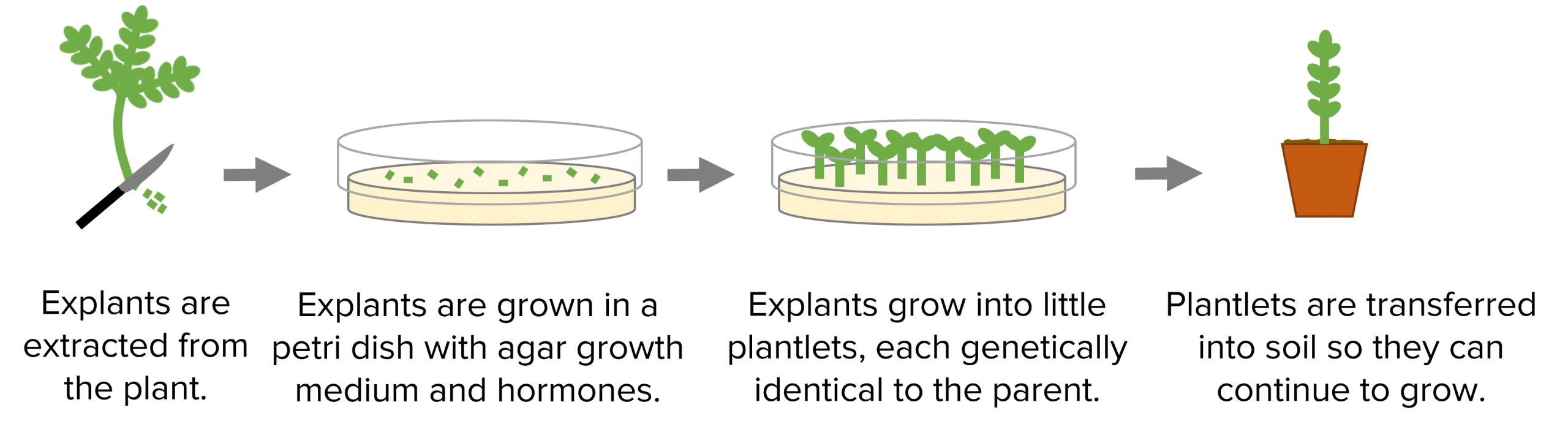
2. Tissue culture (micropropagation) is slightly more complex as whole genetically identical plants are grown from a small sections of plants called explants. Explants are extracted from a plant, put in agar growth medium with plant hormones to make them grow before being transferred into soil to fully develop. This process produces lots of plants quickly and it enables plants to be grown all year round but the process is a lot more complicated. Tissue culture is often used to preserve rare plant species or grow lots of plants in nurseries.
Embryo Transplants and Adult Cell Cloning
Animals can be cloned in 2 ways:
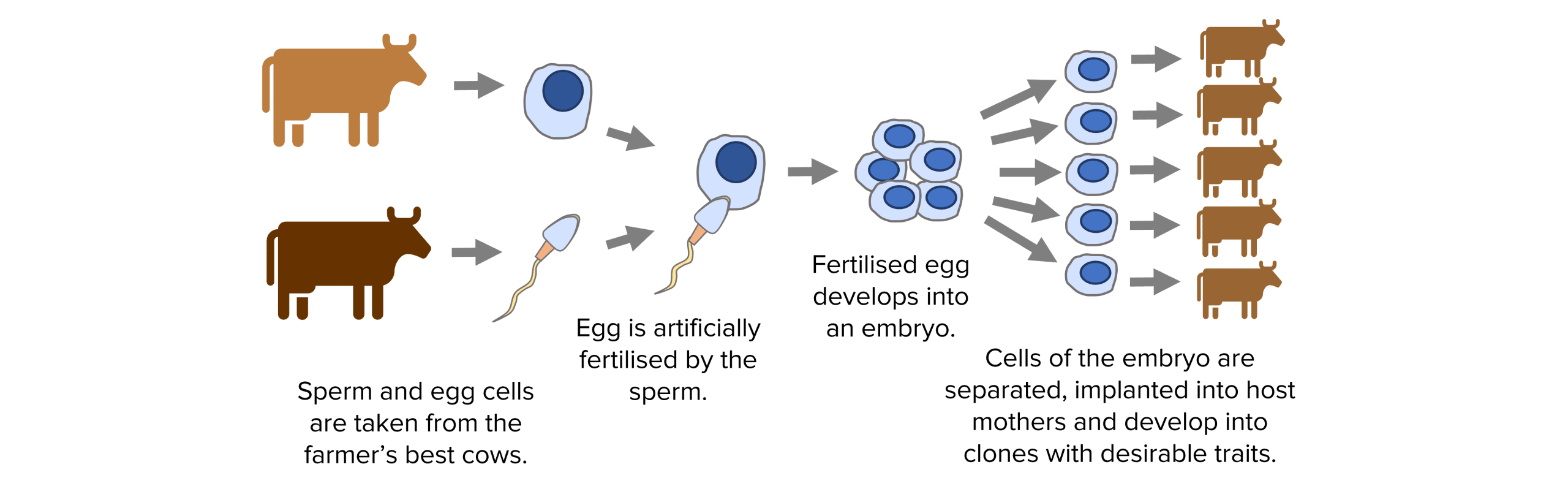
1. Embryo cloning produces cloned offspring and is often used by farmers. They will artificially fertilise an egg from their best female animal with a sperm cell from their best male animal. Before the cells start to specialise, the embryo is split into several clones. The cloned embryos continue developing and get implanted into host mothers. Lots of genetically identical animals with desired characteristics from the original parents will be formed.
