Meiosis
Meiosis Revision
Meiosis
Meiosis is a form of cell division that produces gametes (sex cells) that are essential for sexual reproduction.
Production of Gametes
Gametes required for sexual reproduction are formed in the reproductive organs (testes and ovaries) in a process called meiosis.
Meiosis creates gametes that contain half the amount of genetic information as the parent organism (haploid) so when they fuse together in fertilisation, they have a full set of chromosomes to create a new organism. Each gamete has a different set of chromosomes which creates genetic variation in the offspring.
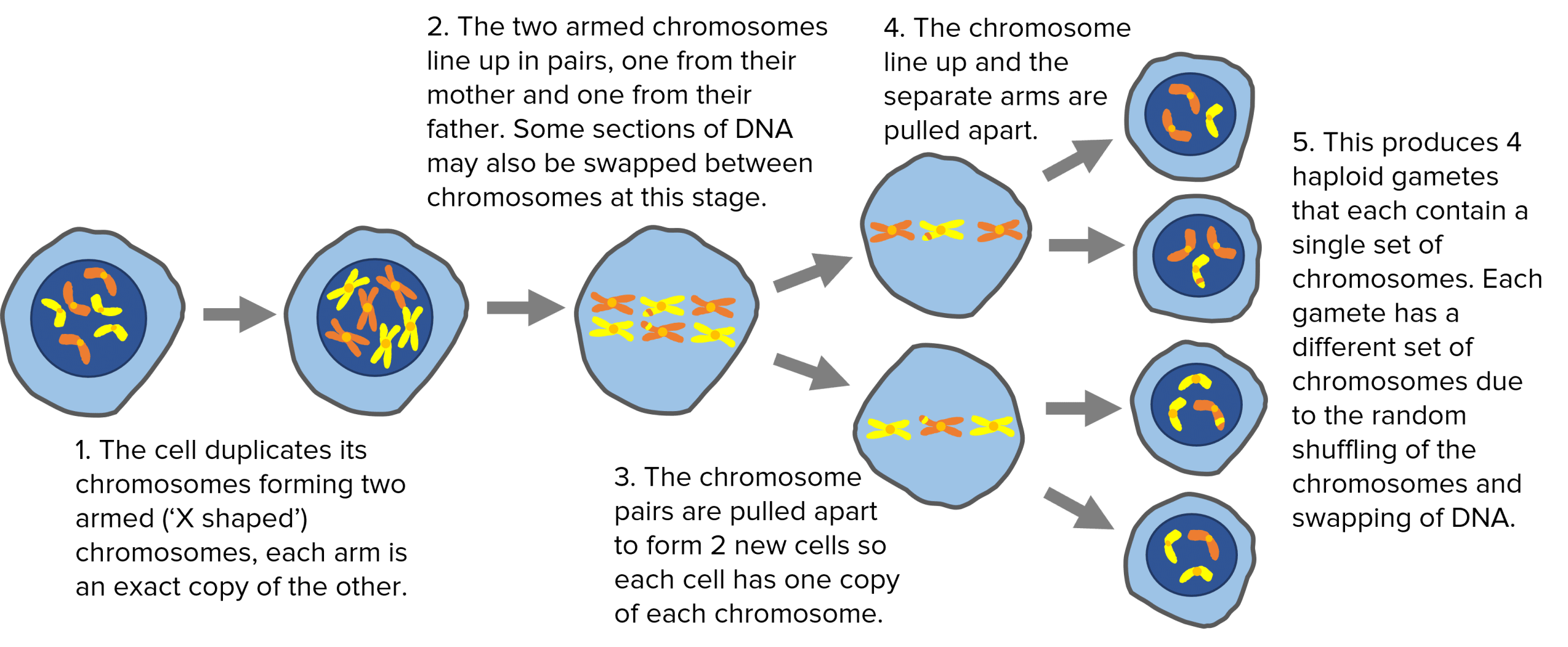
- Cells in reproductive organs begin to duplicate their chromosomes. They form ‘X- shaped‘, two armed chromosomes, each arm is identical to the other arm.
- The chromosomes then line up in pairs along the centre of the cell. Pairs consist of chromosomes inherited from the mother and the father. In this stage there may be some swapping of genetic material between the chromosomes.
- The chromosomes are pulled apart to opposite ends on the cell and the cell divides forming two new cells.
- The chromosomes line up in the centre of the cells again and each arm is pulled to opposite ends.
- Four new haploid cells (gametes) are created, each with different sets of chromosomes and half the amount of genetic material as the original cell.
Fertilisation
In fertilisation, gametes from the male and female organisms meet and their nuclei fuse together. This forms a fertilised egg or zygote that contains a full set of chromosomes (half from the mother and half from the father).
The zygote will then divide multiple times by mitosis to form an embryo (small bundle of cells).
Cells then begin to differentiate into specialised cells that will make up different body tissues and perform specific functions in the new organism.
Mitosis vs. Meiosis
Mitosis and meiosis are both forms of cell division that allow the creation of new life. However there are many key differences between the processes:
| Mitosis | Meiosis |
| Produces 2 daughter cells. | Produces 4 gametes. |
| Involves 1 cell division. | Involves 2 cell divisions. |
| Creates diploid cells (46 chromosomes in humans). | Creates haploid cells (23 chromosomes in humans). |
| Cells created are genetically identical to each other and parent. | Cells created are genetically different to each other and parent. |
| Used for growth, repair and asexual reproduction. | Used to create gametes used in sexual reproduction. |
Meiosis Example Questions
Question 1: How many chromosomes do human gametes contain? Why is this?
[2 marks]
Human gametes have 23 chromosomes/ half the amount of chromosomes of the full organism.
During fertilisation, genetic information from the mother and father combine to create a zygote with the full amount of chromosomes.
Question 2: How many rounds of cell division occur in the process of meiosis? How many cells are produced?
[2 marks]
2 cell divisions
4 sex cells (gametes) produced.
Question 3: Describe how a zygote develops into an embryo and then a functional organism.
[2 marks]
The zygote will divide by mitosis to form an embryo.
Cells continue to divide and begin to differentiate into specialised cells that form tissues and perform different functions within the organism.