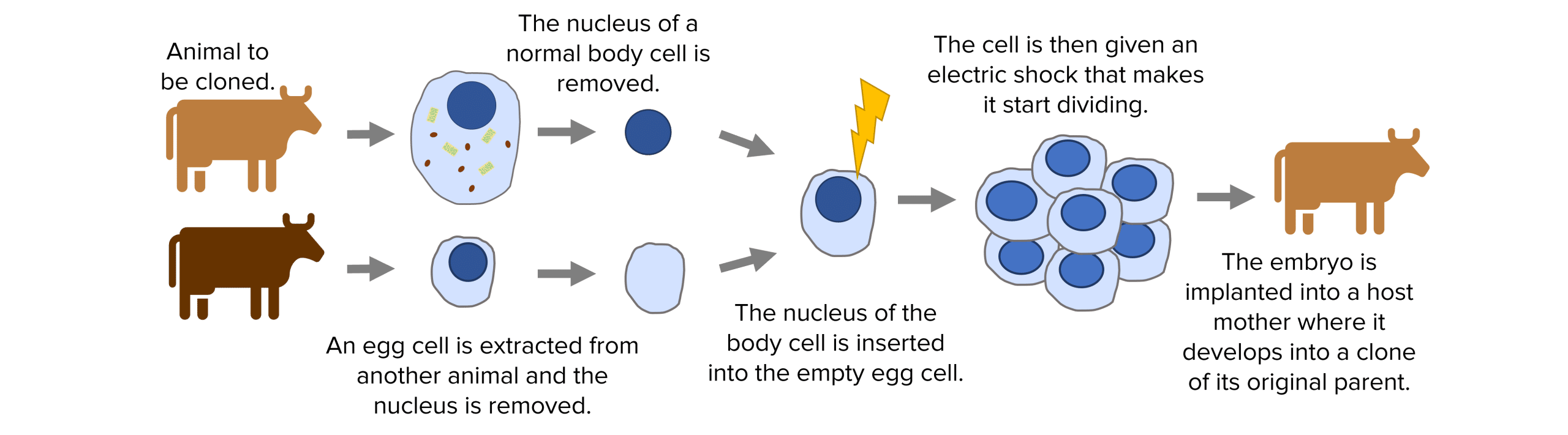
2. Adult cell cloning creates a genetically identical clone of an existing animal, the most famous example being Dolly the sheep. First, the nucleus of an unfertilised egg cell is removed. Then the nucleus of a adult body cell (from the animal you want to clone) is removed and inserted into the empty egg cell. The cell then receives an electric shock which stimulates it to divide into an embryo. The embryo is implanted into a host mother to continue its development into a clone of the original adult.
Issues with Cloning
Cloning is very useful for preserving endangered species, understanding the mechanisms of ageing and the rapid production of high quality food. However, it has many issues:
- It reduces the gene pool in populations making them more likely to be wiped out by a new disease.
- Clones may not be as healthy as the original organism.
- There is potential for human cloning but attempts will likely be unsuccessful and there are several laws in place to prevent it from happening.
- Some people believe cloning is interfering too much into the creation of new life.
Cloning Example Questions
Question 1: Give an advantage of cloning plants using tissue culture.
[1 mark]
Any one from:
- Many plants can be produced quickly.
- Plants can be grown all year round.
Question 2: Describe how farmers use embryo cloning to produce ideal animals.
[6 marks]
- A sperm and and egg are taken from the most ideal animals / animals with desired traits.
- The egg cell is artificially fertilised by the sperm.
- The fertilised egg cell develops into an embryo.
- The cells of the embryo are separated before they start to specialise.
- The cells are implanted into host mothers where they develop normally.
- The offspring are all clones of each other and will have desired traits from the parents.
Question 3: Why do some people believe that cloning is bad?
[1 mark]
Any one from:
- They think it is interfering too much in the creation of new life.
- They believe it may be taken too far and humans may be cloned.
- It may produce unhealthy organisms.
- It reduces the gene pool making populations more likely to be all killed by new diseases.
Cloning Worksheet and Example Questions
Cloning Questions
GCSECombined Science FoundationCombined Science HigherBiology FoundationBiology HigherOfficial MME
MME Premium Membership
£19.99
/monthLearn an entire GCSE course for maths, English and science on the most comprehensive online learning platform. With revision explainer videos & notes, practice questions, topic tests and full mock exams for each topic on every course, it’s easy to Learn and Revise with the MME Learning Portal.
Sign Up Now
